јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Arscott F.M. Ч Periodic Differential Equations: An Introduction to Mathieu, Lame, and Allied Functions
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Periodic Differential Equations: An Introduction to Mathieu, Lame, and Allied Functionsјвтор: Arscott F.M. јннотаци€: Of recent years, the two subjects of special functions and ordinary linear differential equations have (in this country at least) lain somewhat in the penumbra of a partial eclipse. Many mathematicians, not without reason, have come to regard the former as little more than a haphazard collection of ugly and unmemorable formulae, while attention in the latter has been directed mostly to existence-theorems and similar results for equations of general type. Only rarely does one find mention,at post-graduate level, of any problems in connection with the process of actually solving such equations. The electronic computer may perhaps be partly to blame for this, since the impression prevails in many quarters that almost any differential equation problem can be merely "put on the machine", so that finding an analytic solutionis largely a waste of time. This, however, is only a small part of the truth, for at the higher levels there are generally so many parameters or boundary conditions involved that numerical solutions, even if practicable, give no real idea of the properties of the equation. Moreover, any analyst of sensibility will feel that to fall back on numerical techniques savours somewhat of breaking a door with a hammer when one could, with a little trouble, find the key.
язык: –убрика: ћатематика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1964 оличество страниц: 281ƒобавлена в каталог: 28.03.2010ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
see "Mathieu functions of integral order" see "Mathieu functions of fractional order" 203Ч204 see see "Lame functions of the second kind" 128Ч129 92 137 90Ч92 135Ч137 131Ч132 134Ч137 139Ч140 136Ч137 see "Mathieu functions of integral order" see "Mathieu functions of fractional order" 174Ч176 187Ч190 see 186Ч187 Abel identity 28 Addition formulae for Mathieu functions 106 Associated Legendre equation 6 25 164Ч165 Associated Mathieu equation 2 14 27 153 182Ч185 Associated Mathieu functions 182Ч185 Asymptotic expansions for characteristic values 112Ч118 Asymptotic expansions for general Mathieu functions 139 Asymptotic expansions for Ince polynomials 151 Asymptotic expansions for Lame characteristic values 236 Asymptotic expansions for Mathieu functions 88 Chap. Asymptotic expansions for spheroidal wave functions 186 Basically-periodic functions 31 Basically-periodic functions, solutions of Mathieu's equation 31 33Ч47 see Bessel function product series for general Mathieu functions 138 Bessel function product series for Mathieu functions 98Ч99 Bessel function series for Associated Mathieu functions 185 Bessel function series for ellipsoidal wave functions 246Ч248 Bessel function series for Mathieu functions 86Ч88 89 135Ч136 138 Bessel function series for spheroidal wave functions 172Ч176 178 Bessel's equation, in wave problems 4 6 Bouwkamp 177 182 Brillouin 129 143 Burgess 72 Campbell 69 70 130Ч131 132 134 142 145 178 181 182 185 ceh-function 58 cel-, cdel-functions see "Ellipsoidal wave functions" cer-, cei-functions 104 ceu-function 137 Characteristic equation for Mathieu's equation 43 62 64 Characteristic exponent of Hill's equation 142Ч143 149 Characteristic exponent of Mathieu's equation 49 50 131 Characteristic exponent of spheroidal wave equation 161Ч165 169 Characteristic values for ellipsoidal wave functions 239 Characteristic values for Mathieu functions 10 43Ч46 62Ч70 Coexistence problem for Hill's equation 144 Coexistence problem for Mathieu's equation 34Ч37 Continued fractions, use in constructing Mathieu functions 61Ч64 67 del-function see "Ellipsoidal wave functions" Doubly-periodic equations 51 Dougall 79 99 100 Ec-, Es-functions 203 227 231 Eigenvalues see "Characteristic values" el-functions see "Ellipsoidal wave functions" Ellipsoidal coordinates 16Ч19 20 228Ч230 Ellipsoidal harmonics 25 214Ч218 228Ч230 Ellipsoidal wave equation 2 19 25 Chap. Ellipsoidal wave functions of second and third kinds 248Ч250 Ellipsoidal wave functions, Bessel function series for 246Ч248 Ellipsoidal wave functions, Fourier Ч Jacobi series for 