|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Bluman G.W. — Problem Book for First Year Calculus |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
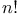 , estimation of 217 [VI.48] , estimation of 217 [VI.48]
 (Pi), estimation of 214 [VI.24] (Pi), estimation of 214 [VI.24]
Absolute convergence (VIII.10.17) [VIII.10.1]
Absolute value 4 96 (1.3 15; 6 9; 2.3 5.5-5.7 6.2 6.4 7.12 9.8 10.11) [VIII.1.1 3.35 5.5-5.7 7.33 11.7 11.8]
Acceleration 95 96 [III.1-9 13) [III.2-10 49]
Acceleration, due to gravity (III.5-7 32) [III.5-8 10]
Acceleration, of automobile (III.1 2) [III.2]
Alternating series see Series
Amplitude [III.55; VIII.1.17]
Angle between curves (VIII.1.5) [VIII.1.10 3.19]
Angular velocity 100 (11.32; 14) [11.48 82 84-87; 53]
Anti-derivative [VII.20; VIII.4.2 13.5] indefinite)
Approximation, by differentials see Differential approximation
Approximation, errors in see Error
Approximation, linear see Linear approximation
Approximation, of definite integrals see Power series Simpson’s Trapezoidal
Approximation, to root 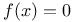 see Newton’s method see Newton’s method
Arc length see Length
Area 35 36 (II.3 4 7-9 13 18 25 27 29; 10) [II.1 2 8-13 15 17 20 25 30 31 42 44-47 63 64 76]
Area, as integral see Integration and area
Area, by parametrization (VIII.8.8) [VIII.8.1 8.17]
Area, in polar coordinates (VII.31; VIII.9.1-9.8) [VIII.9.1-9.17]
Area, of surfaces (VIII.7.16) [11.21 67; 7.43 9.17]
Astroid (VIII.3.4 8.10) [VIII.3.9 13.4]
Asymptote 3 (1.2 4 6-8 11.18; 6 8-10; 6.6) [1.11 15 18 20; 21 22 24; 22]
Asymptotic behaviour of a function see Asymptote
Average cost (IV.12 14) [IV.29 33 40]
Average interest rate (IV.8)
Average rate of change [V.3]
Bacteria growth (V.9) [V.1 10 21]
balance 143 (IV.6 7 9) [IV.21 22]
Ballistics (III.5-7) [III.8 10 14]
BASEBALL (III.6) [11.60]
Beer mug [III.30]
Bessel functions (VII.22)
Binomial series (VI.16 18; [VI.37 39]
Birth-rate 178 (V.5 8) [V.15]
Bounded sequence (VIII.10.10)
Braking distance 132 (III.1 35)
Cable see Catenary
Capacity of a bridge 129 (III.35)
Carbon dating 175 176 (V.3)
Cardioid (VIII.9.4 9.6 9.8) [VIII.9.6 9.8 9.15]
Catenary 127-129 (III.34) [III.58;
Centre of gravity 96 97 [III.29 30]
Centre of mass 96 97 (III.22 23) [III.28]
Centring errors 196 198 (VI.6-9 11 23) [VI.24 25 30 37 43 46 47 50;
Centroid 97-101 (III.15-17 19-21 24 27) [III.24-27]
Chain rule (1.2; 11.25; III.1; VIII.2.1 2.7) [VII.11; 3.35]
Chemical concentration (V.11) [V.12-14 19 20 24]
Chemical mixture [V.12-14]
Chemical reaction 184-187 (V.10 11) [V.19 20 22-24]
circle (1.1 15; 8.2 8.6 9.2) [1.1; 1.13 3.20 7.11 9.2 9.14 9.15]
Comparison tests for convergence of improper integrals (VIII.6.3 6.5 6.6) [VIII.6.4 6.8-6.10]
Comparison tests for convergence of series (VII.20; VIII.10.2-10.4) [VIII.10.3]
Completing the square (1.1; VIII.1.6 5.10 9.2) [1.1; 1.14 1.16]
Components of a vector 96 (III.6-9)
Composite function (1.2) [VII.20; 4.6 5.8]
Compound interest 143 144 (IV.6-9) [IV.17 20-22]
Concavity 2 144 (1.2 4-7 10 12-14 16 II [1.4-21; 41;
Cone (11.26 35 38; [11.16 18 73 75 76; 7.43]
Conic sections (LI) [1.1;
