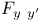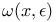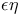|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Bolza O. — Lectures of the Calculus of Variations |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Absolute maximum, minimum 10
Accumulation-point, of a set of points 178 254
Admissible curves 9 11 104 121 206
Amplitude, of a vector 9
Bliss's condition, for the case of two variable end-points 113
Boundary conditions, along segment of boundary 43 149
Boundary conditions, at points of transition 42 150 267
Boundary conditions, when minimizing curve has one point in common with boundary 152 267
Boundary, of set of points 5
Brachistochrone 126 135 146
Brachistochrone, case of one variable end-point 106
Brachistochrone, determination of constants 128
Catenoid see "Surface of revolution of minimum area"
Circle, notation for 9
Class C, C', C''....D', D''.., curves of 8 116
Class C, C', C''....D', D''.., curves of class K 161
Class C, C', C''....D', D''.., functions of 7
Closed region 5
Closed set of points 178 267
Co-ordinates: agreement concerning positive direction of axes 8
Conjugate points 60
Conjugate, case where the two end-points are conjugate 65 204
Conjugate, for isoperimetric problems 221
Conjugate, for the case of parameter-representation 135
Conjugate, geometrical interpretation 63 137
Connected set of points 5
Continuous functions, continuity of compound functions 21
Continuous functions, definitions and theorems on: existence of maximum and minimum 13 80
Continuous functions, integrability 12
Continuous functions, sign 21
Continuous functions, uniform continuity 80
Continuum 5
Convex region 247
Corner, corner-conditions 38 126 210
Corner, defined 8 117
Critical point 109
Curves of class C', C'' 116
Curves of class C, C',.. D' 8
Curves of class K 161
Curves, (a) representable in form y=f(x) 8
Curves, (b) in parameter-representation 115
Curves, Jordan curves 180
Curves, ordinary 117
Curves, rectifiable 116
Curves, regular 117
Curvilinear co-ordinates, in general 181
Curvilinear co-ordinates, Kneser's 184
Definite integrals, connection with indefinite integral 89
Definite integrals, differentiation with respect to a parameter 16
Definite integrals, first mean-value theorem 24
Definite integrals, integration by parts 20
Definite integrals, theorems on: integrable functions 12 89
Derivatives, notation 6 7
Derivatives, progressive and regressive 7
Derivatives, reversion of the order of differentiation in partial derivatives of higher order 18
Differential equations, dependence of the general integral upon the constants of integration 54
Differential equations, existence theorem 28
Differential equations, upon parameters 71 223
Discontinuous solutions 36 125 209
Distance: between two points, notation 9
Domain 5
End-points, variable see "Variable end-points"
Envelope of a set of extremals 62
Envelope of a set of plane curves in general 62 137
Envelope, case when the envelope degenerates into a point 204
Envelope, case when the envelope has cusps 201
Envelope, extension of this theorem to extremals 174
Envelope, theorem on the envelope of a set of geodesics 166
Equilibrium, of cord suspended at its two extremities 211 231 241
Equivalent problems 183 197 228
Erdmann's corner condition 38
Euler's (differential) equation 22;
Euler's (differential) equation, assumptions concerning its general integral 54 130;
Euler's (differential) equation, cases of reduction of order 26 29
Euler's (differential) equation, Du Bois-Reymond's proof of 23
Euler's (differential) equation, Hilbert's proof of 24
Euler's (differential) equation, Weierstrass's form of 123
Euler's isoperimetric rule 210
Evolute, of plane curve 174
Existence theorem for a minimum "im Grossen," 245
Existence theorem for a minimum "im Kleinen," 146
Existence theorem for differential equations 28
Existence theorem, in particular for linear differential equations 50
Extraordinary vanishing of the E-function 142
Extremal, construction of extremal through given point in given direction 28 124
Extremal, construction of extremal through two points, sufficiently near to each other 146
Extremal, defined 27 123 209
Extremal, problems with given extremals 30
Extremal, set of extremals cut transversely by a given curve 111
Extremal, set of extremals through given point 60
Extremum, defined 10 compare "Maximum"
Field for case of parameter-representation 144 176
Field for isoperimetric problems 241
Field, applied to set of extremals through 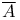 82 82
Field, defined 79
Field, field-integral 266
Field, improper 83
Field, theorem concerning existence of 79
First necessary condition see "Euler's differential equation"
First variation for case of parameter-representation 122 123
First variation for case of variable end-points 102
First variation for isoperimetric problems 209
First variation, defined 17
First variation, transformation by integration by parts 20 22
First variation, vanishing of the 18
