|
Электронная библиотека Попечительского совета механико-математического факультета Московского государственного университета |
| Главная Ex Libris Книги Журналы Статьи Серии Каталог Wanted Загрузка ХудЛит Справка Поиск по индексам Поиск |
© Электронная библиотека попечительского совета мехмата МГУ, 2004-2026 |
|
О проекте |
|
О проекте
|



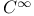
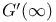
 ”
”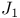
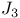
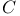 : set of complex numbers, cancellation error
: set of complex numbers, cancellation error  -perturbation
-perturbation 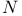 ”
”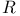 ”
”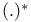 ”
”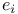 ”
”