|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Stewart G.W. — Afternotes on Numerical Analysis |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Newton's method, retarded convergence 14—15 25
Newton's method, starting values 15
Nonlinear equations 4
Nonlinear equations, analytic solutions 4
Nonlinear equations, bracket for a root 5
Nonlinear equations, condition of roots see "Condition" "Roots
Nonlinear equations, effects of rounding error 6
Nonlinear equations, errors in the function 37 40—42
Nonlinear equations, existence of solutions 4 5
Nonlinear equations, general observations 3—4
Nonlinear equations, hybrid of secant method and interval bisection 37—40
Nonlinear equations, interpolatory method 33
Nonlinear equations, interval bisection qv
Nonlinear equations, Muller's method qv
Nonlinear equations, multipoint method qv
Nonlinear equations, Newton's method qv
Nonlinear equations, polynomial equations 25
Nonlinear equations, quadratic formula qv
Nonlinear equations, quasi-Newton method 4 17n 17 27
Nonlinear equations, root and zero contrasted 9
Nonlinear equations, secant method qv
Nonlinear equations, successive substitutions method qv
Nonlinear equations, two-point method qv
Nonlinear equations, uniqueness of solutions 4
Nonsingular matrix 78 90
Nonsingular matrix, perturbation of 117
Norm and orthogonal matrices 127
Norm of a diagonal matrix 127
Norm of a rank-one matrix 127
Norm, column-sum norm 115
Norm, consistency 114 116 127
Norm, Euclidean norm 114
Norm, Frobenius norm 115
Norm, infinity-norm 113—115
Norm, Manhattan norm 114
Norm, matrix norm 114—115
Norm, max norm 114
Norm, normwise relative error 115—117 120 128
Norm, one-norm 113—115
Norm, row-sum norm 115
Norm, triangle inequality 114
Norm, triangle inequality. 113
Norm, two-norm 72 113—114 115n 127—128
Norm, vector norm 113—114
Numerical differentiation, central-difference formula 183
Numerical differentiation, compared with numercial integration 181
Numerical differentiation, error analysis 184—186
Numerical differentiation, forward-difference formula 182 184
Numerical differentiation, second derivative 183
Numerical differentiation, three-point backward-difference formula 184
Numerical integration 41 157
Numerical integration and Lagrange polynomials 161—162
Numerical integration, change of intervals 158
Numerical integration, compared with numerical differentiation 181
Numerical integration, Gauss — Hermite quadrature 177
Numerical integration, Gauss — Laguerre quadrature 176
Numerical integration, Gauss — Legendre quadrature 176
Numerical integration, Gaussian quadrature qv
Numerical integration, Newton — Cotes formulas 161—162 166 167
Numerical integration, Simpson's rule qv
Numerical integration, Trapezoidal rule qv
Numerical integration, treatment of singularities 167—168
Numerical integration, undetermined coefficients 162—163 167 169
Numerical integration, weight function 167 176
Numerical quadrature 157
Operation count 81—82
Operation count, approximation by integrals 81 95
Operation count, Cholesky algorithm 95
Operation count, divided difference 146
Operation count, Gaussian elimination 102
Operation count, Gaussian elimination for Hessenberg matrices 111
Operation count, Gaussian elimination for tridiagonal matrices 111
Operation count, interpretation and caveats 81—82
Operation count, lower triangular system 81
Operation count, synthetic division 142
Order of a matrix see "Matrix"
Orthogonal function 171
Orthogonal matrix 127
Orthogonal matrix and two-norm 127
Orthogonal matrix, random 129
Orthogonal polynomials 169 171
Orthogonal polynomials, existence 173—174
Orthogonal polynomials, Legendre polynomials 176
Orthogonal polynomials, normalization 172
Orthogonal polynomials, orthogonality to polynomials of lesser degree 172
Orthogonal polynomials, reality of roots 174—175
Orthogonal polynomials, three-term recurrence 174
Outer product 97