250 Ellipsoidal wave functions, integral relations 241Ч243 Ellipsoidal wave functions, main properties 238Ч241 Ellipsoidal wave functions, orthogonality 241 Ellipsoidal wave functions, perturbation series for 243Ч247 Ellipsoidal wave functions, power series for 250 Ellipsoidal wave functions, transformation formulae 250 Ellipsoidal wave functions, zeros 243 Elliptic coordinates 8 10 11 24 Elliptic membrane 10 150 Elliptic wave 84 104 Erdelyi 107 133 194 203 204 227Ч228 fe-, Fe-functions see "Mathieu functions of integral order" fek-, Fek-functions see "Mathieu functions of the third kind" fey-, Fey-functions see "Mathieu functions of the second kind" fl-function 249 Flammer 182 Floquet's theorem 29Ч31 48 194 Fourier Ч Jacobi series 220Ч222 227Ч228 250 ge-, ge-functions see "Mathieu functions of integral order" gek-, gey-functions see "Mathieu functions of the third kind" gey-, gey-functions see "Mathieu functions of the second kind" Goldstein 53Ч54 59 64 101 239 Halphen 213 Haupt 151 Heine 59 Heine, notation for Lame polynomials 202Ч204 hermite 16 194 Heun-type equations 231 Hill's equation 1 2 15Ч16 27 Chap. 190 Hill's equation with three terms (Whittaker Ч Hill equation) 2 16 23 43 141 144Ч146 150Ч151 238 Hill's method for determining stability 124Ч126 142Ч143 hl-function 249 Horn Ч Jeffreys technique 111 114Ч118 Humbert 145 Ince 2 34 47 74 101 104 144Ч145 182 185 194 203 227Ч228 231 232 Ince polynomials 148 149Ч152 Ince's equation (Whittaker Ч Hill equation) 145Ч152 Ince's theorem 34Ч37 65 77 125 Infinite determinant form of characteristic equation 64 67 Integral relations for ellipsoidal wave functions 241Ч243 Integral relations for Ince functions 150 Integral relations for Lame functions 211Ч217 Integral relations for Mathieu functions 40Ч42 79Ч84 85Ч86 Integral relations for spheroidal wave functions 42 180Ч181 184 188 Kelvin 59 Khabaza 231 236 Klotter and Kotowski 144 Lame functions (transcendental) 194 225Ч228 Lame functions (transcendental) of half-integral order 232 Lame functions (transcendental) of the second kind 223Ч225 230 Lame functions (transcendental) with single period 225Ч228 232 Lame polynomials Chap. IX 239 246Ч248 Lame polynomials in potential theory 228Ч230 Lame polynomials, asymptotic formulae 236 Lame polynomials, expansion as series of 222Ч223 Lame polynomials, integral relations for 211Ч214 Lame polynomials, Legendre function series for 218Ч220 Lame polynomials, normalization 208Ч209 Lame polynomials, orthogonality 206Ч208 Lame polynomials, perturbation series for 231 Lame polynomials, tables 230Ч231 Lame polynomials, Tchebycheff polynomial series for 218Ч222 Lame polynomials, transformation of 209Ч211 Lame polynomials, zeros of 197Ч200 202Ч204 210Ч211 227 231 232Ч233 Lamp's equation 2 9 24Ч25 Chap. 237Ч238 Lamp's equation, algebraic forms 192Ч193 Lamp's equation, trigonometric form 193 Laplace's equation 14 19 191 213 228Ч230 Latent roots of matrices 20Ч22 Leitner and Spence 182 Lindemann Ч Stieltjes method for Mathieu's equation 49 Magnus 143Ч145 152 Malurkar 242 Markovic's proof of Ince's theorem 34Ч37 Mathieu 67 Mathieu function series 73Ч74 78 84Ч85 103 Mathieu functions of fractional order 133Ч134 Mathieu functions of integral order 51 Mathieu functions of second kind 37Ч38 70Ч72 76Ч77 89Ч96 98 Mathieu functions of third kind 91Ч98 136Ч137 Mathieu functions, addition formulae 106 Mathieu functions, Bessel function product series for 76 98Ч101 Mathieu functions, Bessel function series for 75Ч76 86Ч88 89Ч90 Mathieu functions, elementary relations 55Ч57 Mathieu functions, integral equations for 41Ч42 79Ч84 86 96Ч98 Mathieu functions, integral relations for 40 85Ч86 96Ч98 Mathieu functions, normalization 53Ч54 64 67 71 Mathieu functions, notation 52 Mathieu functions, orthogonality 57Ч58 Mathieu functions, perturbation method for 67Ч70 76Ч77 Mathieu functions, relations between different orders 103Ч104 Mathieu functions, tables 101 Mathieu functions, trigonometric series for 54Ч55 59Ч67 Mathieu functions, zeros of 47 111Ч114 120 Mathieu's equation 2 9 14 15 167Ч168 Mathieu's equation, algebraic form 11 47Ч49 72Ч73 74 78 Mathieu's equation, general theory Chap. II Mathieu's general equation Chap. VI Mathieu's general equation, notation for solutions 130Ч134 Mathieu's general equation, stable solutions see "Mathieu functions of fractional order" Mathieu's general equation, unstable solutions 