Consumer’s surplus 145 (IV.10) [IV.25 31 37]
Continuity (1.3 16; 9 10; [1.25 26; 3 8-10 13 15 19 20 24 32 36-38 VIII.13.6]
Continuously compounded interest 144 (IV.8) [IV.18 19 21 23]
Convergence, absolute see Series
Convergence, of a sequence 97 (VII.18; [VII.34;
Convergence, of alternating series see Series
Convergence, of improper integrals see Integral
Convergence, of power series see Series
Convergence, of series see Series
Convergence, tests for see Comparison tests for convergence Estimation Integral Ratio
Coordinates, polar see Polar coordinates
Cosines, Law of (III.14) [III.21]
Cost, average (IV.12 14) [IV.29 33 40]
Cost, function 146 (IV.1 3 5) [IV.1 2 4-8 10 16 26 27 31 34 36]
Cost, marginal see Marginal cost
Cost, total 145 (IV.2 5 12 15 17) [IV.3 15 32 35 39 43 44]
Critical point(s) 2 35 (1.2 4-14 17; 35; 9 14-16; 9; VII.12 22; 3.11 3.13 3.14 9.4) [1.4-12 14-21 23-25; 12-15 59; 26-31 33 35 36 41; 21; 27; 7.19 8.6 13.4]
Cross-sectional area 35 36 (II.9 27 28 33-40; 20 27) [11.88-100;
Current value see Present value
Curve(s), demand see Demand curve
Curve(s), length of see Length
Curve(s), parametrization of see Parametric equations
Cusp 16 (1.11)
Cycloid (VIII.8.5) [VIII.8.17]
Cylinder (II.2) [II.7 8 21 70 71; 34 37]
Death-rate (V.5) [V.16]
Deceleration (III.1 2 35) [III.3]
Decreasing function 1 (1.2 4-6 16 17; [1.6 8-10 24; 59 68 69; 41;
Definite integral see Integral
demand 144-146 (IV.14) [IV.33]
Demand, curve 144 145 (IV.10) [IV.25]
Demand, elasticity of 146 (IV.16) [IV.37 38]
Demand, equation 144 (IV.10 15 18 19) [IV.28 29 31 35-38 41 45]
Demand, function 144 (IV.13 15 16 19) [IV.24 27]
Demand, rate (IV.II)
density (III.3 35)
Derivative 1 2 Differentiation Second
Derivative, chain rule see Chain rule
Derivative, definition of (VII.4 5 7 8 19) [1.19; 15 16]
Differentiability 194 (1.3; 6 9) [VII.7-9 17 25]
Differential 146 173 (III.1 2 22 25 30 34; V.9; 4.10 4.12 5.3 5.8 7.8 7.11 7.12 8.9 12.1 12.3 12.4 12.7]
Differential equation(s) 171 (III.33;
Differential equation(s), first order linear (IV.8; VIII.12.7) [VIII.13.5]
Differential equation(s), general solution (VII.23; VIII.12.1 [VIII.12.7]
Differential equation(s), periodic solution 298-300 (VIII.12.7)
Differential equation(s), second order linear (VII.23; VIII.12.5) [VII.35;
Differential equation(s), separable (III.30; IV.8 V.2 6 8-11; 12.4 [IV.34; 12 20-24;
Differential, approximation 146 147 195 (III.32; [IV.30 38 43 44; 49]
Differential, element of area 97-100 (III.16-18 21)
Differentiation, implicit see Implicit differentiation
Differentiation, of integrals (1.17; VI.5; VII.15; VIII.2.7-2.9) [VI.15; 3.35]
Differentiation, of power series 289 (VIII.10.15 [VIII.10.16
Discontinuity (1.3; VII.2 3) [1.26; 37 38]
Discontinuity, essential [VII.3]
Discontinuity, jump (VIII.12.7)
Discontinuity, removable (VII.2) [VII.2 3]
Distance 96
Distance, as definite integral 96 (III.3 4) [III.1-3 11]
Distance, between point and curve 34 [11.43]
Distance, between point and line (III. 12)
Distance, between points (11.12 22-24 28; [11.41 52 54 55 59 62 79; 15 17 20 23]
Divergent improper integral (VIII.6.6 6.7) [VIII.6.3-6.6 6.9 6.10]
Divergent sequence (VII.20) [VII.34; 10.9 10.10]
