|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Wilcox D. Ч Turbulence modeling for CFD |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Algebraic models 23Ч64
Algebraic models, Baldwin Ч Lomax 8 52Ч53 53ff 78 81 133 136 160 195 197 207 209 352 365 368
Algebraic models, Cebeci Ч Smith 8 30 50Ч51 53ff 78 133 136 195 197 212 256f 352 365 368
Algebraic models, Prandtl eddy viscosity 31 48 53 69
Algebraic models, Prandtl mixing length 2 6 8 23 27Ч44 47 77 95 100 352 354Ч359
Algebraic Stress Model 221Ч223 233 243 266
Aliasing 319
ASM see УAlgebraic Stress ModelФ
Asymptotic, consistency 73 133 138Ч146 150Ч153 247 259
Asymptotic, expansion (defined) 338
Asymptotic, sequence (defined) 338
Autocorrelation 91 316 329
Averaging, ensemble 11Ч12
Averaging, Favre 172Ч174
Averaging, phase 14 20
Averaging, Reynolds 11Ч14
Averaging, spatial 11Ч12
Averaging, time 11
Backscatter 327
Backward-facing step 161Ч163 221 261Ч263 266 321 328
Boundary-layer applications, compressible, flat-plate 81 195Ч198
Boundary-layer applications, compressible, nonadiabatic 201Ч202 255Ч256
Boundary-layer applications, compressible, rough-wall 201Ч203
Boundary-layer applications, compressible, separated 203Ч209 263Ч266
Boundary-layer applications, compressible, variable-pressure 198Ч201
Boundary-layer applications, incompressible, curved-wall 215Ч217 253Ч255
Boundary-layer applications, incompressible, flat-plate 59 81 133Ч136 142 253
Boundary-layer applications, incompressible, mass transfer 131Ч132 136Ч138
Boundary-layer applications, incompressible, rough-wall 128Ч130
Boundary-layer applications, incompressible, separated 61Ч64 66Ч68 81Ч82 160
Boundary-layer applications, incompressible, spinning-cylinder 256Ч257
Boundary-layer applications, incompressible, transitional 155Ч159
Boundary-layer applications, incompressible, unsteady 256Ч261
Boundary-layer applications, incompressible, variable-pressure 59Ч61 66Ч67 78 81Ч82 136 142Ч146 253
Boussinesq approximation (defined) 23
Butterfly effect 329
Cascading 4Ч5 314 316 320 327
CFL condition (defined) 293
CFL number (defined) 293
Channel flow 53Ч59 94 132Ч134 154Ч156 248Ч250 364Ч370
Channel flow, rotating 249
Channel flow, skin friction formula 56
Clauser defect law 48 105 111
Common part 106 345
Complete model 7 73 83 99 163
Completely-rough surface 129Ч130
Convective Mach number 186
Convergence, grid 304Ч305
Convergence, iteration 303Ч304
Correlation (defined) 15
Correlation, auto see УAutocorrelationФ
Correlation, single-point 90 227
Correlation, two-point 90 227
Cross-term stress 325
Curved-wall flow see УBoundary-layer applicationsФ
Defect layer 44Ч46 48 110Ч121 127 142 375
Delta formulation 298
Displacement thickness (defined) 197
Dissipating eddies 4 85 89 146 233 314 318 320 323
Dissipation (defined) 75
Dissipation, dilatation 184
Dissipation, Favre-averaged 179
Dissipation, incompressible 74
Dissipation, solenoidal 184
Dissipation, tensor 224
Distinguished limit 343
Drastic surgery 75 89 90 231 233
Dynamic SGS model 327
Dynamical system 328Ч330
echo effect Уsee Pressure-echo effectФ
Eddy shock 183 185
Eddy turnover time 315 320
Energy spectral density 316
Energy-bearing eddies 86 89 233 238 314 316
Enstrophy 86
Entrainment 100 281 284
Equilibrium parameter (defined) 10
Equilibrium turbulence 29Ч30 63 77
Ergodic hypothesis 12
Escudier defect law 48
Far wake 32Ч38 95ff 242 279 355Ч356
Far wake, spreading rate (defined) 99
Fast Fourier transform (FFT) 320
Filter 323Ч325
Filter, function 324
Filter, Gaussian 324
Filter, volume-average box 323
Filter, width 323
Flux Jacobian matrix 298
FourierТs law 175
Friction velocity (defined) 46 190
Gradient-diffusion approximation 76
Grid insensitivity see УConvergence gridФ
Half-equation models 65Ч67
Half-equation models, Hung 64 66
Half-equation models, Johnson Ч King 65Ч67 78 160
Half-equation models, Shang Ч Hankey 63
Heat transfer 63Ч64 158 172 182 195 197Ч198 200Ч201 204Ч205 207Ч210 215 321Ч322 328
Heat-flux vector, laminar see УFourierТs lawФ
Heat-flux vector, turbulent 181
Homogeneous turbulence 12 184 218 235Ч242
