|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Versteeg H.K., Malalasekera W. Ч An introduction to computational fluid dynamics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
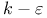 turbulence model 64 67Ч75 81Ч83 218 224 turbulence model 64 67Ч75 81Ч83 218 224
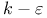 turbulence model, approximate boundary conditions 73 turbulence model, approximate boundary conditions 73
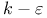 turbulence model, assessment of 74Ч75 turbulence model, assessment of 74Ч75
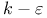 turbulence model, boundary conditions 73Ч75 turbulence model, boundary conditions 73Ч75
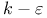 turbulence model, constants 71 turbulence model, constants 71
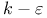 turbulence model, RNG 82Ч83 turbulence model, RNG 82Ч83
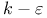 turbulence model, standard 70Ч72 turbulence model, standard 70Ч72
 202 202
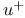 202 202
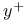 200Ч202 208 200Ч202 208
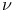 -control volume 141 -control volume 141
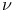 -momentum equation 141 194 204 -momentum equation 141 194 204
'P' function 73 202
Accuracy 3 114 119 171 187Ч188 241
Algebraic equations 3 91 106 131 173
Algebraic stress model (ASM) 64 79Ч80
Algebraic stress model (ASM), assessment of 80
Algebraic stress model (ASM), constants for 79
Analytical solution 92 94Ч95 98 106 108Ч109 122 130 174 177 179 185 235Ч237
Application areas of CFD 1 222Ч239
Arrhenius kinetic rate 215
Auxiliary conditions see Boundary conditions
Back-substitution 158
Backward difference formulae 242
Backward differencing 119 169 171
Backward staggered 139
Body force 15
Body-fitted coordinate system 167 219Ч222 239
boundary conditions 35Ч36 88 93Ч94 94 96Ч97 102 107 121 124 134 192 197Ч209 213
Boundary conditions wall 192 198
Boundary conditions, constant pressure 36 204
Boundary conditions, cyclic 36 192 205
Boundary conditions, for k-E model 73 201Ч202
Boundary conditions, for Reynolds stress equation model 77
Boundary conditions, inlet 36 192 194
Boundary conditions, outlet 36 192 196
Boundary conditions, periodic 192 205
Boundary conditions, symmetry 192 205
Boundary value problem 28
Boundedness 6 110 112Ч113 118 134
Buffer layer 200
Buoyancy term 248
Buoyant flows 218
Calculation of source terms 246
cells 3
Central coefficient 131
Central difference formulae 243
Central differencing 87 103Ч106 109Ч110 114 118 120 123 125Ч126 134 169
Central differencing, assessment of 113
Characteristics 30Ч33
Checker-board pressure field 137 138
Chemical reaction 210Ч211
Classical turbulence models 62
Classification 27Ч30 32Ч33 34Ч5
Classification methods 32Ч3
Classification of flow equations 34Ч5
Closure problem 53
Coefficients 88 93 105 116 122 129 133 139 141 145 195
Combustion modelling 210
Conductive heat transfer 88
Conductive heat transfer, boundaries 11
Conjugate gradient method (CGM) 167
Conservation laws 10
Conservation principle 4
Conservative form of flow equations 14 24
Conservativeness 6 110 118 134
Consistency 6
Constant pressure boundary condition 203 206
Continuity equation 11Ч12 104 135Ч136 138 144 146 151
Control volume 3 11
Control volume method 85
Control volume method, faces 11
Control volume method, integration 4 85 92 103Ч104 168
Control volume method, nodes 11
Convection 26 103 113 135
Convection-diffusion 103Ч104 139 156 168
Convection-diffusion equation 104Ч105 133
Convection-diffusion equation, one-dimensional 104
