|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Shapiro S. — Thinking about Mathematics: The Philosophy of Mathematics |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
A posteriori knowledge 22 91 101 2 108 9
A priori knowledge 22 4 27 9 57 75 76 90 91 2 99 108 9 124 5 130 135 6 211 215 218 19
Abstract counterpart 234 223 4 246 278 285
Abstract objects 26n 32 57 133 162 206 216 33 238 242 243 8 252 4 257-8 261 70 272
Abstract-concrete dichotomy 26n 162n 233
Abstraction 66 8 70 81 2 88 136 8 152 259 60 276 83
Algorithm 43 159 160 1 163 165 181n 183 196 7
Analytic proposition 77 81 84 5 92 107 9 124 30 133 6 190 212 15
Ante rem realism 262 263 70 275 6 279 80 282 285 6
Anti-realism see realism
Anti-realism, semantic 33 194
Application of mathematics 16 18 19 33 9 40 57 8 69 71 76 7 91 113 146 8 149 50 216 20 234 7 252 255 6
Archimedean principle 101
Aristotle 4 54 63 71 76 95 262 3 269
Arithmetic 40 57 60 65 71 75 79n 81 86 9 95 101 109 15 119 125 134 7 147 165 8 210 258
Arithmetic, axioms of 43 95 100 111 120 1 125 127 134 250 284
Arithmetic, finitary 159 165 167 8 174 5 205 209 210 235 253
Arithmetic, primitive recursive 161
Astrology 19
Attributes see concepts; properties
Ayer, A. J. 4 129 30
Azzouni, J. 250 2
Balaguer, M. 229n 252 6 286
Basic Law V. 1 14 15 1 16 134 137 8
Becoming, world of 51 9
Being, world of 51 9 62 3 64 70 205
Benacerraf, P. 31 3 257 265 267 271
Berkeley, G. 4 45 74
Bernays, P. 15 152 167
Bishop, E. 184n 187 189
Bivalence 24 30 33 53 142 173 4 185 193 194 202 209 law
Bolzano 3 4 124
Boolos, G. 137 8
Bounded 159 60 162
Bourbaki, N. 39
Brouwer, L E. J. 8 32 172 174 85 186 189
Burgess, J. 243-49
Caesar problem 111 12 137 157 264 6
Calculation 59 80 87 89 95 8 144 147 159 60 189
Cantor, G. 40 158 208 9
Cardinal structure 277 80
Carnap, R. 4 14 124 32 212 13
Category theory 4 272n
Cauchy sequence 181 3 281
Causal theory of knowledge 244 250 251 252
Certainty 22 61 2 74 76-7 99 102 129 158 161 2 165 211 218 19 252
ch see continuum hypothesis
Character, typographical 140 142 8 161 5 175n 258 276 8 281
Chihara 33 227 237 43 246 8
Choice sequence 181 3 189
Choice, principle of 9n 122 3 182n
class 9 10 40 2 112 14 116 24 158 180 1 10 216 220-4 229 235 238 43 265
Classical logic 8 9 11 13 14 30 172 4 178 81 183 4 185-6 188 9 190 7 209n 242
Coffa, A. 24 91 124 133 184
Coherence principle 286 9
Completeness principle 101 122 181n 227 230 232 243
Completeness theorem 15 287
Computability 4 (see also calculation)
Computation see calculation
concepts 10 22 26 7 40-4 65 68 77 82 84-6 88 90 108 110n 111 14 116 123 128 137 208 216 223 238 9 242 3 263
Concrete objects 10 12 26n 35 53 7 65 71 75 6 81 161 162 164 204 206 8 216 222 32 245 282n 286
Conservative extension 138 163 233-6
Consistency 13 134 138 153 7 158 163 4 166 8 169 235 253 4 274 286 8
Consistency. 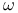 -consistency 166 -consistency 166
Consistency. proof of 134 153 7 164 8 169 70 185 209
Constructibility 240 3
Constructibility quantifier 240 3
Constructivism 184n 187 189
Contingency see necessity
Continuum Hypothesis 42 3 208 10 232 243
