|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Adler S.L. Ч Quaternionic Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Fields |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Spin-1 relativistic wave equation see "Gauge potential"
Spin-1/2 relativistic wave equation see "Dirac equation"
SPIRES keywords 7n.5
SQUID (Superconducting Quantum Interference Device) 519 522
Stability of atoms and nuclei see "Rest masses and
Standard model 3 213Ч214 216Ч217 475 497 497n.1 498n.2 501 504 516 520 533
Standard model as an asymptotic dynamics 497
Standard model, hierarchy problem of 516 525
Standard model, running couplings of 498
Standard model, time reversal violation phenomenology 216Ч217 518
States (in Hilbert space) 61 118 see
States (in Hilbert space), bound and unitarity deficiency 226
States (in Hilbert space), correspond to unit rays 29
States (in Hilbert space), density matrix for 68
States (in Hilbert space), described by vectors 20Ч22
States (in Hilbert space), dispersion of operator in 71
States (in Hilbert space), energy eigenstate expansion of 45 195
States (in Hilbert space), energy eigenstates introduced 43
States (in Hilbert space), expectation defined in terms of 68 71n.8
States (in Hilbert space), free particle in and out, completeness 223Ч224
States (in Hilbert space), free particle in and out, defined 220
States (in Hilbert space), free particle in and out, normalization 225
States (in Hilbert space), free particle in and out, related to full scattering state 221Ч222
States (in Hilbert space), full scattering 218
States (in Hilbert space), full scattering, normalization 225Ч226
States (in Hilbert space), full scattering, not complete when bound states 225Ч227 225n.1
States (in Hilbert space), initial system in decay 201
States (in Hilbert space), stationary see also "Energy eigenstates"
States (in Hilbert space), stationary, methods for approximating 124Ч145 194
States (in Hilbert space), time development of 36Ч37
States (in Hilbert space), wave function defined from 38
Stationary state perturbation theory see "Perturbation theory"
Statistical mechanics 287Ч293 527 532 see
Statistics, Bose 238
Statistics, Fermi 238
Statistics, fractional 238n.2 527
Statistics, para- 238n.2 527
Statistics, spin connection with 481 531
Stone's theorem 31
String theory 3 498
Sturm Ч Liouville system boundary conditions 168 168n.2
Subasymptotic states momentum not well defined on 64
Subsystem density matrix 252Ч253
Subsystem density matrix, cluster decomposition property 253Ч254 295Ч299
Subsystem density matrix, cluster decomposition property, abbreviated notations used in 295n.13 296
Superconductivity, BCS theory of 511
Supermatrix formalism, applied to quaternionic Gaussian integrals 491Ч494 549Ч551
Superposition 5 8Ч10 521
Supersymmetric or supersymmetry and fermionic current in quaternionic field theory 484Ч486
Supersymmetric or supersymmetry, case of Gaussian integral formulas 492Ч494
Supersymmetric or supersymmetry, extensions of Poincare algebra 361 499 532
Supersymmetric or supersymmetry, hints of in operator constraints and Gaussian integrals 465 492Ч493 492n.48 532
Supersymmetric or supersymmetry, quantum mechanics (Witten model) 358Ч359 see two-component
Supersymmetric or supersymmetry, total trace Lagrangian theories 532
Symmetry transformation or generators 29Ч31 34 36 53Ч70 74Ч76 99 112 238 388 397
Symmetry transformation or generators and anti-self-adjoint generators 29Ч31 53Ч68 388 433Ч434
Symmetry transformation or generators in complex quantum mechanics 76 433
Symmetry transformation or generators in complex quantum mechanics, Poincare and internal symmetry 433
Symmetry transformation or generators in generalized quantum dynamics 451Ч452
Symmetry transformation or generators of complex versions of relativistic wave equations 362 384Ч387
Symmetry transformation or generators, complex classification applies in quaternionic case 433Ч434
Symmetry transformation or generators, generators which anticommute with Hamiltonian 75n.9
Symmetry transformation or generators, most general composition law for 100 see projective
Symmetry transformation or generators, Wigner analysis of group representations 53 74Ч76
Symmetry transformation or generators, Wigner analysis of group representations, leads to complex representations 75Ч76 141n.6 166 238
Symplectic component representation 18Ч19 26Ч27 40Ч42 56Ч57 71Ч73 85Ч86 93Ч94 93n.7 114n.17 123 126 132 140Ч141 143 146Ч148 153Ч173 184 201Ч207 218 244 255n.5 259Ч260 272n.1 329 333Ч334 341Ч345 354Ч358 391 395 482n.42 491 541Ч542
Symplectic component representation and embedded fermion fields 427Ч431
Symplectic component representation and running wave solutions 160 171Ч172 218
Symplectic component representation,  component perturbations 246 248 270 295Ч296 component perturbations 246 248 270 295Ч296
Symplectic component representation, bound states in  components 161 334 components 161 334