Convection-diffusion equation, three-dimensional 123
Convection-diffusion equation, transient 181Ч183
Convection-diffusion equation, two-dimensional 123
Convective flux 103 106 129 185
Convective heat transfer 95
Convective mass flux 104 139Ч140
Convective terms 103 105
Convergence 6 167
Correction formulae 143
Corrector step 150Ч151
Crank Ч Nicolson scheme 171 172Ч173
Cyclic boundary condition 36 205
Deformation rate 22 67
Diffusion 26 28 85 103 113
Diffusion coefficient 86
Diffusion coefficient, interface 87
Diffusion term 105Ч106
Diffusion, false 7 119Ч120 132
Diffusion, numerical 7 125
Diffusive conductance 104
Diffusive flux 87 103 121 128 184
Direct methods 156
Discrete control volumes 86
Discretisation 3 4 87 103 139 180Ч181
Discretisation schemes, higher order 125 133
Discretisation schemes, properties of 110
Discretised equations 85Ч90 94 97Ч98 101Ч102 104 106 115-16 121Ч122 129 131 133 136 145Ч146 171 175 178 181 184Ч185 188 192Ч194
Discretised, continuity equation 151
Discretised, momentum equations 142 146 151
Discretised, pressure correction equation 150Ч151
Discretised, v-momentum equation 146
Discretised, w-momentum equation 145
Dissipation, 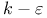 model 67Ч75 model 67Ч75
Dissipation, rate in turbulent flow 70
Dissipation, Reynolds stress equation model 76
Dissipation, viscous 24
Domain 3
Domain of dependence 31
Donor cell differencing 115
Eddy 42Ч43
Eddy-break-up model 211 215Ч216
Eddyviscosity 63 71
Elliptic problem 27
Elliptic problemflow 34
energy equation 17Ч20
Energy equation, internal 20
Energy equation, kinetic 19
Energy equation, specific 19
Enthalpy 20 211
Enthalpy, total 20
Entrainment 55
EPISO 189
Equation of state 21 136
Equilibrium problems 27
Errors 7
Exchange coefficient 212
Explicit scheme 171 172Ч176 179
False diffusion 119Ч120 132
Favre averaged equations 53
Favre averaging 214
Finite difference method 3
Finite element method 4
Finite volume method 4 85 103
Fire modelling 223
First-order 125 169 242
FLOW3D 4
FLUENT 4 125
Flux consistency 111
Forward difference formulae 242
Forward elimination 156
Forward marching 171
Fully implicit 171 173
| Gauss Ч Seidel iteration method 156
Gauss' theorem 25
General transport equation 25 85 103 135 211
Generation term 87 103
Governing equations 10Ч20 92 88 95
Governing equations, energy conservation 19
Governing equations, kinetic energy of mean flow 19 68
Governing equations, mass conservation 12Ч13
Governing equations, momentum conservation 16
Governing equations, turbulent kinetic energy 69
grid 3
Grid generation 86
Grid refinement 3
Guessed pressure field 142
Heat conduction 18
HENSA 9
Higher order differencing schemes 125 133Ч134
How does CFD work? 2
Hybrid differencing scheme 114 120Ч121 123Ч124 133Ч134
Hyperbolic problems 28Ч29
Hyperbolic problems, equations 30
Hyperbolic problems, flow 34
Hyperbolic problems, simple wave solutions 30
Implicit scheme 171 173Ч174 178Ч179 181 188
Indirect methods 156
Initial-boundary value problems 29
Inlet boundary condition 36 72 192 194
Instability, hydrodynamic 44Ч45
Integration constant (wall functions) 60 200
Integration,control volume 4 92 103Ч104 168
Interface diffusion coefficient 87
Intermittency 55
Iterative methods 156
Jacobi iteration method 156
Kinetic energy, equation for 19 68
Kinetic energy, mean 68
Laminar flamelet model 211 216
Laminar flow 42 200
Laminar steady flow 135 142
Laplace's equation 27
Law of the wake 60
Law of the wall 59
Line-by-line method (TDMA) 159
Linear approximation 87 96
Linear extrapolation 128
Linear interpolation 105
Linear sub-layer 59 200 208
Link suppression 102
