|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Tinkham M. Ч Introduction to superconductivity |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Halperin, B. 1 210 292
Halperin, W. P. 297
Hanna, A. E. 283
Harden, J. L. 162
Hardy, W. N. 381n.
Harris, R. E. 30 204n.
Haviland, D. B. 250n.
Heavy fermion superconductors 382Ч383
Hebel Ч Slichter peak 84Ч86 381Ч382
Hekking, F. W. J. 285
Helmholtz free energy 3 22 65Ч66 121 124 158Ч159 326-327
Hempstead, C. F. 185
Hergenrother, J. M. 270 272 286
Hess, H. F. 389
High-frequency electrodynamics 37Ч42 86Ч89 370-373
High-frequency electrodynamics, Coffey Ч Clem model 370Ч373
High-temperature superconductors 16 316Ч382
High-temperature superconductors, anisotropic Ginzburg Ч Landau model for 319Ч330
High-temperature superconductors, anisotropic mass and other parameters 319Ч322 325
High-temperature superconductors, anomalous properties of 373Ч383
High-temperature superconductors, anomalous properties of, energy gap properties 378Ч382
High-temperature superconductors, anomalous properties of, temperature dependence of penetration depth in 380Ч381
High-temperature superconductors, copper oxide planes and chains in 317
High-temperature superconductors, discovery of 316Ч317
High-temperature superconductors, evidence for 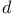 -wave pairing in 376Ч382 -wave pairing in 376Ч382
High-temperature superconductors, evidence for 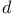 -wave pairing in, from flux quantization 376Ч378 -wave pairing in, from flux quantization 376Ч378
High-temperature superconductors, flux lattice melting field vs. temperature 337 341Ч342
High-temperature superconductors, flux lattice melting transition 334Ч344
High-temperature superconductors, flux lattice melting transition 2D vs. 3D 342Ч344
High-temperature superconductors, flux lattice melting transition, experimental evidence 338Ч342
High-temperature superconductors, flux lattice melting transition, field vs. temperature 337 341Ч342
High-temperature superconductors, flux lattice melting transition, model estimate for temperature of 335Ч338
High-temperature superconductors, flux lattice melting transition, phase diagrams 344
High-temperature superconductors, flux lattice melting transition, relationship to  337Ч338 337Ч338
High-temperature superconductors, granular 363Ч370
High-temperature superconductors, granular, brick-wall model for 369Ч370
High-temperature superconductors, granular, effective medium parameters for 364Ч368
High-temperature superconductors, granular, in relation to continuum models 368Ч369
High-temperature superconductors, resistive transition in 331Ч344 (see also Boson glass model; Layered super-conductors; Type II superconductors; Vortex-glass model)
Hilbert, C. 234
Hole creation operators 69
Hot spot in bridge 431
Houghton, A. 338Ч339 341 344
Hsiang, T. Y. 422
Hu, C. R. 167 400
Huebener, R. P. 36
Hunt, T. K. 126
Hysteresis in critical state 179
Hysteresis losses 190Ч191
Iansiti, M. 254 258 263
IIS 120 393
Inelastic scattering time 402
Ingold, G. L. 253 254
Instability, thermal 186Ч187
Interface energy 25Ч26 120Ч122
Intermediate state 22Ч37 123
Intermediate state, laminar model of 26Ч32
Intermediate state, LondonТs model for wire above 32Ч37
Intermediate state, magneto-optic technique for observation of 36
Intermediate state, of flat slab 25Ч31
Intermediate state, of sphere 31Ч32
Internal energy 65Ч66
Isotope effect 47 58
Ivlev, B. 1 432n.