Divergent series (VII.20; VIII.10.4 [VIII.10.3 10.4 10.9 10.10]
Domain of a function 1 35 (1.2 4 5; 22 38; 5 9; 10; 2.6) [II.1-44; 2.14 2.17 3.23-3.29 13.2]
Doubling time 172 (V.6) [V.1 8-10]
Dynamics see Motion
Effective annual interest rate 144 [IV.21]
Elasticity of demand 146 (IV.16) [IV.37 38]
Electrostatic force 122 (III.28) [III.44]
ellipse (11.33; VIIL8.11) [1.1; 7.21 7.27 8.1 8.2 9.3 9.17]
Ellipsoid (11.33) [VIII.7.20 7.21 7.27]
Energy [III.49 57]
Epidemic 173 (V.7) [V.17]
Equilibrium concentration (V.24)
Equilibrium demand 145 (IV.10) [IV.24]
Equilibrium point 145 (IV.10) [IV.25 37]
Equilibrium price 145 (IV.10) [IV.24]
Equilibrium state of [V.21 22 24]
Equilibrium static (III.34)
Erfx 320 [VIII.10.21]
Error see also Centring errors
Error, effect of step size 197 (VI.10 22) [VI.25 30]
Error, for Newton’s method 196 227 (VI.6-8; [VI. 23 32 33]
Error, for series approximation 198 (VI.11 14-18 20 21 23) [VI.33-35 37-47;
Error, for Simpson’s rule 197 233 (VI.10 22; [VI.28-30]
Error, for Taylor’s formula 197 (VI.11 19; [VI.32 36;
Error, for Trapezoidal rule 197 (VI.9) [VI.25 29 30]
| Error, in measurement 195 (VI.4) [VI.14]
Error, in modelling (V.4; VI.35)
Error, round-off (VI. 18)
Estimation by Taylor’s formula 197 (VI.II) [VI.32 36] Taylor Taylor
Estimation of tails of infinite series 198 (VI.20 21; [VI.34 35 46 47;
Even function 3 20 217 221 222 (1.2 5 13 17; 7; 9.6 9.7) [1.19; VII.37]
Exponential decay 171-173 (V.2 3) [V.2 4]
Exponential functions 144 (III.30; 7-11; 2.6 [IV.42; 20-22 24; 22; 2.16 11.25 11.30]
Exponential functions, derivatives of (1.9 10; 22; 19; [1.15 16; 28; 2.21 2.24 3.33 7.19 8.5 8.8 12.10]
Exponential functions, graphs of (1.9 10; 7.6 12.7) [1.15 IV.28; 7.19 7.23 7.34]
Exponential functions, integrals of (IV.19; VI.17 20 22; 7.13 10.8 11.4) [III.42 48; 38; 6.2 6.9 6.10 7.19 7.30 7.34 7.35 10.21]
Exponential functions, power series for (V.II; VI.11 17; [VI.34 38; 10.21 11.29]
Exponential growth 171 (V.1 4 6) [V.1 3 5-8]
Extrapolation (V.4)
Extremal point see Critical point
Extremum see Critical point
Fluid pressure 100 (III.19-21) [III.18 32-34]
Flux of cars 129 (III.35)
Focal point 126 141 (III.33) [III.56;
Focus see Focal point
force 100 (III.19-29 34) [III.32-49]
Frustum of a cone (11.38)
Function(s), asymptotic behaviour see Asymptote
Function(s), composite see Composite function
Function(s), continuous see Continuity
Function(s), cost see Cost function
Function(s), demand see Demand function
Function(s), derivative of see Differentiability Differentiation Second
Function(s), domain of see Domain
Function(s), even see Even function
Function(s), exponential see Exponential function
Function(s), hyperbolic see Hyperbolic function
Function(s), implicit see Implicit function
Function(s), increasing see Increasing function
Function(s), inverse see Inverse function
Function(s), limit of see Limit
Function(s), logarithmic see Logarithmic function
Function(s), monotonic see Monotonic function
Function(s), odd see Odd function
Function(s), periodic see Periodic function
Function(s), range of see Range
Function(s), roots of see Root
Function(s), symmetry of see Symmetry
