|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Griffits D. Ч Introduction to elementary particles |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Particles, gluon 48 55Ч56 60Ч61 260 275 279Ч281
Particles, graviton 16 48 55Ч56
Particles, J or 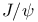 meson (see У meson (see У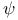 mesonФ) mesonФ)
Particles, K meson, charged 29 31Ч38 128 318
Particles, K meson, kaon (see УK mesonФ)
Particles, K meson, neutral 29Ч30 32Ч38 131Ч133
Particles, muon 4 18Ч19 24Ч25 27 66 100 304Ч309
Particles, neutrino 14 19 22Ч28 124Ч125
Particles, neutron 14 24 27 68 116 135 309Ч314
Particles, nucleon 116
Particles, photon 14Ч17 47 55Ч57 225Ч230
Particles, pion 18Ч19 24Ч25 27 51 68 124Ч125 211
Particles, positron 14 20Ч21 217 230
Particles, proton 4 13 29Ч34 39Ч40 77 116 262Ч275
Particles, r lepton 44 47 261
Particles, s (strange) quark 37 122 31Ч33 182Ч184
Particles, t (top or truth) quark 44 47 122
Particles, u (up) quark 37 122
Particles, W 44Ч47 55Ч56 301
Particles, Z 6 46Ч47 55Ч56 301 340
Parton model 269Ч273
Partons 42 270 УQuarkФ)
Pauli matrices 115 139 216 334 351 379
Pauli principle 1 3 18 41 174Ч176
Pauli spinor 113
Pauli spinor, polarization vector 229
Pauli spinor, wave function 145
Pauli, W 23 125 208
PCAC hypothesis 313 319
Perturbation theory 59
Perturbation theory, nonrelativistic 143 151
Perturbation theory, relativistic (see УFeynman calculusФ)
Perturbative QCD 279 295
Phase space 194Ч195
photoelectric effect 15
Photon 14Ч17 47 55Ч57 225Ч230
Pion 18Ч19 24Ч25 27 51 68 124Ч125 211 314Ч317
Pion decay constant 315Ч316
Planck formula 14 90 149
Planck, M 14
PlanckТs constant 14 108
Plane waves 218 227
Polar vector 126Ч127
Polarization 62Ч63 227Ч229
Polarization vector 227Ч229
Positron 14 20Ч21 217 230
Positronium 143 159Ч64 245Ч246
Potential Coulomb 148 164 194 285 287
Potential Coulomb, four-vector 226Ч228
Potential Coulomb, interquark 165Ч167 279 284Ч289
Potential Coulomb, linear-plus-coulomb 165Ч167
Potential Coulomb, scalar 226
Potential Coulomb, vector 226Ч228
Potential energy term 361 363
Powell, C. F 18Ч19 24Ч25 29 31
Primitive vertex (see УVertexФ)
Proca equation 213 346
Projection matrix 339
Propagator 203 357
Propagator, electron 230
Propagator, gluon 283
Propagator, modified 247
Propagator, photon 230
Propagator, quark 283
Propagator, spin one, massive 302 358
Propagator, spin one, massless 230 359
Propagator, spin one-half 203 358
Propagator, spin zero 203 358
Propagator, unstable particle 329
Propagator, W and Z 302 325 329
Proper time 87
Proper velocity 88
Proton 4 13 29Ч34 39Ч40 77 116 262Ч275
Proton Nucleon-nucleon scattering 118Ч119
Pseudoscalar 126Ч127 223Ч224
Pseudoscalar mesons 34 110 169Ч172
Pseudovector (see УAxial vectorФ)
Quantum chromodynamics (QCD) 3 55Ч56 60Ч65 164 279Ч299 355Ч357
Quantum electrodynamics (QED) 3 18 55Ч60 153 155
Quantum field theory 2 3 10 16 21 135 175 189 343 357
quantum mechanics 2 3 143Ч148 189
Quantum mechanics, distribution functions 273Ч276
Quantum mechanics, masses 53 122
Quantum mechanics, model 37Ч44
Quantum mechanics, number 74
Quantum mechanics, search 39Ч40
Quantum mechanics, table 47 122
Quantum mechanics, weak interactions 317Ч322 (see also УParticlesФ)
Quark-quark interaction 284Ч289
Quarkonium 160 162Ч169 УCharmoniumФ)
Quasi-bound state 162Ч163 166
R 261Ч263
Rabi 1 29 149
Radial equation 147
Radiative corrections 155
Raising operator 140
RANGE 17 51Ч52
Reactor 4 26
Real particle 59Ч60
Reduced mass 160
Reflection 125Ч126
Regularization 208
Reines, F 26
Relativistic correction 151Ч152
Relativistic mechanics 2 87Ч99
Relativity 3 81Ч82
Renormalization 156 209Ч210 246Ч250 360
Representation 107 116
Resonance 120 140 191 262Ч263
Richter, B 42
Right-handed state 27 124 331Ч333
Rochester, G. D 29Ч30
Rosenbluth formula 266 268Ч269
Rotation 105Ч106
Rotation group 107 (see also УGroupsФ)
Rotation matrix 115 137 139
Rubbia, C 46 327