Convention 126 30 237 251
Counterexample, weak 183
Creative subject 181 2
Cumulative hierarchy 118n 131 223 265 272 3 275 287 9
Curry, H. 168 70 188n
Dedekind cut 122 281
Dedekind, R. 11 12 122
Deductivism 148 57 158 164 209 285
Definition 76 92 99 108 9 111 119 124 135-6 154 7
Definition, functional 284n
Definition, implicit 129 152 3 154 5 157 283 9
Definition, impredicative 9 11 116 118 20 121n 122 8 135 180 203 4 241 2
Definition, ostensive 276 8
Descartes, R. 3 73 5 154 177
Diagrams 56 7 63 86 87 9 151
Dialectic 63
Divided line, Plato's 53 5
Double negation, principle of 173 178 9
Dummett, M. 13 32 33 125 190-7
Dynamic/static language 7 45 56 69 179-0
Effectiveness 43 4 131 159 60 165
Empiricism 4 18 19 63 69 74 6 91 2 100 2 124 6 130 1 212 20 Carnap Quine)
Epistemology 6 16 17 21 32 51 2 78 9 92 3 135-6 158 9 201 2 212 221 244 275-6
Equinumerosity 109 10 112 133-4 178 208
Equivalence relation 137n
Euclid's Elements 58n 69 84 7 94 156 231
Excluded middle, law of 8-9 11 13 172 4 178 84 186 9 192 7 201 209n intuitionism;
Existence condition 285 6
Explanation 34 7 64 135 6 217 264
Explanation, intrinsic 237
Extension of concepts 112 15 116 134 137 196
Extension, pure 75 81
External question 14 126 8 169n
Fermat's last theorem 132
Feynman, R. 39
Fiction 68 9 93 4 123-4 227
Fictionalism 227 37 255 6
Field, H. 32 226 7 227 37 246 255 260-1
Finitary arithmetic see arithmetic finitary
Finitism 158-8 195 196
First-order logic/languages 15 40 1 236n 285 287
FORM 27 51 60 64 66 70 262
Formalism 140 70 175 184 188n 192 209 253
Formalism, game 144 8 148 50 158 163 169
Formalism, term 142 4 145 158 162 169
Framework principle 1 29 2 1 3
Free choice sequence 181 3 189
Frege's theorem 111 118 19 134 135 6
Frege, correspondence with Hilbert 154 7 164 253
Frege, G. 33 67 8 82 96 8 108 15 115 16 117 19 124 125n 133 7 143 4 145 8 149 150n 177n 191n 264 267
G del 10 12 15 38 44 165 8 202 11 221 3 incompleteness) del 10 12 15 38 44 165 8 202 11 221 3 incompleteness)
Galileo, Galilei 6
Geometry 8 23 52 3 55 7 65 71 75 81-6 88 91 93 5 114 123 129 30 150 6 176 7 231
Geometry, analytic 44 73 150 153 4 177 231 234 261n
Geometry, non - Euclidean 89 90 130 150 153 176 177
Geometry, synthetic 230 2 261n
Goldbach conjecture 183
Good, The 52 53 54 63
Goodman, Nicolas 33 4
Hale 133 8
Hand, M. 269 70
Hebb, D. 222
Heine, E. 143
Hellman, G. 33 257 274 5
Hermeneutic nominalism 248 9
Heyting predicate calculus 185 187
Heyting semantics 185 6 193 194 5
Heyting, A. 8 9 32 185 9 191n 192
Higher-order logic/languages see second-order logic/languages
Hilbert programme 158-68 210 235 6 253
Hilbert, correspondence with Frege 154 7 164 253
Hilbert, D. 4 5 8 148 65 170 174 5 209 210 253 285 6
Hintikka, J. 81 83 4 85
Holism 17 19 37 130 1 192 3 213 16 218 20 224 239n 282
Homomorphism, representing 235 236n
Hume's Principle 110-12 117 118 134 8 284n
Hume, D. 4 74 75-6 92 99n 110n
Hypothetical-deductive method 17 102
Ideal mathematics 163-5 166 168 175 210 235
Idealism 25 6 28 9 29 30 32 36 38 180
| Idealization 51 55-8 69 71 88 93 5 98 101-2 160 175 177 8 189 194 5 196