Homogeneous turbulence, anisotropic 236
Homogeneous turbulence, isotropic 93 235 326
Homogeneous turbulence, rotating 218 234 242
Homogeneous turbulence, sheared 235 240
Homogeneous turbulence, strained 235 240 321
Hypothesis of local isotropy 224 233 314
Incomplete model 6 23 37 67 68 73 163
Inertial subrange 316
Inhomogeneous turbulence 12 184 227
Inner expansion (defined) 342
Integral scale, length 90 314
Integral scale, time 91
Intermittency 49
Invariant modeling 224
Jet, plane 41Ч44 95ff 242 359Ч360
Jet, radial 103 359Ч360
Jet, round 41Ч44 95ff 242 359Ч360
Jet, spreading rate (defined) 99
KarmanТs constant (defined) 47
Klebanoff intermittency function 49Ч52
Knudsen number (defined) 27
Kolmogorov -5/3 law 316
Kolmogorov scales (defined) 314
kurtosis 186
Law of the wake 117
Law of the wall (defined), classical 47
Law of the wall with suction 71
Law of the wall, compressible 189Ч195
Law of the wall, curved-wall 217
Leonard stress 325
Levy Ч Lees variables 429
Locally homogeneous 227
Log layer 44Ч46 48 51 93Ч94 105Ч110 122 171 189 195 197 217 235 244 322
Mass transfer see УBoundary-layer applicationsФ
Matching (defined) 344
Mean free path 23 25 27
Mixing layer 38Ч41 95ff 242 321 357Ч358
Mixing layer, compressible 172 183Ч189 195
Mixing layer, curved 242Ч243
Mixing layer, spreading rate (defined) 99
Mixing-length hypothesis 6 23 27Ч30
Momentum-integral equation 113
MorkovinТs hypothesis 172
Navier Ч Stokes equation, Favre-averaged 176
Navier Ч Stokes equation, filtered 325
Navier Ч Stokes equation, Reynolds-averaged 16
Navier Ч Stokes operator 17 88 166
Nonstationary turbulence 14
Oldroyd derivative 219Ч220
| One-equation models 77Ч83
One-equation models, Baldwin Ч Barth 8 79 81Ч82 160 197
One-equation models, Bradshaw Ч Ferriss Ч Atwell 8 78Ч79 94
One-equation models, Goldberg 8 78 81
One-equation models, Nee Ч Kovasznay 78
One-equation models, Prandtl Ч Emmons Ч Glushko 6 74Ч79 327
One-equation models, Spalart Ч Allmaras 8 79Ч81 281
Outer expansion (defined) 341
Overlap region (defined) 344
Perfect-gas law 175 423
Permutation tensor (defined) 334
Phase-space portrait 239
Pipe flow 4 53Ч59 132Ч135 154Ч157 248Ч251 364Ч370
Pipe flow, skin friction formula 56
PopeТs modification 102 104 359
Prandtl number, laminar 175 328 423
Prandtl number, turbulent 182 357 423
Pressure diffusion 75Ч76 182Ч183
Pressure dilatation 179 182Ч183
Pressure work 179 183
Pressure-echo effect 229Ч230 235 248Ч249
Pressure-strain correlation 222 224 226Ч231 233 235 243
Pressure-strain correlation, rapid (defined) 226
Pressure-strain correlation, slow (defined) 226
Pressure-strain redistribution see УPressure-strain correlationФ
Production (defined) 75
Pseudo-spectral method 320 323
Rapid pressure strain see УPressure-strain correlationФ
Rapid pressure-strain models, Launder Ч Reece Ч Rodi 229
Rapid pressure-strain models, Lumley 230
Rapid pressure-strain models, Speziale Ч Sarkar Ч Gatski 230
Realizability 220 224 229
Realization 321
Resolvable scale 324Ч325
Return to isotropy 214 220 222 228 239
Reynolds-stress (defined) 16
Reynolds-stress, anisotropy tensor 225
Reynolds-stress, equation 19 179
Reynolds-stress, tensor invariants 230
ReynoldsТ analogy 181
Richardson extrapolation 304Ч305
Richardson number 217
RodiТs ASM approximation 221
Rossby number 252
Rotating channel flow see УChannel flow rotatingФ
Rotation tensor (defined) 218
Round-jet/plane-jet anomaly 102 104 242Ч243
Rubel Ч Melnik transformation 277 281Ч282 286 351 353 371Ч372
Second viscosity, eddy 181
Second viscosity, molecular 175
Second-moment closure models see УSecond-order closure modelsФ
Second-order closure models 223Ч235
Second-order closure models, Daly Ч Harlow 9 228
Second-order closure models, Donaldson 9 224Ч225 228
Second-order closure models, Fu Ч Launder Ч Tselepidakis 231 241
Second-order closure models, Gibson Ч Launder 229 252
Second-order closure models, Gibson Ч Younis 261Ч262
Second-order closure models, Hanjalic Ч Launder 253Ч254
Second-order closure models, Launder Ч Reece Ч Rodi 9 226 231Ч232 235ff.
