|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Dugdale J.S. Ч Entropy and its Physical Meaning |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
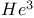 liquid 149Ч151 156Ч158 170 liquid 149Ч151 156Ч158 170
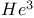 liquid, entropy 156Ч158 liquid, entropy 156Ч158
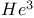 liquid, superfluid phases 150Ч151 liquid, superfluid phases 150Ч151
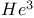 melting curve 150 156Ч158 melting curve 150 156Ч158
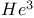 solid 156Ч158 solid 156Ч158
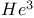 solid, entropy 156Ч158 solid, entropy 156Ч158
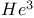 - -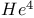 dilution refrigerator 170Ч171 dilution refrigerator 170Ч171
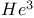 - -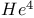 mixtures, liquid 162 170Ч171 mixtures, liquid 162 170Ч171
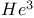 - -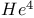 mixtures, solid 162 mixtures, solid 162
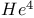 liquid 151Ч152 156Ч157 liquid 151Ч152 156Ч157
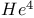 liquid, entropy 156Ч157 170 190 liquid, entropy 156Ч157 170 190
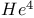 liquid, heat capacity and liquid, heat capacity and  -point 151Ч152 -point 151Ч152
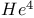 liquid, superfluidity 151 169 liquid, superfluidity 151 169
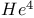 melting curve 156Ч157 melting curve 156Ч157
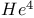 solid 156 solid 156
Absolute temperature scale 35Ч36
Absolute zero 145Ч164 177Ч179
Adiabatic demagnetisation 171Ч174
Adiabatic irreversible process 59Ч62
Adiabatic reversible process 12Ч13 177
Alloys 153Ч154
Assemblies that share energy 93Ч95
assembly 70
Atomic description of large-scale system 67Ч70
Atomic hydrogen 133
Black, Joseph 3Ч5
Blackbody (cavity) radiation 165Ч166
Boltzmann 67Ч68 70 76Ч77 79 118 124 141
Boltzmann distribution of energy 84Ч88
Boltzmann factor 87
Boltzmann's constant 86 98Ч99 125
Born, M. 12 21
Bose Ч Einstein condensation 131Ч133
Bose Ч Einstein distribution 118 129Ч131
Bose Ч Einstein gas 131Ч134 152
Bose Ч Einstein statistics 129 152
Bose Ч Einstein, energy of 135
Bose Ч Einstein, entropy of 136
Bose Ч Einstein, heat capacity of 137
Brownian movement 140
Caloric 5 32
Calorimetric entropy 160Ч162
Calorimetry 5
Carnot cycle 30Ч32 39Ч40 44Ч45
Carnot engine as refrigerator 36 166 176 191
Carnot's theorem 32Ч35
Carnot, Lazare 34
Carnot, Sadi 27Ч32
Cavity (blackbody radiation) 165Ч167
Characteristic temperature 91 106Ч108 156
Chemical equilibrium and the third law 163
chemical potential 182
Chemical reactions 12 163
Clapeyron equation 48
Classical gas 115Ч125 128 134
Classical gas, energy of 135
Classical gas, entropy of 136
Classical gas, heat capacity of 137
Classical statistics 118 128
Classical statistics, range of application in gases 129Ч131
Claude 167
Clausius 33 42 62
Clausius statement of the second law 33
Clausius theorem 40
Clausius Ч Clapeyron equation 51Ч53 155Ч156
Collins helium liquefier 168
Conducting wall 12Ч13
Cooling by evaporation 168Ч170
Critical point (temperature) 47Ч48 52 149 169
Curie's law 155 162 174
Degeneracy, parameter 130Ч131
Degeneracy, quantum 105
Degeneracy, temperature 131
Degree, size of 13 36
Degree, size of, Kelvin 36
Dilution refrigerator 170Ч171
Disorder and entropy 101Ч102
Disorder and entropy, frozen-in 102 162Ч163
