|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Tinkham M. Ч Introduction to superconductivity |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Penetration depth, with diffuse scattering 102 105 441
Penetration depth, with specular scattering 102 105 440Ч441
Perfect conductivity 2 18
Perfect diamagnetism 2
Persistent current 2 128 180 185 403
Phase of wavefunction 13Ч14 113 149
Phase slip 206 288Ч295 299 428Ч431
Phase-number uncertainty relation 52 68 256Ч259 274Ч275
Phase-slip centers 417 427Ч432
Phase-slip centers, difference in electrochemical potentials in 428Ч430
Phillips, J. R. 236
Phillips, W. A. 84
Phonon structure in tunneling 78Ч79
Phonon-mediated attraction 47Ч48
Photon-assisted tunneling 211Ч214
Pines, D. 47
Pinning effects 166 176 345Ч363
Pinning force 166
Pinning frequency 176
Pinning mechanisms 181 345Ч348
Pippard coherence length 7 11 118Ч119
Pippard nonlocal electrodynamics 6Ч8
Pippard, A. B. 6Ч8 95 107 422
Prange, R. E. 304Ч307
Prober, D. E. 308n.
proximity effect 197
Quality factor 41Ч42
Quasi-particle disequilibrium 404Ч432
Quasi-particle disequilibrium, energy-mode vs. charge-mode 405Ч407 (see also Charge-mode disequilibrium; Energy-mode disequilibrium)
Quasi-particle energies 61Ч71
Quasi-particle energies, in vortex core 388Ч389
Quasi-particle energies, shifted by current 387Ч388
Quasi-particle excitations 61Ч62 67Ч71 386-399
RCSJ model, definition of 202Ч205 (see also Josephson junctions)
Reif, F. 397
Relaxation time, electron-phonon 401Ч402 407Ч408
Relaxation time, for energy and charge 407Ч408 431
Relaxation time, Ginzburg Ч Landau 308 314 401
Resistance of wire, above 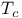 312 312
Resistance of wire, above type 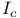 , type I 32Ч37 , type I 32Ч37
Resistance of wire, above type 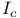 , type II 171Ч173 , type II 171Ч173
Resistance of wire, below 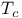 288Ч293 288Ч293
Resistive voltage from flux motion 163 166Ч170
Resistively shunted junction model see RCSJ model
Resnick, D. J. 239
Rice, T. M. 376Ч378
Richards, P. L. 247n.
Rinderer, L. 36
Rosenblum, B. 176 372
Rotation-induced flux 114
Roth, L. M. 146
Rowell, J. M. 79
Ruggiero, S. T. 323Ч324
Russer, P. 212
Rzchowski, M. S. 240 241 243n.
Safar, H. 339Ч341
Saint Ч James, D. 135 138 140Ч142
SBT model of phase-slip center 428Ч431
Scalapino, D. J. 78 409
Sch n, G. 15 405 420 n, G. 15 405 420
Schawlow, A. L. 107
Schmid Ч Sch n formalism 405Ч408 416 431 n formalism 405Ч408 416 431
Schmid, A. 15 167 302Ч304 399 401 405 410 412 420
Schmidt, H. 304
Schrieffer, J. R. 9 78
Schubnikov phase 12
Screened Coulomb repulsion 48
Second-order phase transition 19 112 132
Semiconductor model 73Ч78 423Ч421
Shapiro steps 211Ч212 214 242Ч243 431
Shapiro steps, giant 242Ч243
Sharvin, Yu. V. 36
Shepherd, J. G. 422
Shoenberg, D. 107
Sigrist, M. 376Ч378
SilsbeeТs rule 21 33
Sine Ч Gordon equation 221Ч224
Single-electron tunneling 264Ч286
Singlet state 44 374Ч375
Skalski, S. 395Ч398
Skocpol, W. J. 428Ч431
Slichter, C. P. 84 381Ч382
Small Josephson junctions 248Ч286
Small Josephson junctions, Coulomb charging energy in 249 264Ч267
Small Josephson junctions, damping by lead impedance 249Ч256
Small Josephson junctions, phase diffusion branch of  curve 252Ч256 263Ч264 curve 252Ч256 263Ч264
Small Josephson junctions, quantum effects of small capacitance 256Ч264
Small Josephson junctions, retrapping current, effect of lead impedance on 250Ч252 (see also Double tunnel junction circuit)
Smith, P. F. 187 191 194
Soliton 218Ч224
Solomon, P. R. 30 176
Sommerhalder, R. 157
Sonier, J. E. 381
Specific heat 64Ч66
Spectroscopic energy gap 68 99
Spectroscopic energy gap, vs. gap parameter 396
Spurway, A. H. 194
SQUID devices 224Ч234
SQUID devices, choice of parameters for 227
SQUID devices, dc 224Ч229
SQUID devices, flux-locked loop 229
SQUID devices, limits on sensitivity 228
SQUID devices, magnetometers, gradiometers, and susceptometers 213 232Ч233
SQUID devices, quantum limits 228 234
SQUID devices, rf 229Ч231
SQUID devices, screening in 225Ч227
SQUID devices, voltmeters and amplifiers 233Ч234
Stability criterion 189
Steglich, F. 383
Stephen, M. J. 13 167 401
Stewart, W. C. 204
Str ssler, S. 398Ч399 ssler, S. 398Ч399
Strnad, A. R. 185
Subharmonic energy gap structure 425Ч427
Sum rule, oscillator strength 38 88 99 115