134Ч135 Matrices (notation for) 21 McLachlan 9 54 64Ч65 82Ч83 129 132Ч134 137 Meissner equation 151 Meixner 44 69Ч70 74 92 106 119 128 136Ч137 169Ч170 176 179 181 Modified Mathieu equation 24 26 59 Modified Mathieu functions 58Ч59 Modified Mathieu functions, asymptotic behaviour 88 Moeglich 239 241 248 National Physical Laboratory 231 Ne-functions 92Ч98 137 Orthogonality of ellipsoidal wave functions 241 Orthogonality of Ince functions 149 151 Orthogonality of Lame polynomials 206Ч208 Orthogonality of Mathieu functions 39Ч40 50 Orthogonality of spheroidal wave functions 179 187 189 Oscillation 22 Paraboloidal coordinates 23 Periodic function (definition) 7 Periodicity equation 31Ч33 49 121 Periodicity exponent 31Ч33 49 121 Periodicity factor 31Ч33 49 Perron's rule 65Ч66 73 226Ч227 Perturbation method for ellipsoidal wave functions 243Ч246 Perturbation method for Ince functions 149Ч150 Perturbation method for Mathieu functions 67Ч69 138 Poincare 128Ч129 Ps-, Ps-functions 169Ч170 188Ч190 see Pseudo-periodic solutions of doubly-periodic equations 51 Pseudo-periodic solutions of Mathieu's equation 31Ч34 49 127 138 Pseudo-periodic solutions of systems of equations 50 Qs-, Qs-functions 169Ч172 171Ч175 see Roper 231 Schaefke 44 69Ч70 74 92 106 128 131 136Ч137 169Ч170 seh-function 58 sel-, scel-, sdel-, scdel-functions see "Ellipsoidal wave functions" Separation constant 3 Separation method of 1Ч2 6 9 13 18 23 seu-function 137 Shenitzer 143 Singularities of differential equations 1 Spherical Bessel functions 173 Spherical harmonics 25 Spherical harmonics, relations with ellipsoidal harmonics 214Ч218 Sphero-conal coordinates 24Ч25 Spheroidal coordinates 12 15 153 189 Spheroidal wave equation 2 12 27 Chap. 238 Spheroidal wave functions 159 163 176Ч181 186 Spheroidal wave functions, connexion with Associated Mathieu functions 182Ч183 Stability diagram for Mathieu's equation 122Ч124 Stability of solutions of periodic equations 50 Stable solutions of Mathieu's equation 121Ч122 Stable zone for Mathieu's equation 120 Stationary phase, method of 120 Stieltjes's theorem on Lame polynomials 197Ч198 233Ч234 Stokes phenomenon 110 Stratton et al. 181Ч182 Strutt 144 Sturm oscillation theorem 22Ч23 Sturm Ч Liouville expansions 74 Systems of periodic differential equations 50 Titchmarsh 74 Transcendental Ince functions 149 Transcendental Lame functions 194 226 Transformation of wave equation 13 uel-functions see "Ellipsoidal wave functions" Unstable solutions of Mathieu's equation 121Ч122 Urwin 151 Von Koppenfels 83 Wave equation in 2-dimensions 2 7 Wave equation in 3-dimensions 6 7 237Ч238 Wave equation in elliptic coordinates 8Ч10 59 Whittaker 53 145 Whittaker Ч Hill equation 16 23 43 142 144Ч146 150 238 Whittaker's 143 Whittaker's 129 137 Winkler 143Ч145 152 Zeros of ellipsoidal wave functions 243 Zeros of Ince polynomials 148 149 150 Zeros of Lame functions 197Ч200 202Ч204 210Ч211 227Ч228 231 233 Zeros of Mathieu functions 10 47 54 74 111Ч114 120 Zeros of spheroidal wave functions 186 Zeros, Sturm's theorem on 22Ч23
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



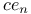 -,
-, 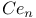 -functions
-functions 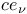 -,
-, 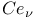 -functions
-functions 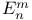 -function
-function 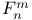 -functions
-functions 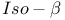 and
and 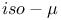 curves
curves 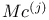 ,
, 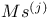 -functions
-functions 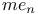 ,
, 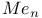 -functions
-functions 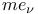 ,
, 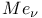 -functions
-functions 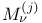 - functions
- functions 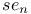 -,
-, 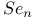 -functions
-functions 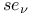 -,
-, 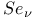 -functions
-functions 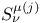 -functions
-functions 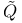 -,
-, 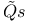 -functions
-functions  -method for Hill's equation
-method for Hill's equation