|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Landau L.D., Lifschitz E.M. Ч Statistical physics (vol. 9 of course of theoretical physics) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 -point 92 -point 92
acceptor impurity 277
Antiferromagnetic resonance frequency 313
Antiferromagnetism 284
Band, energy 224 274
BCS model 173
Black-body radiation 323
Bloch, electron 223
Bloch, functions 223
Born approximation 21
Bose Ч Einstein condensate 103
Bose, branch of spectrum 18 68Ч71
Bose, gas, degenerate 98Ч102
Bose, liquid 85Ч140
Bose, spectrum 85
Chronological, operator 147
Chronological, product 31
Coherence length 158
Collision integral 13
Compensated metals 254
condensate 99Ч109
Condensate, Bose Ч Einstein 103
Conduction, band 275
Conduction, electrons 252
Cooper effect 153 219
Correlation function in a liquid 347Ч350 368 377Ч378
Critical fields, upper and lower 190Ч193
Critical velocity 115
Crystal, electrons in (VI) 223Ч283
Cyclotron mass of electron 238
De Haas Ч Van Alphen effect 260
Debye temperature 347n.
Deformation potential 267
Diagram technique 47
Diamagnetic domains 266
Direct gap 275
dispersion relation 142
Dispersion relation for elementary excitations 1
donor impurity 277
Doped semiconductor 277
DysonТs equation 59
Effective mass, of electron 243
Effective mass, of quasi-particle 6
Electron trajectory 238
Electron-phonon interaction 266Ч274
Electron-type Fermi surface 253
Energy band 224
Exchage integrals 300
Excitations, elementary 1
Excitations, elementary, in quantum Fermi liquid 1Ч7
excitons 274
External lines 51
Fermi gas, almost ideal, GreenТs function 78Ч84
Fermi gas, degenerate 21Ч27 153
Fermi gas, ideal, GreenТs function 38Ч40 144
Fermi gas, superfluid 157Ч171
Fermi liquid, dynamic form factor 380Ч383
Fermi liquid, energy spectrum 2 33Ч38
Fermi liquid, GreenТs functions 28Ч84
Fermi liquid, magnetic susceptibility 12Ч13
Fermi liquid, normal (I) 1Ч27
Fermi liquid, spin waves in 19Ч20
Fermi spectrum 2
Fermi sphere 2
Fermi surface in metals 252Ч255
Ferrites 284
Ferromagnetic resonance frequency 293
ferromagnetism 284
Ferromagnetism, weak 285n.
Feynman diagram 49
Fluctuations, electromagnetic (VIII) 314Ч359
Fluctuations, electromagnetic field 319Ч321
Fluctuations, hydrodynamic 369Ч378
Form factor, dynamic 361Ч367 380Ч383
Form factor, static 361 366
Form factor, summation rules 364Ч367
FrenkelТ exciton 276
Gap, energy 274
Gaseousness parameter 27
Ginzburg Ч Landau, equations 181
Ginzburg Ч Landau, parameter 182
GreenТs function 30
GreenТs function at non-zero temperatures (IV) 141Ч152
GreenТs function for interacting particles 43Ч46
GreenТs function in Bose liquid 118Ч127
GreenТs function in Fermi gas 38Ч40 78Ч84 144 164Ч171
GreenТs function in Fermi liquid 28Ч84 141Ч144
GreenТs function in superfluid Fermi gas 164Ч171
GreenТs function of phonon field 124 267
GreenТs function of photon 314Ч319
GreenТs function, advanced 143
GreenТs function, anomalous 121 164
GreenТs function, derivatives of 71Ч76
GreenТs function, retarded 141 315
GreenТs function, temperature 147Ч152 169Ч171 327Ч330
GreenТs function, time 147
GreenТs function, two-particle 56Ч60
Heisenberg Hamiltonian 300n.
Helium II 92n.
| hole 253n.
Hole trajectory 238
Hole-type Fermi surface 253
Holes within Fermi sphere 7
Impurity semiconductor 277
Indirect gap 275
Insulators, electron spectrum of 274Ч277 279Ч283
Interaction function of quasi-particles 8
Interaction representation 43
Intermediate state of superconductor 190n.
Internal lines 51
Intrinsic semiconductor 277
Josephson effect 204Ч208
Kramers Ч Kronig relation 142
Landau, damping 17n.
Landau, sub-bands 241
Landau, theory 18 76
London, equation 175
London, penetration depth 176
London, superconductor 176
LuttingerТs theorem 253
Magnetic breakdown 237
Magnetic flux quantum 177
Magnetic induction 317n.
Magnetic lattice 249
Magnetic sub-group 249
Magnetic sub-lattice 310
Magnetic translation operator 248
Magnetism (VII) 284Ч313
Magnetoactive body 316
Magnetostatic part 292
Magnons 285
Magnons in antiferromagnet 310Ч313
Magnons in ferromagnet 289Ч310
Mass, cyclotron, of electron 238
Mass, effective, of electron 243
Mass, effective, of quasi-particle 6
Mass, operator 54
Matsubara 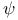 operators 146 operators 146
Meissner effect 175
Metals, electron GreenТs function in 255Ч259
Metals, electronic spectra of 251Ч255
Mixed state of superconductor 190 193Ч200
Molecular interaction between solids 338Ч347
Nominal magnetization 284 296
Normal current in superconductor 173
Notation xi
Number density of superconducting electrons 173
Periodic field, electron in 223Ч251
Permittivity, longitudinal and transverse 351
Phonon-electron interaction 266Ч274
Pippard case 176
Pippard penetration depth 216
Plasma, degenerate 353Ч359
Polarization operator 329 357
Potential rotation 111
Quantum of magnetic flux 177
Quasi-classical, energy levels 240Ч243
Quasi-classical, trajectories 236Ч240
Quasi-momentum of electron 224
Quasi-momentum of two-electron system 225
Quasi-momentum, generalized 233
Quasi-particles 1
Quasi-particles, disintegration of 131Ч140
Quasi-particles, interaction of 8Ч11
Renormalization 21
Renormalization constant 38
Rotons 87
Self-energy function for Bose systems 127
Self-energy function for Fermi systems 53
Semi-metal 254
Semiconductor, electrons and holes in 277Ч283
Semiconductor, gapless 283
Skeleton diagram 55
Spin waves 285
Spin waves in Fermi liquid 19Ч20
Superconducting alloys 216Ч219
Superconductivity 171Ч222
Superconductivity, current 173
Superconductor, first and second kinds 190
Superfluid Fermi gas 157Ч171
Superfluidity 88Ч140
Susceptibilities, generalized 316
Trajectories, electron and hole 238
Valency band 275
Van der Waals forces 331Ч337
Vertex function 57 60Ч71
Vertex function, temperature 219
Vertices of Feynman diagram 51
Vertices of Feynman diagram, incomplete 125
Vortex filaments 111Ч118 194
Vortex lines 111
Vortex rings 115
Wannier Ч Mott exciton 276
WickТs theorem 47
Zero sound 15Ч19
Zero-gap superconductivity 218
УEasy axisФ ferromagnet 289
УEasy planeФ ferromagnet 289
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -point
-point 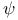 operators
operators