Function(s), trigonometric see Trigonometric function
Fundamental theorem of calculus (II.4; 5; VII.15 VIII.2.7-2.9) [VI.15; 3.35]
Geometric sequence 173
Geometric series 198 (VI.14; [VIII.10.19 10.24]
Geometrical rate of convergence 196
Graph(s) 1 2 98-101 195-197 (1.1—17; 6-18 22 25 33 35-40; 5 8 9 25 27 31 33-35; 20; 5 8-11; 8 20 24; 13; 2.6 3.7 3.9 5.10 7.1-7.15 8.1-8.6 8.10 9.3-9.7 [1.1-26; 72 94; 21 27 29 43 56 58; 39; 2.17 2.18 7.8 7.17 7.36 7.39 7.42 8.3 8.12 8.17 9.2 9.3 9.12 9.13 13.2 13.4]
Gravity, centre of 96 97 [III.29 30]
Half-life 172 (V.3) [V.2 22]
Hanging cable 127-129 (III.34) [III.58]
Headway 130 (III.35)
Heat flow 123 (III.30) [III.15 50-52]
Hooke’s law 123 (III.29) [III.45-47]
Hyperbola (1.3 15; [1.12; 8.12]
Hyperbolic function(s) 129 233 275 315 (III.34; [1.17; 2.18 7.39 8.12
Implicit differentiation 35 (II.9 24-28 30-32; IV.17; VII.23; 2.6 3.3 3.4) [H.45-87; 2.16-2.18 3.16 3.19 13.2]
Implicit function 35 (III.10 33-35; [VII.35 39; 12.5-12.8]
Improper integral see Integral
Increasing function 1 (1.2 4 6 11.19 20 25 29; 3.12) [1.6 8 9 24; 46 52 59 61-65 67 72 75 76; 28 39 41; 3.21]
Indefinite integral see Integral
Indeterminate forms 144 294 (1.10; 35; 5 7 8 20; 6.6 6.7 11.1-11.15) [1.15 19; 50; 21 22; 11.1-11.30 13.2]
Induction (VIII.10.9) [VIII.5.14]
Inelastic demand see Elasticity of demand
Inequalities (1.15; IV.7; VII.9 11 13; 3.12 7.5 [1.22; 21 22 31 32 39; 3.5 7.9 13.4 13.6]
Infinite series see Series
Inflection point 2 (1.4-6 8-13 5 7; [1.4-12 25;
Initial condition(s) 95 96 298-300 (11.22 24; 5-7 13 33; 7-11; 12.3-12.5 [III.5-8 V.1-24; 13.5]
Integral(s) see also Integration
Integral(s), definite 196 (III.1-5; 9 11 19; 5.5-5.7) [IV.23; 26;
Integral(s), improper (VIII.6.1-6.7 7.14) [V.26; 7.34 7.35]
Integral(s), indefinite 95 96 (III.6) [VIII.4.1 13.5]
Integral(s), Riemann 97 (VII.14; [VII.26;
Integral(s), rules for approximating see Simpson’s Integral(s) rule Trapezoidal
Integral(s), test (VIII.10.7) [VIII.10.6]
Integration see also Centre of gravity Centre of Centroid Length Moment of Surface Work
Integration, and area 97-100 145 197 (1.17; 15; 31; 20; 21; 5.10 7.1-7.7 7.15 8.8 9.7) [1.23; 7.1-7.19 7.33 7.35 7.42 8.11 8.17 9.5-9.17 13.3]
Integration, and distance 96 (III.3 4) [III.1 3
Integration, and volume 35 (11.33-40; [11.88-100; 7.41-7.43]
Integration, by partial fractions (VII.16; VIII.4.3 4.12 5.9) [VIII.4.7-4.18 5.9-5.11]
Integration, by parts (VIII.7.8 7.10) [VIII.5.8 5.14 5.16]
Integration, by substitution (11.34 35 38; 4.8 4.12 4.13 5.4 5.7 5.8 7.12 7.13 8.9 8.10 12.1) [VII.28 29]
Integration, by trigonometric substitution (VIII.4.7 7.8)
Integration, of rational functions of the sine and cosine (VII.16; VIII.4.13) [VIII.4.16-4.18 5.11]
Integration, of series (VI.14 23; [VI.38-45;
Interest 143 144
Interest, compound 143 (IV.6-9) [IV.17 20-22]
Interest, continuously compounded 144 (IV.8) [IV.18 19 21 23]
Interest, rate 143 144 (IV.6-9) [IV.17-23]
Interest, rate, effective annual 144 [IV.21]
Interest, rule 144 (IV.9)
Interest, simple 143 [IV.21]
Intermediate Value Theorem 232 [VII.25]
Interpolation see Linear interpolation
Inventory (IV.11 14) [IV.32 33]
Inverse function(s) 144 (VIII.1.9 1.10 2.6 7.8) [VII.35; 2.18 13.2]