Symplectic component representation, coupled complex equations for 126 160 166 196
Symplectic component representation, defined and notation introduced 13
Symplectic component representation, exponential decay of  component 160 164Ч165 167 178 188 192n.16 517 component 160 164Ч165 167 178 188 192n.16 517
Symplectic component representation, positive and negative energy states in 314
Symplectic component representation, sign reversal for kinetic energy of  component 160 component 160
Symplectic component representation, use in complex Lagrangians 381Ч384
Symplectic component representation, use in Foldy Ч Wouthuysen method 325Ч327
Symplectic group 13n.13
T-matrix see "Transition matrix"
Tensor, product problem 240Ч245 250 271
Tensor, three-index antisymmetric 11Ч12
Thermo field dynamics 527
Three-body problem 240Ч242
Time development or evolution see "Dynamics"
Time reversal violation 4 159 174Ч175 531
Time reversal violation and tests for quaternionic effects 518
Time reversal violation in elementary particle physics 194 213Ч217 387 518 see violation"
Time reversal violation, conditions for vanishing 114Ч115 174 191 215
Time reversal, bosonic states with eigenvalues 1 and -1 related 215n.11
Time reversal, notation T in quaternionic quantum mechanics and 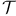 in complex quantum mechanics and phenomenology 214Ч217 217n.14 in complex quantum mechanics and phenomenology 214Ч217 217n.14
Time reversal, relationship between complex and quaternionic definitions 482n.42
Time reversal, symmetry transformation or invariance 29 35 75n.9
Time reversal, symmetry transformation or invariance in complex Lagrangian field models 381Ч382 385Ч387
Time reversal, symmetry transformation or invariance in quaternionic field theories 481Ч483
Time reversal, symmetry transformation or invariance in spin zero systems 112Ч119 122 510Ч511
Time reversal, symmetry transformation or invariance in systems with spin 119Ч122 510Ч511
Time reversal, symmetry transformation or invariance of quaternionic harmonic oscillator 122Ч123
Time reversal, symmetry transformation or invariance, implemented by complex conjugation 47n.19 49 112 214 386 386n.9
Time reversal, symmetry transformation or invariance, not implementable by conjugation 112
Time reversal, symmetry transformation or invariance, real phase factors in 386 481 483
Time reversal, unitary operator 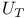 for invariance 112Ч118 for invariance 112Ч118
Time reversal, unitary operator 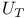 for invariance and complex antiunitary operator for invariance and complex antiunitary operator 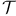 118Ч119 118Ч119
Time reversal, unitary operator 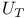 for invariance and constant phase of for invariance and constant phase of 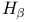 114n.17 188 191 114n.17 188 191
Time reversal, unitary operator 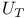 for invariance and linear dependence of for invariance and linear dependence of 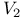 and and 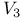 114Ч115 191 114Ч115 191
Time reversal, unitary operator 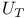 for invariance and right algebra element for invariance and right algebra element 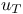 114 114
Time reversal, unitary operator 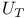 for invariance in generalized quantum dynamics 481Ч483 for invariance in generalized quantum dynamics 481Ч483
Time reversal, unitary operator 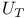 for invariance, action on energy eigenstates 115Ч117 121Ч122 for invariance, action on energy eigenstates 115Ч117 121Ч122
Time reversal, unitary operator 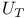 for invariance, action on momentum/angular momentum 114 118Ч119 for invariance, action on momentum/angular momentum 114 118Ч119
Time reversal, unitary operator 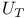 for invariance, action on operators 116Ч117 for invariance, action on operators 116Ч117
Time reversal, unitary operator 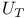 for invariance, action on S-matrix 113 117 192 231Ч232 for invariance, action on S-matrix 113 117 192 231Ч232
Time reversal, unitary operator 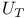 for invariance, dependent on structure of Hamiltonian 114Ч115 for invariance, dependent on structure of Hamiltonian 114Ч115
Time reversal, unitary operator 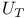 for invariance, extended for systems with spin 119 for invariance, extended for systems with spin 119
Time reversal, unitary operator 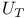 for invariance, necessary condition for 112Ч113 for invariance, necessary condition for 112Ч113
Time reversal, unitary operator 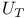 for invariance, not universal 113Ч114 for invariance, not universal 113Ч114