Second-order closure models, Mellor Ч Herring 225
Second-order closure models, Shih Ч Lumley 231 241
Second-order closure models, Wilcox multiscale 232Ч235 235ff 277 352 364Ч365 368 371 373 391 408Ч409 412 424
Second-order closure models, Wilcox Ч Rubesin 225 232 238 256Ч257
Secondary motion 165 214 218 220Ч223 255 266
Self preserving (defined) 30
Self similar see УSelf preservingФ
SGS Reynolds stress 325
Similarity-solution method 33Ч36
Similarity-solution method, existence conditions 35
Single-point correlation 90 227
Singular perturbation problem, defined 339
Slightly-rough surface 278 364 371
Slow pressure strain see УPressure-strain correlationФ
Smagorinsky model 326Ч327
Specific dissipation (defined) 85Ч87
Spectral method 319 320 323 324
Spinning, segmented cylinder 256Ч257
Spreading rate (defined), far wake 99
Spreading rate, jet 99
Spreading rate, mixing layer 99
Stability, analysis 293Ч297
Stability, conditional 294
Stability, unconditional 290 291 294
Stanford Olympics, first 60
Stanford Olympics, second 60
Stationary turbulence 11 12 14
Stiffness 273Ч275 303
Strain-rate tensor (defined) 218
Strange Attractor 328Ч329
Stratification 214 218 224 266
Streamline curvature 7 50 110 214 215Ч217 222Ч223 243 253Ч255 412
Subgrid scale (SGS) 323Ч324 326Ч327
Surface mass transfer see УBoundary-layer applicationsФ
Surface roughness see УBoundary-layer applicationsФ
Taylor microscale 315
Term-by-term modeling see УDrastic surgeryФ
thermal conductivity 175
Transcendentally small (defined) 338
Turbulence Mach number (defined) 184
Turbulence Reynolds number (defined) 139 152
Turbulent transport 76 182 225Ч226
Turbulent/nonturbulent interface 38 40 94 98 118 279Ч286 305 320 354
Two-equation models 83Ч92
Two-equation models, 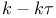 , Zeierman Ч Wolfshtein 91 94 , Zeierman Ч Wolfshtein 91 94
Two-equation models,  , Chien 139Ч145 154 194 196 198Ч200 261Ч262 278 291 408 428 , Chien 139Ч145 154 194 196 198Ч200 261Ч262 278 291 408 428
Two-equation models,  , Dutoya Ч Michard 139 142Ч143 , Dutoya Ч Michard 139 142Ч143
Two-equation models,  , Fan Ч Lakshminarayana Ч Barnett 139 291 408 428 , Fan Ч Lakshminarayana Ч Barnett 139 291 408 428
Two-equation models,  , Hassid Ч Poreh 139 142Ч143 , Hassid Ч Poreh 139 142Ч143
Two-equation models,  , Hoffmann 139 142Ч143 , Hoffmann 139 142Ч143
Two-equation models,  , Jones Ч Launder 87 139Ч142 144Ч145 154 198 205 287 291 408 427 , Jones Ч Launder 87 139Ч142 144Ч145 154 198 205 287 291 408 427
Two-equation models,  , Lam Ч Bremhorst 139Ч145 154 278 291 408 427 , Lam Ч Bremhorst 139Ч145 154 278 291 408 427
Two-equation models,  , Launder Ч Sharma 87Ч89 92ff. 198 204 232 242Ч243 252 291 352 355 357 359 375 408 427 , Launder Ч Sharma 87Ч89 92ff. 198 204 232 242Ч243 252 291 352 355 357 359 375 408 427
Two-equation models,  , Myong Ч Kasagi 139 , Myong Ч Kasagi 139
Two-equation models,  , Reynolds 139 , Reynolds 139
Two-equation models,  , Rodi 205 207 209 , Rodi 205 207 209