Overflow see "Floating-point arithmetic"
Overwriting 92 93 102
Partitioning 14 90
Partitioning by columns 74
Partitioning, conformity 74
Partitioning, matrix operations 74
Partitioning, paritioned sum 74
Partitioning, partitioned product 74
Partitioning, positive-definite matrix 90
Perturbation analysis 51
Perturbation analysis, linear system 116—117
Perturbation analysis, sum of n numbers 57
Pivoting see "Gaussian elimination"
Polynomial interpolation 131
Polynomial interpolation at Chebyshev points 151—153
Polynomial interpolation, approximation to the sine 150
Polynomial interpolation, convergence 150—153 161
Polynomial interpolation, error bounds 149—150
Polynomial interpolation, error in interpolant 147—149
Polynomial interpolation, existence 137—138
Polynomial interpolation, extrapolation and interpolation 149—150
Polynomial interpolation, failure of convergence 151 153
Polynomial interpolation, general features 137
Polynomial interpolation, Lagrange interpolation 137—138 141
Polynomial interpolation, linear interpolation 149
Polynomial interpolation, natural basis interpolation qv
Polynomial interpolation, Newton interpolation qv
Polynomial interpolation, quadratic interpolation 135—136
Polynomial interpolation, Runge's example 151
Polynomial interpolation, shift of origin 136
Polynomial interpolation, uniqueness 138—139
Polynomial interpolation, Vandermonde matrix qv
Polynomial, bases 143n 172
Polynomial, evaluation by synthetic division 141—142
Polynomial, monic 172
Polynomial, number of distinct zeros 138
Positive-definite matrix 89
Positive-definite matrix, calculation of inverse 95
Positive-definite matrix, nonsingularity 90
Positive-definite matrix, partitioned 90
Positive-definite matrix, without symmetry requirement 89n
PRECISION see "Floating-point arithmetic"
PRODUCT 70
Product and transposition 72
Product of partitioned matrices 74
Product of triangular matrices 101
Product, associativity 72
Product, conformity 71
Product, distributivity 72
Product, inner product 72
Product, inverse of 78
Product, matrix 70—71
Product, matrix-vector 71 75
Product, noncommutativity of matrix product 72 74
Product, rank-one matrix and a vector 73
Product, recipe for matrix product 71
Quadratic convergence 14 19—20
Quadratic convergence of Newton's method 14 19
| Quadratic convergence, doubling of significant figures 14
Quadratic formula 61—63
Quadratic formula, discriminant 63
Quadratic formula, revised 63
Rank-one matrix 73
Rank-one matrix, computing with 73
Rank-one matrix, storing 73
Rank-one matrix, two-norm of 127
Reciprocal calculated by Newton's method 11
Regression 89
Relative error 7 57 128
Relative error and rounding error 49
Relative error and significant figures 7—8
Relative error as convergence criterion 8
Relative error, normwise see "Norm"
Relative residual 128
Relative residual and stability of linear systems 128—129
Residual 128
Rounding error 40 47—49
Rounding error and relative error 49
Rounding error in linear systems 120
Rounding error, accumulation 55 58—59 65
Rounding error, adjusted rounding unit 55
Rounding error, cancellation qv
Rounding error, chopping 48—49
Rounding error, computation of the rounding unit 49
Rounding error, difference equation 63—65
Rounding error, error bounds 48—49 59
Rounding error, error bounds for floating-point operations 50
Rounding error, general observations 65—66
Rounding error, inferiority of chopped arithmetic 58—59
Rounding error, machine epsilon 49
Rounding error, magnification 65
Rounding error, rounding 48
Rounding error, rounding unit 49 120 123
Rounding error, statistical analysis 59
Rounding error, truncation 48
Rounding unit see "Rounding error"
Rounding-error analysis, accuracy of a sum of positive numbers 58—59
Rounding-error analysis, accuracy of computed sum 58
Rounding-error analysis, backward error analysis qv
Rounding-error analysis, cancellation qv
