јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Aho A.V., Ullman J.D. Ч The Theory of Parsing, Translation, and Compiling. Volume II: Compiling
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: The Theory of Parsing, Translation, and Compiling. Volume II: Compilingјвторы: Aho A.V., Ullman J.D. јннотаци€: The book, Theory of Parsing, Translation and Compiling, by Alfred V. Aho, and Jeffrey D. Ullman, is intended for a senior or graduate course in compiling theory. It is a theoretical treatment of a practical computer science subject. Since computer science is an ever changing area of study, this book emphasizes ideas, rather than specific application details. The algorithms and concepts presented in the book should survive to new generations of computer technology, programs and systems. Numerous examples are given, with specific context, rather than on the large complicated contexts normally found in implementations, even in cases where the theoretical ideas are difficult to understand in isolation.
язык: –убрика: Computer science /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1973 оличество страниц: 471ƒобавлена в каталог: 09.12.2009ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
598Ч600 588Ч597 601 613 616 (1, 0)-bounded-right-context grammar 690 699Ч701 708 (1, 1)-bounded-right-context grammar 429Ч430 448 690 701 (2, 1)-precedence grammar 426 448 666 690 702Ч707 Aanderaa, S.D. 34 Absolute machine code 720Ч721 Acceptable property 815 Acceptance 96 see Accessible configuration 583 Accessible state 117 125Ч126 Accumulator 65 Ackley, S.I. 263 Action function 374 392 Active variable 849 937 Adjacency matrix 47Ч51 Aho, A.V. 102Ч103 192 251 399 426 563 621 645 665 709 757 787 878 960 Algebraic law 846 867Ч873 910Ч911 Algol 198Ч199 234 281 489Ч490 501 621 Algorithm 27Ч36 Allard, R.W. 906 Allen, F.E. 936 960 Alphabet 15 Alternates (for a nonterminal) 285 457 Ambiguous grammar 143 163 202Ч207 281 489Ч490 662Ч663 678 711Ч712 see Ancestor 39 Anderson, J.P. 906 Antisymmetric relation 10 Arbib, M.A. 138 ARC see "Edge" Arithmetic expression 86 768Ч773 778Ч781 878Ч907 Arithmetic progression 124 209 925Ч929 Assembler 59 74 Assembly language 65Ч70 721 863 879Ч880 assignment statement 65Ч70 Associative law 23 617 868Ч873 876 891 894Ч903 Associative tree 895Ч902 Asymmetric relation 9 atom 1Ч2 Attribute see "Inherited attribute" "Synthesized "Translation Augmented grammar 372Ч373 427Ч428 634 Automaton see "Recognizer" "Transducer" Available expression 937 Axiom 19Ч20 Backtrack parsing 281Ч314 456Ч500 746Ч753 Backus Ч Naur form 58 see Backus, J.W. 76 Backwards determinism see "Unique invertibility" Baer, J.L. 906 Bar-Hillel, Y. 82 102 211 Barnett, M.P. 237 Base node 39 Basic block see "Straight-line code" Bauer, F.L. 455 Bauer, H. 426 Beals, A.J. 578 Beatty, J.C. 906 Becker, S. 426 BEGIN block 913 938 Belady, L.A. 906 Bell, J.R. 563 811 Berge, C. 52 Binary search tree 792Ч793 Birman, A. 485 Bisection 10 Blattner, M. 211 Block see "Straight-line code" Block-structured language, bookkeeping for 792 812Ч813 816Ч821 BNF see "Backus Ч Naur form" Bobrow, D.G. 82 Book, R.V. 103 211 bookkeeping 59 62Ч63 74 255 722Ч723 781Ч782 788Ч843 Boolean algebra 23Ч24 129 Booth, T.L. 138 Border (of a sentential form) 334 369 