Time reversal, unitary operator 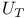 for invariance, sufficient conditions for 113Ч115 120 for invariance, sufficient conditions for 113Ч115 120
Time translation generator see "Hamiltonian"
Time-ordering operators 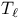 , , 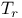 , applied 70 149 151Ч152 209 229 231Ч232 353 , applied 70 149 151Ч152 209 229 231Ч232 353
Time-ordering operators 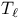 , , 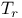 , defined 37 , defined 37
Total trace dynamics see "Generalized quantum dynamics"
Total trace functional or Trace functional 398Ч399 442Ч489 499 see generalized" "Generalized "Operator-valued
Total trace functional or Trace functional, action principle for 444Ч446
Total trace functional or Trace functional, energy-momentum tensor 483Ч484 533
Total trace functional or Trace functional, expectation and transition probabilities expressed in terms of 448Ч449
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Hamiltonian 399 446 499 523
| Total trace functional or Trace functional, Hamiltonian, constrained 455 529
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Hamiltonian, nonunitary dynamics may be chaotic 524n.19
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Hamiltonian, operator equations of motion 446
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Hamiltonian, transformation to Schroedinger picture 454
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Hamiltonian, unitary dynamics a special case 453Ч454 524 524n.18
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Lagrangian 399 444 523 528Ч529
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Lagrangian and complex quantum mechanics 455Ч475
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Lagrangian and constrained systems 455 455n.26 529
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Lagrangian for quaternionic field models 475Ч478 483
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Lagrangian, gauge-fixing conditions 455
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Lagrangian, operator equations of motion 446
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Lagrangian, operator-valued gauge invariance of 449Ч450
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Noether theorem generalized to 450Ч452
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Noether theorem generalized to, and generator algebra closure 452
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Noether theorem generalized to, for linear transformations 451Ч452
Total trace functional or Trace functional, Noether theorem generalized to, Poincare generators 451
Total trace functional or Trace functional, operator derivative and 445
Total trace functional or Trace functional, operator derivative and, higher derivatives not defined 445
Total trace functional or Trace functional, operator derivative and, Leibnitz product rule for 448
Total trace functional or Trace functional, operator derivative and, relation to matrix element derivatives 539
Total trace functional or Trace functional, operator Euler Ч Lagrange equations for 446
Total trace functional or Trace functional, operator Euler Ч Lagrange equations for, as operator constraints 455
Total trace functional or Trace functional, operator Euler Ч Lagrange equations for, operator gauge covariant 450
Trace operation, tr defined for octonion 51n.20
Trace operation, tr defined for quaternion 12
Trace operation, Tr defined for quaternion operators 15 443
Trace operation, Tr defined for quaternion operators and Witten index 443n.22
Trace operation, Tr defined for quaternion operators, cyclic property 15 290 443
Trace operation, Tr defined for quaternion operators, properties of 443Ч444 443n.22 459 459n.30 463 529
Trace operation, tr defined for quaternion, cyclic property 12 318 376
Trace operation, tr defined for quaternion, over left-acting algebra 280 431
Transformation function see "Probability amplitude" "Wave
Transition matrix 173 196Ч201 see "Scattering amplitude"
Transition matrix and outgoing wave function 201
Transition matrix, coupled equations for 197
Transition matrix, operator form for 200
Transition matrix, related to S-matrix 173
Translation group see "Momentum"
Translation invariant multiparticle system see "Hamiltonian in
Translation invariant system see "Hamiltonian"
Transpose of column vector 21
Transpose of product 15
Transpose, defined for quaternion matrix 15
Transpose, use of 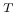 as notation for 15 39 41 191 309 323 330 367 408n.4 477 490 as notation for 15 39 41 191 309 323 330 367 408n.4 477 490
Trotter product formula 109
Two-body problem 239Ч240
Uncertainty principle 47n.19 53 70Ч74
Unification of forces 3
Unitarity of S-matrix 228
Unitarity, deficiency and Moeller wave operators 226 265
Unitarity, failure in octonionic Hilbert space quantum mechanics 51Ч52 52n.22