Rounding-error analysis, Cholesky algorithm 98
Rounding-error analysis, difference equation 64—65
Rounding-error analysis, Gaussian elimination qv
Rounding-error analysis, numerical differentiation 184—186
Rounding-error analysis, simplification of error bounds 54—55
Rounding-error analysis, single error strategy 65
Rounding-error analysis, sum of n numbers 53—55
Rounding-error analysis, sum of two numbers 50—51
Row index see "Matrix"
Row orientation 83—84 87 98n
Row orientation and level-two BLAS 109
Row orientation, general observations 86
Row vector see "Vector"
scalar 70
Scalar as 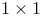 matrix 69 matrix 69
Scalar, multiplication by 70
Scalar, represented by lower-case Latin or Greek letter 70
Secant method 27 34
Secant method as an interpolatory method 33
Secant method, combined with interval bisection 37—40
Secant method, convergence 21 see
Secant method, failure 34 37
Secant method, geometric derivation 28
Secant method, Newton's method as confluent case 29
Secant method, quasi-Newton method 17
Significant figures and quadratic convergence 14
Significant figures and relative error 7—8
Simple zero 24
Simpson's rule 158
Simpson's rule as a partial Gauss quadrature 169
Simpson's rule, composite rule 165—166
Simpson's rule, derived by undetermined coefficients 162—163
Simpson's rule, error formula 166
Simpson's rule, error in composite rule 167
Simpson's rule, exact for cubics 167 169
Simpson's rule, half-simp rule 166
Singular matrix 123
Spline interpolant 153
Square root, calculated by Newton's method 11
Stable algorithm 41 55 128—129
Stable algorithm, backward error analysis qv
Stable algorithm, dialogue on stability 55—56
Stable algorithm, Gaussian elimination 125
Stable algorithm, synthetic division 142
Stewart, G.W. 103
Sublinear convergence 20n
Successive substitution method 21
Successive substitution method, convergence 21
Successive substitution method, geometric interpretation 21
SUM 70
Sum and transposition 72
Sum of partitioned matrices 74
Sum, associativity 72
Sum, comformity 70
Sum, commutativity 72
Sum, distributivity 72
Sum, matrix 70
Sum, vector 71
Superlinear convergence 20
Superlinear convergence, not of order p 21n
Superlinear convergence, two-point methods 32
Symmetric matrix, economization of operations 92
Synthetic division 141—142
Synthetic division, evaluation of Newton interpolant 142
Synthetic division, operation count 142
Synthetic division, stability 142
TRANSPOSE 69—70 72
Transpose and matrix operations 72
Transpose, inverse of 78
Trapezoidal rule 158—160
Trapezoidal rule, analytic derivation 159
Trapezoidal rule, composite rule 160 181
Trapezoidal rule, error formula 159—160
Trapezoidal rule, error in the composite rule 160—161
Trapezoidal rule, geometric derivation 158—159
Triangle inequality see "Norm"
Tridiagonal matrix 111
Tridiagonal matrix and Gaussian elimination 111
Two-point method 28
Two-point method, convergence analysis 29—32
Two-point method, rate of convergence 32
Underflow see "Floating-point arithmetic"
Vandermonde matrix 137 144
Vandermonde matrix, ill-conditioning 136
Vandermonde matrix, nonsingularity 135 138
Vector 69
Vector as 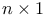 matrix 69 matrix 69
Vector supercomputer 109
Vector, column vector 69
Vector, component 69
Vector, dimension 69
Vector, n-vector 69
Vector, represented by lower-case Latin letters 70
Vector, row vector 69 72
Vector, vector operations see "Multiplication by a scalar" "Sum" "Product" "Transpose"
Virtual memory 83 84 86
Virtual memory, page 83
Virtual memory, page hit 83
Virtual memory, page miss 83—85
Weierstrass approximation theorem 176
Weight function 171
Wilkinson, J.H. 37 110
Zero matrix see "Matrix"
Zero of a function 9
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



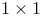 matrix
matrix 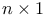 matrix
matrix