Identity 67 110 112 137 143 239 259 265 6 268n
Impredicativity 9 10 11 116 118 23 127 128 135 180 203 4 241 2 impredicative)
In re realism 262 3 270 1 275 279
Incompleteness 15 43-4 131 2 165 8 170 196 7 210 2 5 6
Indefinite extensibility 196 7
Independent propositions 42 4 153 208 10 224 232 243
Indispensability 37 8 216 18 220 1 227 34 244 6 254 6 282
Induction, empirical 37 92 4 96 100 1 210 212
Induction, mathematical principle of 100 102 111 120 258 264
infinity 10 25 28 9 79 86 7 98 101 2 111 117 19 135 158 159 181-2 197 232 260 272 279 81
Infinity, principle of 119 121 138 222 3 243
Instrumentalism 146 7 163 235
Internal question 126 8 266
Intrinsic explanation 237
Intuition 27 8 99 100 150 3 154 7 169 176 8 204 8 211 221 4 244 5
Intuition, Kantian 23 4 77 79 91 136 150 3 154 7 162 176 207
Intuitionism 8 9 32 87 172 97 207 209n
Intuitionistic logic 9 13 30 79n 172 4 180 1 83 185 187 190 193 7 law
Kant, I. 23 4 73 76 91 91-2 107 113n 161 162 174-8 207 Kantian)
Kitcher, P. 91 2 101 2 265 7
Klein, Jacob 59 60
Knowledge see epistemology
Knowledge-of 205 6
Knowledge-that 205-6
Kreisel, G. 29
Kronecker, L. 12
Kuhn, T. 50
L wenheim - Skolem theorem 40-2 285 wenheim - Skolem theorem 40-2 285
Lakatos, I. 44 5
Language 11 13 14 16 25 6 29 31 2 41 124 33 5 153-4 184 5 186 7 190 5 212 15 239-42 248 256
Lear, J. 68
Leibniz, G. 3 4 73 74 230
Limit concept 93
Linguistic framework 126 33
Linguistic turn 125 184
Logic 4 6 24 29 40-1 45 79n 83 4 92 3 101 14 121 3 125n 127 129 30 134 6 6 149 53 155 7 159 61 184 5 187 190 202 214 15 219 2 8-9 246 274 5 285 288-9
Logical positivism 4 14 124 33 212 13 214 15
Logical terminology 108 110 111 122 3 136 149-50 190 193 4
Logicism 107 24 125 127 148n 150n 157 161 166 202
Logicism, neo 133 8 166n 264 5 283n
logistic 59 60
Maddy, P. 11n 18 20 32 97 8 220 4
Malament, D. 229n
Manifestation requirement 190-1 193 5
McLarty 273n
Meaning-is-use thesis 190-3 256
Mechanism 43 4 202n
Meta-mathematics 153-5 158 161n 164 5 169 70 187 253 4 proof model
Mill, J. S. 4 91 102 124 128 131 212 215 224
Modality 5 71 218 237 46 273-5
Model theory 5 40 2 123 150 153 197 234 238 253 4 264 272 275 287 9
Nagel, E. 130 151
National debt 279
Natural number structure 258 263 4 265 7 269 70 274 5 280 1 283n 287
naturalism 16 20 24 28 90 92 126 131 212 220 1 224 244 247 8
Necessity 21 23 4 27 28 9 75 6 81 89 99 113 124 5 129 135 211 218 19 229 30 246 252 258n 273 274
Neo-logicism 133 8 166n 264 5 283n
Neurath, ship of 17
Newton, I. 73 216 17 229
No class theory 123 4 238 239
Nominalism 26 27 29 33 216 17 218 226 56 260 1 263 273
Nominalistic language 216 17 228 37 240 2
Non - Euclidean geometry see geometry non
Number, cardinal 41 1 5 6 277 80
Number, integer 121 2 144 267 8 281
Number, natural 25 40 1 57 60 65 8 71 75 80 82 86 7 95 100 109 14 115 117 21 131 2 134 5 142 159 62 164 176 7 222n 242 3 258 263 7 281
Number, rational 58 71 121 2 177 183
Number, real 40 44 45 71 101 113 122-3 138 144 148n 158 177 181 2 208 217 228 231 232 3 237 243 260 1 281
Object see singular term
One-over-many see Form; universals
Ontological commitment 228 240 248 9 250