Superconducting electrons, density of 4 9 37 113Ч116
Superconducting layered compounds see Layered superconductors
| Superconducting quantum interference device see SQUID devices
Superconducting slab 20 25 178Ч179
Supercooling transition 134Ч135 138 303
Supercurrent velocity 113
Surface energy 25Ч26 121Ч122
Surface resistance 40
Surface sheath superconductivity 136Ч138
Takayama, H. 306
Tate, J. 114
Tewordt, L. 389
Thermal stability of magnet 186Ч187
Thermodynamic critical field 3 21 23 65Ч66 113 161
Thermodynamic quantities 64Ч66
Thomas, G. A. 314
Thompson, R. S. 167 400
Thouless, D. J. 238
Thuneberg, E. V. 346
Tien Ч Gordon formula 213 245
Tilted-washboard potential see RCSJ model
Time-dependent Ginzburg Ч Landau theory 308Ч 309 399Ч401 412-421
Time-dependent Ginzburg Ч Landau theory, application to time-varying field 400Ч401
Time-dependent Ginzburg Ч Landau theory, phonon-limited 412Ч421
Time-reversed pairs 384Ч387 390
Tindall, D. A. 422
Tinkham, M. 8Ч9 87Ч88 100 21n. 139 169 174 270 272 283 286n. 292 304Ч306 333 364n. 397Ч399 408 415 417 420 421n. 428Ч431
Tomasch effect 74
Tonomura, A. 174
Tra ble, H. 30 ble, H. 30
Transition probabilities 79Ч89
Transmissivity of thin films 99
Tsuei, C. C. 369 378
Tucker quantum theory of mixers and detectors 245Ч247
Tunneling of electrons 71Ч79
Tunneling of electrons, differential conductance 76 426
Tunneling of electrons, matrix element 72
Tunneling of electrons, negative resistance in 77
Tunneling of electrons, normal-normal 75
Tunneling of electrons, normal-superconductor 75Ч76
Tunneling of electrons, phonon structure in 78Ч79
Tunneling of electrons, single-electron 264Ч286
Tunneling of electrons, superconductor-superconductor 77Ч78 (see also Josephson effect)
Tunneling transistor, superconducting 277
Tuominen, M. T. 269 271 273 327
Twist pitch, critical value of 193Ч194
Twisted composite conductors 190Ч195
Two-fluid model 37Ч40 83Ч86
Two-fluid model, temperature dependence 20 101 103 108 381 392
Type I superconductors 18Ч43 136 161
Type II superconductors 11Ч13 122 148Ч195
Type II superconductors, Campbell penetration depth in 373
Type II superconductors, Coffey Ч Clem model of high-frequency losses in 370Ч373
Type II superconductors, complex penetration depth in 371Ч373
Type II superconductors, critical state in 176Ч179
Type II superconductors, diffusion Ч London equation for 371
Type II superconductors, flux creep in 179Ч187
Type II superconductors, flux flow in 166Ч176
Type II superconductors, in time-varying magnetic fields 187Ч195
Type II superconductors, magnetization curves of 155Ч162
Type II superconductors, thermally activated flux flow in 180Ч182 332Ч334
Type II superconductors, vortices in 149Ч155 (see also High-temperature superconductors)
Ultrasonic attenuation 82Ч84
Uncertainty relations, phase-number 52 68 256Ч259 274Ч275
Unconventional pairing 375Ч376
Usadel, K. D. 201
Valatin, J. G. 60
van der Zant, H. S. 240
van Gurp, G. J. 174 177
van Ooijen, D. J. 174 177
van Son, P. C. 410
Vidal, F. 176
Villard, C. 330
Vinokur, V. M. 347 361
Viscous drag coefficient 166Ч169
Volkov, A. F. 423 1
voltage bias 39
Vortex bundles 174 180Ч181 355
Vortex lines, interaction between 154Ч155
Vortex, core 149 152
Vortex, core, normal 167Ч168
Vortex, core, quasi-particle states in 388Ч389
Vortex, energy of 153Ч154
Vortex, entropy transport by 176
Vortex, high- approximation 151Ч155 approximation 151Ч155
Vortex, in film in parallel field 142Ч143
Vortex, isolated 149Ч154
Vortex, London approximation 152Ч155
Vortex, magnetic field in 152
Vortex, moving, electric field in 168Ч169
Vortex, pinning of see Pinning effects
Vortex, quasi-normal core of 167Ч168 389
Vortex-glass model 356Ч360
Vortex-glass model, empirical scaling functions in 358Ч360
Vortex-glass model, in two dimensions 360Ч361
Waldram, J. R. 107
Walters, C. R. 187
Warburton, R. J. 292
Weak link see Josephson junction
Weak-coupling approximation 45 57
Webb, W. W. 292
Wells, B. O. 379
Wellstood, F. C. 228
White, W. R. 324
Wilkins, J. W. 78 305
Wilson, M. N. 187
Wollman, D. A. 378
Wolter, J. 414
Woolf, M. A. 397
Worthington, T. K. 363
Wyatt Ч Dayem effect 409
Wyder, P. 398Ч399
Yamafuji, K. 140
Yanson, J. K. 218 370
Yeshurun, Y. 333
Yu, M. L. 422
Zaitsev, A. V. 423
Zeldov, E. 335n.
Zorin, A. B. 276
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 , type I
, type I n, G.
n, G.  curve
curve  ssler, S.
ssler, S. ble, H.
ble, H.  approximation
approximation