|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Allen M.P., Tildesley D.J. Ч Computer simulation of liquids |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 57 306 57 306
Acceptance ratio 121Ч123
Averages 33
Averages, calculation of 46
Averages, correction of 198
Averages, errors in 192
Averages, non-equilibrium 242
Averages, quantum 277Ч278
boundary conditions 24
Boundary conditions, periodic see УPeriodic boundary conditionsФ
Boundary conditions, spherical 32
Boundary conditions, using walls 27 72Ч73 287 312ff
Brownian dynamics 257ff 283 318
Brownian dynamics in quantum simulations 282Ч285
Brownian dynamics with hydrodynamic effects 266
Brownian dynamics with memory 264
Bulk viscosity 61
Bulk viscosity, calculation of 204ff 250
chemical potential 42; (see also УFree energyФ)
Chemical potential, calculation of 49Ч50 166 217 219
Cluster identification 288
Computer hardware 320Ч322
Conservation 72
Conservation of angular momentum 72 108
Conservation of energy 73 98Ч99
Conservation of linear momentum 72
Constraints 16 47 68Ч70 92ff
Constraints, RATTLE method 96
Constraints, SHAKE method 95
Density profile 287 313
dielectric constant see УRelative permittivityФ
Diffusion coefficient 60
Diffusion coefficient, calculation of 204ff 251
Direct correlation function 199Ч201
Distribution functions 54ff 299 337
Distribution functions, calculation of 168 183Ч185
Distribution functions, errors in 195
Distribution functions, extending 199Ч203
Distribution functions, smoothing 203
Distribution functions, spherical harmonic expansion 56
Dynamic structure factor 63
Einstein frequency 62
Einstein relation 59Ч61 204Ч208
Ensembles 33ff; (see also УMolecular dynamics and Monte CarloФ)
Ensembles, constant-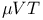 or grand-canonical 42 or grand-canonical 42
Ensembles, constant-NPH or isobaric isoenthalpic 233
Ensembles, constant-NPT or isothermal-isobaric 41Ч42
Ensembles, constant-NVE or microcanonical 39Ч40
Ensembles, constant-NVT or canonical 40Ч41
Ensembles, non-equilibrium 242
Ensembles, transforming between 43ff
Equations of motion for hard systems 102 108
Equations of motion, Hamiltonian form 71
Equations of motion, Lagrangian form 71
Equations of motion, non-equilibrium 241 248ff
Equations of motion, quaternion 88Ч90
Equations of motion, rotational 86Ч87 91
Equilibration 168 171Ч173
Error estimation 191ff
Euler angles 86Ч88
EulerТs equations 86Ч87
Ewald sum 156ff 164 315
Finite-difference methods 73ff
Fluctuations 45 51
Fluctuations, errors in 195
force 71 140ff 329ff;
Force, mean squared 62 66
FORTRAN 18 322ff 343
Fourier transform 336ff
Fourier transform, calculation of 338
Fourier transform, discrete 337
Fourier transform, spatial 58 63
Fourier transform, temporal 63 67 188Ч191 208Ч211
Free energy 40; (see also УChemical potentialФ)
Free energy, calculation of 49Ч50 128 213ff 295
Friction coefficient 259
Friction coefficient, dynamical 230
Gear algorithm see УPredictor-correctorФ
Gibbs Monte Carlo method 239
Hamiltonian 6 71 229 233 270
Hamiltonian, non-equilibrium 242
heat capacity 51ff
Importance sampling see УMonte CarloФ
Initial configuration 168Ч170
Initial velocities 170
Input/Output 174
Interfaces 26Ч27 286Ч291 312Ч318
Intermediate scattering function 63
Intermolecular potential see УPotentialФ
Isothermal compressibility 51ff
Kirkwood g-factor 57 161Ч162
LaddТs method 164
Lagrangian 71 229 233 237
Langevin equation 259 318