Ontological option 272 273
Ontology see realism in ontology
Ontology, relativity of 41 2 267 8 269
Open sentence 239 43
Ostension 276 8
Parsons 86 7 268n 271 282n
Pasch, M. 151
Pattern 257 258 60 261 3 ante
Pattern recognition 276 83
Peano axioms see arithmetic axioms
Perception 18 23 27 64 5 75 80 2 83 4 87 9 93 4 97 8 99 100 162 176 8 204 7 221 3
Philosophy-first principle 9 16 17-18 20 90 91 2 212 244
Philosophy-last principle 13 15 17 18 20
Physical objects see concrete objects
Physics 34 38 67 89 90 99n 183 204 5 208 211 215 20 222 228 229 32 235-6 246 9
Places-are-objects perspective 268-70 284
Places-are-offices perspective 268 70 271
Plato 3 5 6 7 8 50 63 66 69 74 88 179 205 262
Platonism 8 15 27 8 70 1 75 221 233 234 257 8 264 5
Platonism, full-blooded 252 4 256 286
Poincare, H. 9-10 176
Positivism, logical see logical positivism
Possible worlds 5 238
Postulate system 250 2
Postulation 52 68 119 121 282
Posy 79n 195
Primitive notion 108 129 151 209 230 254 275 287 8
Proclus 56
proof 4 22 3 36 43 45 56-7 62 3 79n 86 9 151 164 5 167 8 185 7 192 193
Proof theory 161n 187 253 4
Properties 10 26 7 44 65 68 108 109 110n 111 14 116 123 4 128 137 157 208 216 222n 238 9 242 3 262 268
Psychology 66 76 219 222 276
Putnam, H. 41 214 216-18 221 238
Quantifier 127 194 5 197 216 240 3
Question, external 14 126 8 169n
Question, internal 126 8 266
Quine, W. V. 4 16-20 37 92 130 1 136 192 3 212 20 237 8 239 240 251 267
Ramsey, FP 121n 128
Rationalism 3 4 50 63 74 6 88
Real analysis see number real
Realism 9 12 15
Realism in ontology 25 9 31-3 36 53 66 8 113 125 133 143 174 201 56 257 8 264 5
Realism in truth-value 29 33 37 8 42 3 53 66 8 174 185 202 216 220 226 7
Realism, ante rem see ante rem realism
Realism, in re see in re realism
Reducibility, principle of 120 1 122 3 127
Reference 5 25 29 41 203-4 250 1
Reference, thick/thin/ultrathin 251
Relationalism 229 30
Relativity of ontology 41 2 267 8 269
Resnik, M. 32 230 257 60 264 267 8 269 282 285-6 287
Revisionism 13-14 16 30 172 97 227 241
Revolution 21 2 50
Revolutionary nominalism 247 8 249
Rigour 49 50 63 74 149 150 168
Rosen, G. 243 9
Rosser, J. 166n
Rule-following 145n
Rule-governed procedure 140 181 3
Russell 3 114 15 115 24 125 127 202 3 204 8 238 9 268n
Russell's paradox 114 15 116 158 9 206
Satisfaction 40 134 5 138 153 238 239 43 246 253 4 272 275 285 9
Schroder - Bernstein theorem 178
Second-order logic/languages 41 2 110 120n 134 135 6 178 239n 285 287
Semantic tradition 124 5 133 184
Semantics 16 29 30 31 36 45 173 185 6 190 5 240
Semantics, compositional 193
Semantics, molecular 193 4
Set 9 10 40 2 52 101 116 18 158 178 181 10 222 3 229 235 238 43 265
Set theory 18 27 40 102 118 136 158 10 219 20 222 4 253 4 265 272 275 287 9
Set theory, Zermelo - Fraenkel 42 3 118 209 224
Shapes 142 3 262 277
Shapiro, S. 32 42 232 235 236n 267 269 282 283n 284 5
Singular term 31 45 83 4 110 134 137 239 251 270 284
Skolem paradox 40 2
Skolem, T. 15 40 41
Socrates 60 2
Socratic method 51 60 1 62 63
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 -consistency
-consistency  del
del