Unitarity, sum rule 163 174 204Ч207
Unitary operator see "Operator quaternion
Vacuum spontaneous symmetry breaking 75n.9 387 387n.10 396Ч397 508 526
Vacuum state 273
Vacuum state, doublet 429n.14
Variational principles 144Ч145
Variational principles for mean field approximation 297
Variational principles for smallest eigenvalue of Hamiltonian modulus 145
Variational principles, Rayleigh Ч Ritz analog 145
Vector potential 93Ч98 239Ч240
Vector potential, "string" for monopole 97n.8
Vector potential, quaternion imaginary 94
Vector-like theory 508 511
Vectors in coordinate space, conventions for three-vectors and four-vectors 53n.1 320n.6
Vectors in Hilbert space see "Hilbert space vectors
Velocity operator 93 235
Vierbein 513
Virial theorem 108Ч109 352Ч353
Wave equation, effective see "Optical potential" "Quantum complex"
Wave equation, effective, relativistic 303Ч388 397 see "Gauge "Klein "Lagrangian
Wave equation, effective, two-component semirelativistic 58 66n.6 87n.1 111n.14 165n.1 179n.8 348 350Ч361 429n.14
Wave equation, effective, two-component semirelativistic and supersymmetric quantum mechanics 358Ч359
Wave equation, effective, two-component semirelativistic and Witten model 358Ч359
Wave equation, effective, two-component semirelativistic, Ehrenfest and virial theorems 352Ч353
Wave equation, effective, two-component semirelativistic, energy eigenstates 351
Wave equation, effective, two-component semirelativistic, Feynman path integral 353Ч354
Wave equation, effective, two-component semirelativistic, probability current conservation 352
Wave equation, effective, two-component semirelativistic, scattering theory and bound states 354Ч358
Wave equation, effective, two-component semirelativistic, self-adjoint generators 351
Wave equation, effective, two-component semirelativistic, transformation to complex form 360Ч361 441
Wave function 19Ч20 26 see "Momentum representation"
Wave function for energy eigenstate (giving time-independent Schroedinger equation) 97
Wave function for identical particles 238 270Ч271
Wave function, asymptotic scattering see "Asymptotic scattering states"
Wave function, bound state normalization 161 168
Wave function, boundedness 160 172 183n.12 186
Wave function, complex, related to real 49
Wave function, continuity conditions for 161Ч162 400 403
Wave function, eikonal form for 156
Wave function, four-component quaternionic 184 308 367
Wave function, four-component quaternionic, spinor 329 332n.13
Wave function, free particle 180 219Ч221
Wave function, junction conditions 160 162 164 355
Wave function, n-component 39
Wave function, phase, methods based on 145Ч158
Wave function, relative coordinate, in multiparticle system 239 241 245
Wave function, rotational invariance analysis for 68 80 179
Wave function, single-component 40 58 64 84 87 91n.5 98 240
Wave function, two-component complex 40 272n.1 358 382 407Ч409 528
Wave function, two-component quaternionic 84 312Ч314
Wave function, two-component quaternionic, spinor 329n.12
Wave function, two-component semirelativistic 58 see
Wave packet 227 227n.2 266Ч267 405Ч407
Wave packet, group velocity for 406
Weisskopf Ч Wigner approximation 202n.7 204Ч206
Weyl ordering 460Ч461
Wigner analysis of symmetries of Hamiltonian 53
Wigner theorem for unit ray mappings 29Ч31 36 112
Witten index 443n.22
Witten model for supersymmetric quantum mechanics 358Ч359 see two-component
WKB approximation 156Ч158 527
WKB approximation, connection formulas not known in quaternionic case 158n.13 527
WKB approximation, equations for real components of eikonal integrand 157Ч158
WKB approximation, Riccati equation and 158 527
WKB approximation, Riccati equation and, algebraic equation in complex limit 158
WKB approximation, slow variation assumption 156
wronskian 169Ч170 183n.12
Yang Ч Mills gauge potential and field 363 442 460n.31 488 488n.45 527
Yang Ч Mills gauge potential and field, identification of observables for 453n.24
Yang Ч Mills gauge potential and field, identification of observables for, path-ordered integrals used 453n.24
Yang Ч Mills gauge potential and field, operator gauge-invariant extension 472Ч475
Yang Ч Mills gauge potential and field, supersymmetric 484
Yang Ч Mills gauge potential and field, ubiquitous appearance in standard model physics 501
Zero energy states see "Energy zero
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 component perturbations
component perturbations 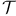 in complex quantum mechanics and phenomenology
in complex quantum mechanics and phenomenology 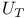 for invariance
for invariance 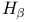
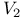 and
and 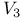
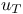
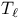 ,
, 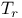 , applied
, applied 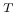 as notation for
as notation for