Log-law 60 66 200 208
Mach number 10 34Ч35
Marching problems 28
Mass conservation 10 11Ч13
Mass conservation, compressible flow 12
Mass conservation, incompressible flow 13
MATLAB 91
Matrix equation 91 117
Matrix form 94 97 107 122 129 179
mesh 3
Mixing length 65 66
Mixing length model 62 64Ч67
Mixing length model, assessment of 67
Mixing length model, Baldwin and Lomax 67
Mixing length model, Cebeci and Smith 67
Mixture fraction 212Ч215 218
Modelling skills 7
Momentum equation 14Ч17 135Ч136 139
Moving walls 203
Navier Ч Stokes equations 21Ч24
Neighbour coefficients 102 116 133Ч134 171 180
Neighbouring nodes 101 102 104
Neighbours 86 99 139
Newton's law of viscosity 22
Newton's second law 10 14
No-slip condition 200
Nodal point 86Ч87 89Ч90 93 96 106
nodes 3 89 101Ч102 107 111Ч112 121 129
Non-linear 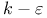 model 82 model 82
Non-orthogonal grid system 220
Non-uniform grids 244
Notation 86 137 139
Numerical diffusion 125
Obstacles 193 207
One-dimensional, convection-diffusion 104 106 120Ч121 125 127
One-dimensional, heat conduction 88
One-dimensional, steady state diffusion 86 88 102
One-dimensional, unsteady heat conduction 169
One-step reaction 212
Operator, skills 7
Outlet, boundary condition 36 192 196
Parabolic equations 28
Parabolic flows 34
Parabolic problems 28
Peclet number 112 114 120Ч122
Periodicity boundary condition 36 192 205
PHOENICS 4
PISO algorithm 150Ч153 187 189
PISO algorithm, transient 187
Post-processor 2 5
Power law 114 124 133Ч134
Prandtl number 71 201Ч202
Pre-processor 2
Predictor step 150 187
Pressure boundary condition 36
Pressure control volume 138
Pressure correction 38 145Ч147
Pressure correction equation 136 146 151 187 194 196
Pressure gradient source term 139
Pressure-velocity coupling 135
Problem solving 5
Propagation of information 28Ч30
Pseudo-velocities 147
Quadratic interpolation 111 125 130
Quadratic upwind differencing scheme 125
QUICK scheme 111 125 127Ч128 131Ч134 156 166 182Ч183 243
QUICK scheme, assessment of 130
Rate of change 25
Rate of change, following fluid element 14
Rate of change, following fluid particle 13
Reference pressure 196
refinement 3; see grid refinement
Renormalisation Group (RNG) 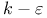 model 82Ч83 model 82Ч83
Residuals 7
Reynolds equations 52
Reynolds number 10 36 40Ч49 57 60 69Ч70 73Ч78 114 120 203 222 224
Reynolds number, critical 42
Reynolds number, large eddy 43
Reynolds stress 52 54 63
Reynolds stress equation model 64 75Ч78
Reynolds stress equation model, approximate boundary conditions 78
Reynolds stress equation model, assessment of 78
Reynolds stress equation model, boundary conditions for 77
Reynolds stress, flat plate boundary layer 61
Reynolds stress, in jets 57Ч58
Reynolds stress, mixing layer 58
Reynolds stress, wake 58
Richardson number 219
Rough walls 203
Roughness 200
Scalar control volume 138 144
Second-order 125 173 188
Self preservation 55 56
Shear force 200
SIMPLE algorithm 38 136 142Ч143 146 148 150Ч153 187Ч189 198 223
SIMPLE algorithm, transient 186
Simple Chemical reacting system 211 212
SIMPLEC algorithm 148 154 187
SIMPLER algorithm 146Ч148 152Ч155 187Ч188 222 236
Solution of algebraic equations 2Ч4
Source terms 86Ч87 92 102Ч103 168 192Ч193 202Ч203
Source terms, calculation of 246
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



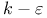 turbulence model
turbulence model 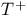
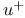
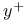
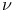 -control volume
-control volume