Lattice sum see УEwald sumФ
Leap-frog algorithm 80 231 234
Leap-frog algorithm for quaternions 89
Leap-frog algorithm for vectors 91
Liouville equation 35 257Ч259
Liquid crystals 300ff
Liquid drops 286ff
LISTS see УNeighbour listsФ
Long-range corrections 64Ч65 125
Long-range forces see УPotentialФ
Long-time tails 204Ч205 310ff
Lorentz Ч Berthelot rules 21
Markov chain 114
Maximum entropy method 209Ч211
Melting 292ff
Memory function 258
Metropolis method see УMonte CarloФ
Microscopic reversibility 116
Minimum image convention 28Ч29
Model see УPotentialФ
Molecular Dynamics 71ff; (see also УEnsemblesФ)
Molecular dynamics of atoms 71ff
Molecular dynamics of hard molecules 101ff 167
Molecular dynamics of non-rigid molecules 92ff
Molecular dynamics of rigid linear molecules 90ff
Molecular dynamics of rigid non-linear molecules 85ff
Molecular dynamics with changing box 232
Molecular dynamics with pressure constraint 234
Molecular dynamics with stochastic collisions 227
Molecular dynamics with temperature constraint 230
Molecular dynamics with thermal reservoir 228
Molecular dynamics with three-body forces 154
Molecular dynamics with wavepackets 279ff
Molecular dynamics, accuracy 76Ч78 98Ч101
Molecular dynamics, constant-NPH 232ff
Molecular dynamics, constant-NPT 232ff
Molecular dynamics, constant-NVT 227Ч232
Molecular dynamics, debugging programs 98Ч101
Molecular dynamics, multiple time-step method 152Ч155
Molecular dynamics, non-equilibrium 240ff 312
Molecular dynamics, path integral methods 275ff
Monte Carlo 110ff; (see also УEnsemblesФ)
Monte Carlo of hard molecules 123 126 134 167
Monte Carlo of non-rigid molecules 135
Monte Carlo of rigid molecules 131
Monte Carlo on lattices 16Ч18 131Ч132 137Ч138 303
Monte Carlo, acceptance ratio 121Ч123
Monte Carlo, asymmetrical solution 116
| Monte Carlo, Barker method 117
Monte Carlo, cavity-bias 223
Monte Carlo, constant-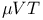 126ff 126ff
Monte Carlo, constant-NPT 123ff
Monte Carlo, constant-NVT 118ff
Monte Carlo, force-bias 224Ч225
Monte Carlo, Gibbs method 239
Monte Carlo, importance sampling 114
Monte Carlo, many-atom moves 122
Monte Carlo, Metropolis method 116 118ff
Monte Carlo, non-Boltzmann sampling 213ff
Monte Carlo, path integral methods 275ff
Monte Carlo, preferential sampling 220
Monte Carlo, quantum random walk method 282
Monte Carlo, sample mean method 112
Monte Carlo, simple integration 111
Monte Carlo, smart method 225Ч226
Monte Carlo, symmetrical solution 117
Monte Carlo, umbrella sampling 213ff
Monte Carlo, virial-bias 226
Multiple time-step method 152Ч155
Multipoles 13
Neighbour lists 146ff
Neighbour lists, linked 149Ч152 247 314
Neighbour lists, Verlet 147Ч149
Order parameter, rotational 171 304Ч306
Order parameter, translational 171
Pair distribution functions see УDistribution functionsФ
Pair potential see УPotentialФ
Particle insertion 50 166Ч167 217
Particle-particle particle-mesh (PPPM) algorithm 164
Partition function 37ff
path integral 272
Periodic boundary conditions 24ff 326
Periodic boundary conditions, cubic 25Ч32
Periodic boundary conditions, non-cubic 26Ч27
Periodic boundary conditions, sheared 246
Phase transistions 25Ч26 239 292Ч296 300Ч306 316Ч317
Polymers 137Ч139
Potential 7
Potential, argon 7
Potential, atom-atom 12 20Ч21 126
Potential, atom-surface 315
Potential, bond-bending 330
Potential, calculation 18ff
Potential, construction 20ff
Potential, effective 9