Iye, Y. 333
Jackel, L. D. 430
Jacobs, A. E. 389
Jaycox, J. M. 229
Jellium model 47Ч48
Johnson, A. T. 250Ч251 255
Josephson critical current, Ambegaokar Ч Baratoff formula for 200Ч201 333
Josephson critical current, in 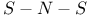 junctions 201Ч202 junctions 201Ч202
Josephson critical current, in metallic weak links 198Ч201
Josephson effect 196Ч286
Josephson effect, cos  term in 204 term in 204
Josephson effect, coupling energy in 198
Josephson effect, frequency relation 14 166 196
Josephson effect, in extended junctions 215Ч224
Josephson effect, in inhomogeneous junctions 217Ч218 370
Josephson effect, in presence of magnetic flux 213Ч224
Josephson effect, pendulum analogy 219Ч220
Josephson effect, quantum interference of currents 213Ч218
Josephson effect, time-dependent solutions 221Ч224
Josephson junction arrays 234Ч243
Josephson junction arrays, as microwave source 243
Josephson junction arrays, fluxons in 236Ч241
Josephson junction arrays, fluxons in, pinning of 240Ч242
Josephson junction arrays, frustration in 235
Josephson junction arrays, giant Shapiro steps in 242Ч243
Josephson junction arrays, in magnetic field 239Ч242
Josephson junction arrays, in rf fields 242Ч243
Josephson junction arrays, in strongly commensurate fields 241Ч242
Josephson junction arrays, Kosterlitz Ч Thouless transition in 237Ч239
Josephson junction arrays, plaquettes in 234Ч235
Josephson junction arrays, screening length in 236
Josephson junction arrays, vortices in 236Ч241
Josephson junctions,  characteristics of 205Ч211 characteristics of 205Ч211
Josephson junctions, capacitive mass parameter 205
Josephson junctions, critical current of, fluctuation effects on 198 207Ч209
Josephson junctions, damping parameter of 204
Josephson junctions, fluxons in 218Ч224
Josephson junctions, hysteretic 206
Josephson junctions, plasma frequency of 204 223
Josephson junctions, quality factor of 204
Josephson junctions, retrapping current of 206 209Ч210
Josephson junctions, rf-driven 211Ч214
Josephson junctions, slow waves in 222Ч224
Josephson junctions, small see Double tunnel junction circuit; Small Josephson junctions
Josephson junctions, solitons in 218Ч224
Josephson junctions, solitons in, pendulum analog for 219Ч220
Josephson junctions, types of 197
Josephson junctions, zero-field steps in 224
Josephson penetration depth 219
Josephson vortices 216 218 219
Josephson vortices, pinning of 218
Josephson, B. D. 14 69 196
Joyez, P. 278
K mmel, R. 389 mmel, R. 389
Kadin, A. M. 430Ч431
Kamerlingh Onnes, H. 1 2 316
Kaplan, S. B. 407
Karrai, K. 114
Kautz, R. L. 253
Keller, J. 314
Kes, P. H. 346
Ketchen, M. B. 228
Kim, Y. B. 173 180 183 185
Kinetic energy of current 113 123Ч125
Kirchner, H. 30
Klapwijk, T. M. 409 425Ч427
Kleiner, W. H. 146
Koch, R. H. 227 358Ч360
Kogan, V. G. 326Ч327 330Ч331
Kommers, T. 409
Korenman, V. 314
Koshelev, A. E. 343
Kosterlitz Ч Thouless transition, in arrays 237Ч239
Kosterlitz Ч Thouless transition, in films 294Ч295
Kosterlitz Ч Thouless transition, in layered superconductor 344
Kramer, L. 432n.
Kramers Ч Kronig relations 88 247
Krusin Ч Elbaum, L. 347Ч348
Kulik, I. O. 201
Kunchur, M. N. 170
Kurkij rvi, J. 305Ч306 rvi, J. 305Ч306
Kuzmin, L. S. 250n.
Kwok, W. K. 340Ч341 346
Lafarge, P. 273
LAMH theory 292Ч293
Laminar model 26Ч32
| Landau branching model 30
Landau levels 134
Landau, L. D. 9 25 30 122
Langer, J. S. 289Ч292
Langevin force 309
Larkin, A. I. 16 199 312Ч313 321 398 405 418 420
Larkin-Ovchinnikov theory see Collective pinning
Laurmann, E. 107
Lawrence Ч Doniach model of layered superconductors 16 308 318Ч326 342
Layered superconductors, anisotropic Ginzburg Ч Landau description 319Ч330
Layered superconductors, crossover to two-dimensional behavior 322Ч326 330
Layered superconductors, Helmholtz free energy of 326Ч327
Layered superconductors, irreversibility line in 332Ч333
Layered superconductors, Lawrence Ч Doniach model of 16 308 318Ч326 342
Layered superconductors, lock-in transition in 330Ч331
Layered superconductors, magnetization of 326Ч331
Layered superconductors, scaling to isotropic model 321Ч322
Layered superconductors, torque in magnetic field 328Ч330
Ledvij, M. 330Ч331
Lee, P. A. 305Ч306
Lehoczky, S. L. (A.) 315
Levine, J. L. 126 397
Lewin, J. D. 187 194
Lifetime, of persistent currents 2 180 185 403
Lifetime, of quasi-particles 86 402
Likharev, K. K. 201 274 276
Lindemann criterion for melting 336 343
Lindhard, J. 115
Little Ч Parks experiment 128Ч130
Little, W. A. 127 290
Lobb, C. J. 238n. 240 364n.
London equations 4Ч6 18Ч21 37
London gauge 6113 130 150n.