Distinguishable and indistinguishable particles 81 115
Distribution numbers 71Ч67
Distribution of velocities in a gas 68Ч69 123
Dulong Ч Petit law of heat capacities 108
Einstein solid 105Ч108
Energy distribution 68Ч69 71Ч72 76Ч78 82Ч87 128Ч129
Energy, equipartition of 124
Energy, forms of 69Ч70
Energy, states, levels 80Ч81 124
Energy, zero point 80 106 149
Enthalpy 50Ч51 54
Entropy , statistical interpretation 77Ч78 98Ч101 164 171Ч172
Entropy and disorder 101Ч102
Entropy and heat capacity 43Ч44 111Ч112
Entropy and heat flow 57Ч59
Entropy and latent heat 46Ч48
Entropy and probability 99 141
Entropy at low temperatures 145Ч164
Entropy constant of a gas 122
Entropy in irreversible processes 57Ч62
Entropy in statistical mechanics 95Ч100 159Ч160 169
Entropy measurement of 43Ч44 160Ч161
Entropy of alloys 153Ч154
Entropy of closed systems 62
Entropy of Einstein solid 106Ч107
Entropy of gas mixtures 122
Entropy of ideal gas 42 44 119Ч122 131 133 136
Entropy of magnetic solid 110Ч112 191
Entropy of melting 47 155Ч158
Entropy of mixtures 122 152Ч154
Entropy of perfect gas 42 44 119Ч122 131 133 136
Entropy of solid-like assembly 103Ч105
Entropy of vaporisation 46Ч47 159Ч160 190
Entropy, definition of 39Ч40
Entropy-temperature diagrams 44Ч45 47 107 136 157Ч158 169 171 178 190
Equation of state 14 49 125
Equipartition of energy 124
Extensive variables 15 118 122
External work method of liquefaction 167Ч168
Fahrenheit 3
Fermi Ч Dirac distribution (statistics) 127Ч130
Fermi Ч Dirac gas 131 133Ч135 149Ч150 156
Fermi Ч Dirac gas, entropy of 134 136
Fermi Ч Dirac gas, heat capacity of 134 137
Fermi Ч Dirac gas, internal energy of 134Ч135
First law of thermodynamics 19Ч24 33 48 163 177
Fluctuations 139Ч141
Fluctuations and the second law of thermodynamics 140Ч141
Free energy 50Ч53 104 106 124Ч125 148 156
Frozen-in disorder 102 162Ч163
Gas mixtures 122
Gas scale of temperature 13Ч14 35 165 173
Gas-like assemblies 81 115Ч137
Gases and the third law 159Ч162
Gases, liquefaction of 167Ч168
Gibbs free energy 50Ч53 182
Gibbs paradox 183
| Glasses 43 162Ч163
heat capacity 3Ч4 6 23 43Ч44
Heat capacity near absolute zero 158Ч159
Heat capacity of Einstein solid 107Ч108
Heat capacity of gases 122 134 137 159
Heat capacity of magnetic solid 111Ч112
Heat capacity of two-level solid 89Ч91
Heat engines 27Ч35
Heat engines and thermodynamics 27Ч28
Heat exchanger 167
Heat switch 173
Heat, definition of 20Ч21
Heat, mechanical equivalent of 7Ч8
Heat, nature of 5Ч8 22
Helmholtz free energy 104 106 124Ч125
Hydrogen, atomic 133
Hydrogen, liquid 169
Insulating wall 12Ч13
Intensive variables 15
Internal energy (function) 11 19Ч24 70 156 163
Internal energy (function), atomic interpretation 22Ч23 70
Internal energy (function)of perfect gas 24 45 134Ч135
Inversion temperature 167
Irreversible processes 15Ч16 43 59Ч62
Irreversible processes, entropy changes in 59Ч62
Isotopic mixtures 152Ч153 162
Joule 7Ч8 24
Joule Ч Thomson effect 53Ч55 167Ч169
Joule's law 24
Kelvin (William Thomson) 33 35Ч36 140 177
Kelvin (William Thomson), absolute temperature scale 35Ч36
Kelvin (William Thomson), first temperature scale 35 42
Kelvin (William Thomson), statement of second law 33
Lambda point in liquid 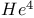 151Ч152 156Ч157 169 151Ч152 156Ч157 169
Latent heat 3 46Ч48 156 168
Lattice vibrations 108 159
Law of increase of entropy in closed systems 62
Linde 167
Linde method of liquefaction 167 176 191
Liquefaction of gases 167Ч168 176 191
Localised elements 81Ч82 118
Localised elements, assembly of 82Ч91
Low temperatures, measurement of 173Ч175
Low temperatures, production of 166Ч173