Potential, electron gas 7
Potential, electrostatic dipole-dipole 155 165 333
Potential, electrostatic ionic 11Ч13 155 164 297 315
Potential, electrostatic multipolar 332
Potential, flexible molecules 16 97Ч98 135Ч139 330Ч332
Potential, Gaussian overlap 15 302
Potential, hard ellipsoid 302 304
Potential, hard spherocylinder 302
Potential, hard-sphere 9 102 310 313
Potential, Lebwohl Ч Lasher 303
Potential, Lennard Ч Jones 9 11
Potential, long-range 155ff; (see also УElectrostaticФ)
Potential, quantum 270
Potential, repulsive Lennard Ч Jones 11 287
Potential, restricted primitive model 298 314
Potential, rough sphere 106
Potential, shell model 12
Potential, shifted 145Ч146
Potential, site-site 12 20Ч21 126
Potential, soft-sphere 10
Potential, spherical cutoff 29
Potential, square-well 10 313
Potential, tabulated 143Ч145
Potential, tapered 163
Potential, three-body 8 334Ч335
Potential, torsion 16 330
Potential, Tosi Ч Fumi 298 314
Potential, truncation 27Ч29 145Ч146
Predictor-corrector method 74
Predictor-corrector method, Gear version 82 340Ч342
Pressure 47Ч49 56
Pressure, calculation of 167 201Ч203
Pressure, tensor 290 312
Quantum corrections 65Ч68 166
Quantum potential 270
Quantum simulations 270ff
Quaternions 88 134
Radial distribution function see УDistribution functionsФ
Random force 258
Random variables 345ff
Random variables, exponential 348Ч349
Random variables, Gaussian 191 225Ч226 260Ч269 347Ч348
Random variables, uniform 119 124 129 345Ч346
Random variables, von Neumann method 349
Random vectors 133Ч134 349
RATTLE algorithm 96
Reaction field method 162ff
Recurrence effect 197Ч198
Reduced units 327Ч328
Relative permittivity 157 162
Relative permittivity, calculation of 161Ч163 165 253
Rotation matrix 85Ч88
SHAKE algorithm 95
Shear viscosity 60
Shear viscosity, calculation of 204ff 243 247
Specific heat see УHeat capacityФ
Spectra 336
Spectra, smoothing of 208
Spherical cutoff see УPotentialФ
Statistical inefficiency 117 193
Structure factor 58 337;
Structure factor, dynamic 63
Surface tension 289
Surface tension, calculations of 290Ч291
Temperature 46
thermal conductivity 61
Thermal conductivity, calculation of 204ff 250
Thermal expansion coefficient 51ff
Thermal pressure coefficient 51ff
Thermodynamic integration 50 219Ч220
Thermodynamic properties see УAverages and fluctuationsФ
Time correlation functions 58ff 167
Time correlation functions, angular velocity 307
Time correlation functions, calculation of 185Ч191
Time correlation functions, errors in 196Ч198
Time correlation functions, Fourier transforms of 188Ч190 336
Time correlation functions, linear velocity 60 62
Time correlation functions, long-time tails 204Ч205 310ff
Time correlation functions, orientational 64 306ff
Time reversibility 73
torque 85 329 333Ч334
Torque, mean squared 66
Transition probability 115 220ff
Transport coefficients 58ff
Transport coefficients, calculation of 204ff 240ff
Umbrella sampling see УMonte CarloФ
Underlying matrix 116 118 128 220ff
Verlet algorithm 78ff
Verlet algorithm, leapfrog version 80 231 234
Verlet algorithm, velocity version 81
Virial coefficient 22Ч23
Virial function 47Ч49
Virial theorem 46
viscosity see УBulk viscosity and shear viscosityФ
Wetting 314
Windowing functions 208Ч209
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



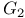
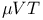 or grand-canonical
or grand-canonical