Two-equation models,  , Shih-Hsu 139 , Shih-Hsu 139
Two-equation models,  , Speziale Ч Abid Ч Anderson 139 , Speziale Ч Abid Ч Anderson 139
Two-equation models,  , Yang Ч Shih 139 291 408 428 , Yang Ч Shih 139 291 408 428
Two-equation models,  , Zhang Ч So Ч Speziale Ч Lai 139 198 201Ч202 , Zhang Ч So Ч Speziale Ч Lai 139 198 201Ч202
Two-equation models,  , Kolmogorov 7Ч8 83Ч88 92 , Kolmogorov 7Ч8 83Ч88 92
Two-equation models,  , Speziale Ч Abid Ч Anderson 85 , Speziale Ч Abid Ч Anderson 85
Two-equation models,  , Wilcox 9 84Ч87 92ff 194 196 198 216 223 260 265 277 352 355 357 359 364Ч365 368 371 373 375 391 408 412 424 , Wilcox 9 84Ч87 92ff 194 196 198 216 223 260 265 277 352 355 357 359 364Ч365 368 371 373 375 391 408 412 424
Two-equation models, 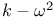 , Saffman 8 84 88 94 123 281 284 , Saffman 8 84 88 94 123 281 284
Two-equation models, 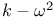 , Saffman Ч Wilcox 9 85 190 203 , Saffman Ч Wilcox 9 85 190 203
Two-equation models, 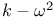 , Spalding 85Ч86 124 , Spalding 85Ч86 124
Two-equation models, 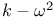 , Wilcox Ч Alber 9 85Ч86 183 , Wilcox Ч Alber 9 85Ч86 183
Two-equation models, 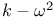 , Wilcox Ч Rubesin 9 85Ч86 110 114 123 142Ч144 151 214 219 238 256Ч257 289 , Wilcox Ч Rubesin 9 85Ч86 110 114 123 142Ч144 151 214 219 238 256Ч257 289
Two-equation models, 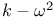 , Wilcox Ч Traci 9 85 , Wilcox Ч Traci 9 85
Two-equation models, 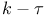 , Speziale Ч Abid Ч Anderson 92 123Ч124 , Speziale Ч Abid Ч Anderson 92 123Ч124
Two-equation models, 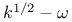 , Coakley 85 , Coakley 85
Two-equation models, k-kl, Ng-Spalding 91
Two-equation models, k-kl, Rodi Ч Spalding 91
Two-equation models, k-kl, Rotta 83 90
Two-equation models, k-kl, Smith 91
Two-equation models, k-kl, Vollmers Ч Rotta 281
Two-equation models, k-l, Rotta 83
Two-point correlation 90 227
Universal equilibrium theory 314 316
Unsteady flow 14 256Ч261 292 296
Van Driest damping function (defined) 47
Velocity thickness (defined) 50
Viscous sublayer 44Ч46 48 122Ч125 128 130Ч132 142 152 244Ч247 261 277 305 322 373Ч374
Viscous-interface layer 284Ч286 308
Von Neumann stability analysis see УStability analysisФ
Vortex stretching 3 4 94 103
Wake see УFar wakeФ
Wake-strength parameter 117Ч120 375
Wall functions 126Ч128 133 142 161f 195 204f 244f 248 255 261ff 275f 305
Wall-reflection effect see УPressure-echo effectФ
Weak solution 279Ч284
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



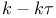 , Zeierman Ч Wolfshtein
, Zeierman Ч Wolfshtein  , Chien
, Chien  , Kolmogorov
, Kolmogorov 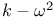 , Saffman
, Saffman 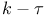 , Speziale Ч Abid Ч Anderson
, Speziale Ч Abid Ч Anderson 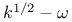 , Coakley
, Coakley