Running coupling constant (see УCoupling constantФ)
Rutherford scattering 12Ч13 40 193Ч194 232Ч233 240Ч241 309 313
Rutherford, E 12Ч13 249
Rydberg formula 151
S (see УStrangenessФ)
s (strange) quark 37 122
Salam, A 56 323 330
scalar 87 224
Scalar product 86
Scaling (see УBjorken scalingФ)
| Scattering 2 (see also УBhabha scatteringФ УCollisions: УCross УElectron-muon УElectron-positron УElectron-proton УGolden УMailer УMott УNeutrino-electron УRutherford
Scattering amplitude 119 (see also УAmplitudeФ)
Scattering angle 191Ч192
Schrodinger equation 143Ч148 213Ч214 217
Schwinger, J. S 56 153 155 208
screening 62Ч64 249 294
SEA (see УDirac seaФ)
Sea quarks 275Ч276
Semileptonic decay 67 318Ч319
Separation of variables 145Ч146
Sextet 288 2 182Ч184
Simultaneity 82
Singlet 112 118 158Ч159 singletФ)
SLAC 5 8 40 258 273 327
slash notation 235Ч236 238
SO(N) (see УGroupsФ)
Solar neutrinos 26
Spacelike four-vector 86
Spectator quark 68 70
Spectrum 148 150Ч151 155 162Ч163 167
Spherical harmonics 147Ч148 186
Spin (see УAngular momentumФ)
Spin and statistics 175
Spin matrices 113Ч115 139 221
Spin-averaged amplitude 236
Spin-orbit coupling 151 153Ч154 157
Spin-spin coupling (see УHyperfine structureФ)
Spinor 113Ч115 (see also УDirac spinorФ)
Spontaneous symmetry-breaking 323 343 360 362Ч365
Stable particle 72Ч73
Standard model 3 46Ч48 121Ч122 322 325 350 367Ч368
State 3
Statistical factor 195
Stevenson, E. C 18
Storage rings 5
Strange particles 28Ч33
Strangeness 32Ч34 37Ч39 47 118
Street, J. C 18
Strength 55 76 78
Strong force 17 32Ч33 55Ч56 279
Structure constants 282 297
Structure functions 264Ч276 (see also УQuark distribution
Subparticles 48 53
Sum rules 276 278
Supermultiplet 36 43 121 171Ч80 decupletФ УBaryon octetФ)
Symmetric state 112 118 174
Symmetric tensor 100
Symmetry 103Ч141
t quark 44 47 122
TCP theorem 3 135
Tensor 86Ч87 9
Thomas precession 153
Thomson, J. J 11Ч12
Three-jet event 258Ч260
Threshold 22 96Ч97 101 261Ч263
Time dilation 83
Time reversal 103 134Ч135
Timelike four-vector 86
Ting, C. C 42
Top 44 47
Top quark (see Уt quarkФ)
Toporiium 167
Total cross section 193
Trace 237Ч239
Trace theorems 238Ч239 380
Transformation, Dirac spinor 222Ч223
Transformation, four-vector (see УLorentz transformationsФ)
Transformation, tensor 86Ч87 (see also УCharge conjugationФ УParityФ УTime
Transition probability 3
Translation 105
Transverse gauge (see УCoulomb gaugeФ)
Transverse polarization 228
Tree-level diagram 206 249 282
Triangle function 101
Triplet 112 118 158Ч159
Truth 44 47
Two-jet event 258Ч259
Two-neutrino hypothesis 27Ч28
tТHooft, G 210 323 360
u quark 37 122
U(n) (see УGroupsФ)
Uncertainty principle 51Ч52 73
Unification 31 76Ч78 330Ч337
Unitary matrix 106 351
UNITS 8 9 200Ч201 230 347
Up quark (see Уu quarkФ)
Upness 47
V-A interaction 303 324 330
V-events 29
VACUUM 362Ч364
Vacuum polarization 63 156 246 293
Valence quarks 275Ч276
Vector 224
Vector interaction 302Ч303 309 313 324 330 332
Vector meson 110 169Ч172
Vector potential 226Ч228
Velocity addition rule 83 88
Vertex 73
Vertex, ABC 201
Vertex, QCD 60Ч61 280 282Ч283 359
Vertex, QED 56Ч57 230 359
Vertex, weak 65Ч67 69Ч71 302 317 322 336Ч337
Virial theorem 144
Virtual particle 58Ч60 78 257Ч258
W boson 46Ч47 48 55Ч56 301
Ward identity 250
Wave function 3 145 176 214 347
Weak force 32 55Ч56 123 301Ч341
Weak hypercharge 333Ч335
Weak interaction 65Ч72
Weak interaction, charged 65 67 301Ч304 317Ч322
Weak interaction, neutral 66 69 322Ч330
Weak isospin 333Ч335
Weak mixing angle 324 336
Weinberg angle (see УWeak mixing angleФ)
Weinberg, S 56 323 330
Weyl, H 125 350 354 356
work function 15
Wu, C. S 123
Yang Ч Mills 354
Yang Ч Mills theory 350Ч355
Yang, C. N 56 122 128 350
Yukawa coupling 368
Yukawa meson 14 17Ч18 47 51 65
Yukawa, H 17Ч18 47 56
Z boson 6 46Ч47 55Ч56 301 340
Zweig, G 37
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



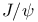 meson
meson 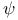 mesonФ)
mesonФ)