Magnetic method of cooling 167 171Ч174
Magnetic solid 109Ч112 155 173Ч176
Magnetic susceptibility and the third law 155
Maxwell 68 140
Maxwell Ч Boltzmann distribution of velocities 68Ч69 123
Maxwell's demon 140
Maxwell's thermodynamic relations 49Ч51
Mayer 7
Mechanical equivalent of heat 7Ч8
Melting curve at low temperatures 155Ч158
Microstate 72 80Ч81
Molecules with two energy levels, an assembly of 87Ч91
Molecules, energy levels of 80Ч81
Negative temperatures 113
Nernst 145
Nernst heat theorem 145 163
Noise in electrical circuits 140
Non-equilibrium states 99 162Ч163
Nonlocalised elements 81 118
Nuclear demagnetisation 172Ч173
Nuclear paramagnetism 172Ч173
Open systems 12 182
Order-disorder transition 171
Ordering at low temperatures 101Ч102 164
Paramagnetic salts 89 109 171Ч172
Paramagnetism, electronic 171Ч172
Paramagnetism, nuclear 172Ч173
Partition function 104Ч105 119Ч121 123 125
Pauli exclusion principle 118 127 149 152
phase diagram 52Ч53 149
Phase separation in liquids 153
Phase separation in solids 153
Planck 70 80 99Ч101 124 165
Planck's discussion of 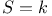 100Ч101 100Ч101
Probability, Thermodynamic 99
Quantum energy states 80Ч81 124
Quantum statistics 127Ч137
Quasi-static processes 14Ч15 32 96
Recurrence paradox in statistical mechanics 141
Reversible change, reversibility 15Ч16 32Ч33 43 58 96 146 166 171 177Ч178
Ruhemann, B. 145
Ruhemann, M. 145
Rumford, Count (Benjamin Thompson) 5Ч7
Sackur Ч Tetrode equation 121Ч122 134Ч135 160
Second law of thermodynamics 27Ч36 49 140Ч141 163 177
Simon 145 163Ч164 179
Simon liquefier 168 175
Solid Einstein model 105Ч108
Solid magnetic 109Ч112 135 171Ч174
Solid of molecules with two energy levels 87Ч91
Solid-like assembly 82Ч84 87Ч91
Stationary states 80Ч81
Statistical entropy 160Ч162
Statistical mechanics 68 77 93Ч102 141
Stirling's approximation 83
Superconductivity 147Ч149
Superconductor, heat capacity 148 159
Superfluidity in 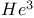 150Ч152 150Ч152
Superfluidity, 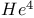 133 151Ч152 169 133 151Ч152 169
Temperature 3 11Ч13 35Ч36 165Ч166 173Ч175
Temperature in statistical mechanics 93Ч99
Temperature, absolute 35Ч36 173Ч175
Temperature, definition 13
Temperature, scales 13Ч14
Temperatures, negative 113
Thermal equilibrium 3 13Ч15
Thermal expansion and the third law 154
Thermodynamic functions and appropriate variables 49Ч51
Thermodynamic, coordinates 11Ч12
Thermodynamic, equilibrium 12
Thermodynamics, characteristic variables 11Ч12
Thermodynamics, first law 19Ч24 33 48 163 177
Thermodynamics, second law 27Ч36 49 140Ч141 163 177
Thermodynamics, third law 102 106 110Ч111 122 145Ч164 177Ч179
Thermodynamics, zeroth law 3 13 49
Thermometer 3 13 175
Third law of thermodynamics 102 106 110Ч111 122 145Ч164 177Ч179
Third law of thermodynamics and chemical equilibrium 163
Third law of thermodynamics and unattainability of absolute zero 177Ч179
Thompson, Benjamin (Count Rumford) 5Ч7
Thomson W. (Lord Kelvin) 33 35Ч36 140 177
Triple point 47 52 149 168Ч169
Unattainability of absolute zero 177Ч179
Vapour pressure 168Ч170
Velocity distribution in a gas 68Ч69 123
Work in irreversible processes 15Ч16
Work in quasi-static processes 14Ч15
Work in statistical mechanics 96
Work of liquefaction 176 191
zero point energy 80 106 149
Zeroth law of thermodynamics 3 13 49
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



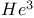 liquid
liquid 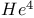 dilution refrigerator
dilution refrigerator  -point
-point