Inverse hyperbolic function(s) 233 302 [VII.35;
Inverse square law (III.28) [III.44]
Inverse trigonometric function(s) (11.11; 3 VII.15 23; 4.2 4.9 5.8 7.7 7.8 [III.28; 2.8 2.17 3.6 4.5 4.8-4.12 4.14 5.9 9.16 13.5]
Isosceles triangle (II.9 27) [11.15 42;
Jump discontinuity (VIII.12.7)
Kinematics 95 96 99 (III.1-9 13) [III.1-10 49]
kinetic energy 100 140 [III.49]
Law of Cosines (III.14) [III.21]
Law of natural decay 171 (III.3) [III.2]
Least squares method (III.4)
Lemniscate (VIII.9.7) [VIII.9.13 9.17]
Length of a curve 141 232 233 (IIL34; 8.9-8.11 9.8) [III.58; 7.41 7.42 8.13-8.17 13.4]
Limit Comparison Test 227 (VII.20)
Limit, infinite (1.10 11.15 18; 6.6 6.7 9.4 [1.19;
Limit, left-hand (1.10; 11.15; VII.1; VIII.3.16) [VII.2 3 37 38; 11.7 11.8 11.28]
Limit, of a function 144 (1.9 16; 35; 8-10; 5 7 8 VIIL4.9-4.12 6.1 6.3 6.7 7.14 9.4 [1.15 26; 20-22 24; 8 9 17 21 22 36; 7.35 11.1-11.22
Limit, of a sequence 97 (VII.14 20; 10.4 10.5 10.8 10.10 10.11) [IV.21; 34; 10.10 10.22 11.23 11.27]
Limit, right-hand (1.10 14; 18; 3.16 6.2 6.4 6.6 11.9 11.16 [VII.2-5 37 38; 11.14 11.21 11.25 11.26 11.28]
Linear approximation 146 (IV.18 1-5) [IV.43 44;
Linear interpolation 195 (VI.24) [VI.
Linear momentum 99
Lions Gate Bridge 129 131 (III.35)
Lipschitz condition 231 [VII.19]
Local maximum/minimum see Maxima and minima
Logarithmic functions 172 (IV.19; VIII.4.3 4.4 4.13 5.9 6.7 7.5 [IV.2; 22 31 36; 4.1 4.8-4.18 5.9 5.13 11.14 11.16 11.26 11.27]
Logarithmic functions, differentiation of (1.10 IV.17; [1.19 20; 2.3 2.7 3.2 3.17 8.8]
Logarithmic functions, graphs of (1.10 V.4) [1.19 20]
Logarithmic functions, integration of (VII.21) [IV.45; 40 48; 6.3 6.9 7.16 7.40]
Logarithmic functions, series for (VI.14 [VI.36 VIII.10.15]
Logarithms 172 (IV.7 8; 3 6 7; 2.6 7.6 7.13) [III.8; 45; 5 22; 31; 5.9 6.3 7.6 11.26]
Logistic equation 173 174 (V.6-8 10 11) [V.15-22]
Logistic growth curve 173 174 (V.6 10)
L’H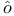 pital’s rule (1.9 VIII.9.4 (see pital’s rule (1.9 VIII.9.4 (see
Maclaurin series 198 (VI.19; [VI.37; (see
Malthusian growth law 171 (V.1 4 6 9) [V.1 3 5-8]
Marginal 146 147
Marginal cost 146 (IV.17) [IV.34 39 40 43 44]
Marginal demand (IV.18) [IV.38]
Marginal profit 146
Marginal revenue 146 (IV.19 20) [IV.41 42 45]
Market equilibrium 145 [IV.25 37]
Market value 145
Mathematical induction (VIII.10.9) [VIII.5.14]
Maxima and minima 2 34 35 (1.2 9 II.1-18 22; 35; 9 V.5 9; 3.11 3.13-3.16) [1.4-11 20; 59; 59; 20 26-29 31 33 35 36 42; 21 22; 27 39; 3.20-3.35 8.6 13.4 13.6]
Maxima and minima, second derivative test 2 (1.6-9 12; 10 12-14; 12 14 16; 9) [IV.16]
Maxima and minima, strategy for finding 2 34 35
Mean value theorem 232 (VII.9) [1.26; 25 32]
Mean Value Theorem, Cauchy’s [VII.32]
Mixing problems [V.12-14]
Moment of inertia 100 (III.18) [III.31]
Monopoly (IV.15) [IV.25 41 45]
Monotonic function (III.35)
Monotonic sequence (VIII.10.4 10.10)
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



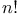 , estimation of
, estimation of  (Pi), estimation of
(Pi), estimation of 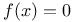
 pital’s rule
pital’s rule