Focal point: of a transverse curve on an extremal, according to Kneser 200
Focal point: of a transverse curve on an extremal, case where end-point B coincides with focal point 204
Focal point: of a transverse curve on an extremal, defined 109
Focal point: of a transverse curve on an extremal, equation for its determination, according to Bliss 108 155
Focal point: of a transverse curve on an extremal, geometrical interpretation 111 156
Fourth necessary condition see under "Weierstrass"
Free variation, points of 41
Function 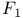 121 121
Function 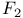 132 132
Function 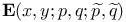 , defined 138 , defined 138
Function 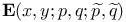 , homogeneity properties 140 , homogeneity properties 140
Function 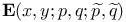 , Kneser's geometrical interpretation 195 , Kneser's geometrical interpretation 195
Function 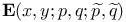 , ordinary and extraordinary vanishing 142 , ordinary and extraordinary vanishing 142
Function 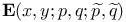 , relation between E-function and , relation between E-function and 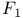 141 141
Function 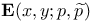 , defined 34 75 , defined 34 75
Function 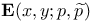 , geometrical interpretation of this relation 77 , geometrical interpretation of this relation 77
Function 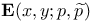 , relation between , relation between 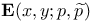 and and 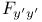 76 76
Function 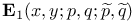 145 145
Function 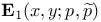 76 76
Fundamental lemma, of the Calculus of Variations 20
Generalized integral 157 248 compare
Geodesic curvature 129
Geodesic distance 176
Geodesic parallel co-ordinates 164
Geodesics 128 146 155
Geodesics, Gauss's theorems on 164 165
Geodesics, theorem on the envelope of a set of 166
Hilbert's construction 253
Hilbert's existence theorem 245
Hilbert's invariant integral 92 195
Homogeneity condition 119
Homogeneity, consequences of 120
Implicit functions, theorem on 35
Improper field 83
Improper maximum, minimum 11
In a domain, use of the word explained 5 6
Infinitesimal 6
Inner point 5
Integrability condition 29
Integrable functions, theorems on 12 89
Integral for case of parameter-representation 117
Integral, condition for invariance under parameter-representation 119
Integral, extension to curves without a tangent, (a) Weierstrass's 157
Integral, extension to curves without a tangent, (b) Hilbert — Osgood's 248
Integral, taken along a curve, definition and notation 8
| Integration, by parts 20 20
Interval, defined 5
Invariance, of E and 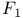 183 183
Isoperimetric constant 209
Isoperimetric constant, Mayer's theorem for case of discontinuous solutions 209
Isoperimetric problems, in general 206—244
Isoperimetric problems, special 4 210 229 238
Isoperimetric problems, with variable end-points 113
Jacobi's condition 67
Jacobi's condition for case of one variable end-point 109 155 200
Jacobi's condition for isoperimetric problems 225 226
Jacobi's condition, Kneser's form of 136
Jacobi's condition, proofs of its necessity 65 66
Jacobi's condition, Weierstrass's form of 135
Jacobi's criterion 60 135
Jacobi's differential equation 49 133
Jacobi's theorem concerning the integration of Jacobi's differential equation 54 135
Jacobi's transformation of the second variation 51
Jacobian 57
Jordan curve 180
Kneser's curvilinear co-ordinates 184
Kneser's sufficient conditions 187
Kneser's theorem on transversals 172
Kneser's theory 164—205
Lagrange's differential equation 22
Legendre's condition 47
Legendre's condition, for isoperimetric problems 217
Legendre's condition, Legendre's differential equation 46
Legendre's condition, Weierstrass's form of 133
Length of a curve, Jordan's definition 157
Length of a curve, Peano's definition 249
Limit attained by continuous function 13 80
Limit, criterion for the existence of 258
Limit, definition and notation 7
Limit, lower and upper 3 10
Limit, uniform convergence to a 19
Limit-point see "Accumulation-point"
Limited variation, functions of 258
Lindeloef's construction 64
Linear differential equations of the second order, Abel's theorem 58
Linear differential equations of the second order, existence theorem 50
Linear differential equations of the second order, Sturm's theorem 58
Lower limit 3 10
Maximum see "Minimum"
Mayer's law of reciprocity for isoperimetric problems 229 244
Mean-value theorem, first, for definite integrals 24
Minimum for case of parameter-representation 121
Minimum Hilbert's a-priori existence proof of a minimum "im Grossen," 245—263
Minimum of a continuous function 13 80
Minimum of a definite integral, absolute and relative 10
Minimum, existence of a minimum "im Kleinen," 146
Minimum, proper and improper 11
Minimum, semi-strong in case of isoperimetric problems 244