London penetration depth, calculation of 90Ч93 113 437Ч441
London, F. 14 33 127
Lorentz force 13 155 163Ч167 177 354
Lu, J. G. 270 272
Lukens, J. E. 292
M hlschlegel, B. 65 103 hlschlegel, B. 65 103
M ller, K. A. 1 16 316 322 ller, K. A. 1 16 316 322
Maassen van den Brink, A. 286
Macroscopic quantum tunneling, damping effect on 262Ч263
Macroscopic quantum tunneling, of charge 284
Macroscopic quantum tunneling, of phase 259Ч264
Magnetic perturbations, effect of, on density of states 390Ч399
magnetization 20 155Ч162 302Ч308 326-331
Magnetization curve, area under 20 161
Magnetization, at intermediate flux density 157Ч159
Magnetization, at low flux density 156Ч157
Magnetization, fluctuation-induced 302Ч308
Magnetization, near 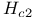 160Ч161 160Ч161
Magnetization, of layered superconductors 326Ч331
Magneto-optic technique for observation of intermediate state 36
Magnetometers see SQUID devices
Magnets for time-varying fields 187Ч195
Maki terms in fluctuation conductivity 313Ч314
Maki, K. 161 162 167 306 313Ч315 390Ч392 401
Maley, M. P. 354
Malozemoff, A. P. 333 369
Mannhart, J. 369
Mansky, P. A 331
Mapother, D. E. 66
Martinez, J. C. 329Ч331
Martinis, J. M. 253 263 277
Mason, W. P. 84
Masuda,Y. 86
Mathai, A. 378
Matricon, J. 167 349 389
Mattis, D. C. 87
Matveev, K. A. 278
McCumber, D. E. 204 291 292
McGrath, W. R. 247n.
McLachlan, D. S. 135 138
McMillan, W. L. 58 79
Meissner effect 2Ч3 5 19Ч22 303
Meissner effect, in Josephson junctions 219Ч220
Meissner effect, transverse, in layered superconductors 330Ч331
Meissner, W. 2
Mendelssohn, K. 8
Mercereau, J. E. 422
Metastable equilibrium 403
Meyer, J. D. 427Ч428
Miller, P. B. 102
Millstein, J. 397Ч399
Minnhagen, P. 237n.
Missing area in sum rule 88 99
Mitescu, C. D. 126
Mixed state 12 123 143Ч147 155Ч162
Model-hamiltonian 59
Mooij, J. M. 238 409
Morse, R. W. 83
Mukherjee, B. K. 35
Multifilamentary superconductors 187Ч195
Murakami, M. 347
Nazarov, Yu. V. 269 285
Nelson, D. R. 347 361
Newbower, R. S. 292Ч293
Newrock, R. S. 239n.
Noise, from flux motion 174
Noise, in SQUID 227Ч228 232 234
Nonequilibrium superconductivity 15 403Ч432
Nonlocal electrodynamic response 5 91 93Ч96 115
Nonlocal electrodynamic response, calculation of 93Ч96
Nonlocal electrodynamic response, Chambers 6 96
Normal core of vortex 167Ч168
Normal electrons 37 85
Nuclear relaxation 84Ч86
Nucleation, at surfaces at 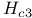 135Ч139 135Ч139
Nucleation, in bulk samples at 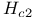 134Ч135 134Ч135
Nucleation, in films 139Ч143
Nucleation, in films, angular dependence 139Ч141
Ochsenfeld, R. 2
Octavio, M. 418Ч421 427
Ohmic conduction channel 38
Omel'yanchuk, A. N. 201
Order parameter 55 112
Orlando, T. M. 238 240n.
Orthodox theory of single-electron tunneling 280Ч283
Oscillator strength sum rule 38 88 99 1 15
Otter, F. A. 176
Ovchinnikov, Yu. V. 16
Pair creation operators 69
Pair-breaking perturbations 390Ч394
Pairing hamiltonian 53
Pairing potential 385Ч388
Pals, J. A. 414
Pancake vortices 327 330 334 342
Paramagnetic current term 90
Parks, R. D. 127 314
Pastoriza, H. 335n.
Paterno, G. 218
Patton, B. R. 305 314
Payne, M. G. 305Ч306
Peak effect 352
Pearl, J. 105 106
Penetration depth 4Ч6 18 100Ч108 437-441
Penetration depth, by Fourier analysis 101Ч102 437Ч441
Penetration depth, dependence on magnetic field 132
Penetration depth, impurities, effect of 96Ч97 102
Penetration depth, in arrays 236
Penetration depth, in extreme anomalous limit 102 440
Penetration depth, in high-temperature superconductors 108
Penetration depth, in local approximation 102 440
Penetration depth, in Pippard superconductors 100Ч101
Penetration depth, in thin films 104Ч106
Penetration depth, mean free path, effect of 96Ч97 102
Penetration depth, measurement of 106Ч108
Penetration depth, parallel vs. perpendicular field 105Ч106
Penetration depth, temperature dependence of 103Ч104 380Ч381
Penetration depth, theory of 100Ч106 437Ч441
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -wave pairing in
-wave pairing in 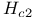
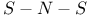 junctions
junctions  term in
term in 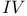 characteristics of
characteristics of  mmel, R.
mmel, R. 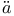 rvi, J.
rvi, J.