Minimum, weak and strong 69 70
Neighborhood of a curve 10
Neighborhood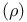 of a curve 13 121 of a curve 13 121
Neighboring curve 14
Numerable set of points 261 268
One-sided variations see also "Boundary conditions"
One-sided variations, analytic expression for 42 148
One-sided variations, necessary conditions for a minimum with respect to 42 149
One-sided variations, sufficient conditions 42
Open region 5
Ordinary curves, defined 117
Ordinary vanishing of the E-function 142 266
Osgood's theorem concerning a characteristic property of a strong minimum 190
Parameter representation, curves in 115
Parameter-transformation 116
Partial derivatives see "Derivatives"
Partial variation, of a curve 37
Point of a set 12
Point-by-point variation, of a curve 41
Positively homogeneous 119
Progressive derivative 7
Proper minimum 11
Rectifiable curves 116 250 251 251 251 compare
Region, closed 5
Region, defined 5
Region, open 5
Regressive derivative 7
Regular curves 117
Regular functions 21
Regular problems 29 40 97 125
Relative maximum or minimum 10 10
Second necessary condition see "Legendre's condition"
Second variation 44—67
Second variation for case of variable end-points 102
Second variation for case of variable end-points in parameter-representation 102 155
Second variation for isoperimetric problems 216—225
Second variation, Jacobi's transformation of 51
Second variation, Legendre's transformation of 46
Second variation, Weierstrass's transformation of, for case of parameter-representation 131
Semi-strong extremum 244
Semi-strong extremum, sufficient conditions for 244
Set of points, accumulation points of 178
Set of points, boundary point of 5
Set of points, closed 178 267
Set of points, connected 5
Set of points, continuum 5
Set of points, definition 10
Set of points, inner point of 5
Set of points, numerable 261 268
Set of points, upper and lower limits of one-dimensional set 3 10
Sign of square roots, agreement concerning 2
Slope restrictions 101
Solid of revolution, of minimum resistance 73 142
Strong extremum, defined 70
Strong extremum, sufficient conditions for see "Sufficient conditions"
Strong variation 72
Sturm's theorem, on homogeneous linear differential equations of the second order 58
Substitution symbol 5 6
Sufficiency proof, for geodesics 165
Sufficient conditions for strong minimum for case of parameter-representation, Weierstrass's 143—146
Sufficient conditions for strong minimum for isoperimetric problems, Weierstrass's 237 243
Sufficient conditions for strong minimum for one-sided variations 42
Sufficient conditions for strong minimum, extension to curves without a tangent, Weierstrass's proof 161
Sufficient conditions for strong minimum, in case of one movable end-point 109
Sufficient conditions for strong minimum, in case of two movable end-points 113
Sufficient conditions for strong minimum, in terms of 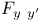 96 96
Sufficient conditions for strong minimum, Kneser's sufficient conditions for case of one movable end-point 187
Sufficient conditions for strong minimum, Osgood's proof 192
Sufficient conditions for strong minimum, when x independent variable, in terms of E-function 95
Sufficient conditions for weak minimum 70
Surface of revolution of minimum area 1 27 48 64 97 153
Taylor's theorem 14
Third necessary condition see "Jacobi's condition"
Third variation 59
Total differential 25
Total variation 14
Transversal, degenerate 169
Transversal, Kneser's theorem on transversals 172
Transversal, to set of extremals 168
Transverse for isoperimetric problems 210
Transverse in parameter-representation 155
Transverse, condition of transversality 36 106
Transverse, curve transverse to an extremal 106
Unfree variation, points of 41
Uniform continuity 80
Uniform convergence, to a limit 19
Upper limit 3 10
Variable end-points, case when both end-points movable on given curves 113
Variable end-points, general expression of first variation for case of 102
Variable end-points, of second variation 102
Variable end-points, one end-point fixed, the other movable on given curve, treated (a) by the method of differential calculus 102—113
Variable end-points, one end-point fixed, the other movable on given curve, treated (b) by Kneser's method 164—205 for "Focal "Sufficient
Variation for case of parameter-representation 122 122
Variation of a curve 14
Variation of type 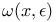 18 18
Variation special variation of type 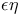 15 15
Variation, definition for first, second, etc. 16
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



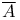
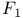
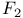
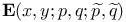 , defined
, defined 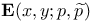 , defined
, defined 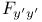
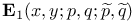
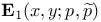
 of a curve
of a curve