Borodin, A. 36 Bottom-up parsing 178Ч184 268Ч271 301Ч307 485Ч500 661Ч662 740Ч742 767 816 see "Floyd-Evans "LR(k) "Precedence Bounded context grammar/language 450Ч452 Bounded-right-context (BR) grammar/language 427Ч435 448 451Ч452 666 699Ч701 708 717 see 1)-BRC "(1 0)-BRC Bovet, D.P. 966 Bracha, N. 878 Breuer, M.A. 878 Brooker, R.A. 77 313 Bruno, J.L. 787 Brzozowski, J.A. 124 138 Burkhard, W.A. 787 Busam, V.A. 936 960 Canonical collection of sets of valid items 389Ч391 616 621 Canonical grammar 692Ч697 699Ч700 Canonical LR(k) parser 393Ч396 Canonical parsing automaton 647Ч648 657 Canonical set of LR(k) tables 393Ч394 584 589Ч590 625 Cantor, D.G. 211 Cardinality (of a set) 11 14 Cartesian product 5 Catalan number 165 Caviar 667 Caviness, B.F. 878 CFG see "Context-free grammar" CFL see "Context-free language" Chaining 808Ч809 Characteristic function 34 Characteristic string (of a right sentential form) 663 Characterizing language 238Ч243 251 Cheatham, T.E. 58 77 280 314 579 Chen, S.C. 906 Chomsky grammar 29 see Chomsky hierarchy 92 Chomsky normal form 150Ч153 243 276Ч277 280 314 362 689 708 824 Chomsky, N. 29 58 82 102 124 166 192 211 Christensen, C. 58 Church Ч Turing thesis 29 Church, A. 25 29 Circuit see "Cycle" Circular translation scheme 777Ч778 Clark, E.R. 936 Closed portion (of a sentential form) 334Ч369 Closure of a language 17Ч18 197 Closure of a set of valid items 386 633 Closure, reflexive and transitive 8Ч9 Closure, transitive 8Ч9 47Ч50 52 Cluster (of a syntax tree) 894Ч895 CNF see "Chomsky normal form" Cocke Ч Younger Ч Kasami algorithm 281 314Ч320 Cocke, J. 76 332 936 960 Code Generation 59 65Ч70 72 74 728 765Ч766 781Ч782 863Ч867 see Code motion 924Ч925 Code optimization 59 70Ч72 723Ч724 726 769Ч772 844Ч960 Cohen, R.S. 500 Collision (in a hash table) 795Ч796 798Ч799 Colmerauer grammar 492 497Ч500 Colmerauer precedence relations 490Ч500 Colmerauer, A. 500 Column merger [in LR(k) parser] 611Ч612 Common subexpression see "Redundant computation" Commutative law 23 71 867 869Ч873 876 891Ч903 Compatible partition 593Ч596 601 627 Compile time computation 919Ч921 Compiler 53Ч57 see "Code "Code "Error "Lexical "Parsing" Compiler-compiler 77 Complementation 4 189Ч190 197 208 484 689 Completely specified finite automaton 117 Component grammar see "Grammar splitting" Composition (of relations) 13 250 Computation path 914Ч915 944 Computational complexity 27Ч28 208 210 297Ч300 316Ч320 326Ч328 356 395Ч396 473Ч476 736 839Ч840 863 874 944 958Ч959 Computed goto (in Floyd-Evans productions) 564 Concatenation 15 17 197 208Ч210 689 Configuration 34 95 113Ч114 168Ч169 224 228 290 303 338 477 488 582 Conflict, precedence see "Precedence conflict" Congruence relation 134 Consistent set of items 391 Constant 254 Constant propagation see "Compile time computation" Context-free grammar/language 57 91Ч93 97 99 101 138Ч211 240Ч242 842 Context-sensitive grammar/language 91Ч93 97 99 101 208 399 Continuing pushdown automaton 188Ч189 Conway, R.W. 77 Cook, S.A. 34 192 Core [of a set of LR(k) items] 626Ч627 Correspondence problem see "Post's correspondence problem" Cost criterion 844 861Ч863 891 Countable set 11 14 Cover, grammatical see "Left cover" "Right CSG see "Context-sensitive grammar" CSL see "Context-sensitive language" Culik, K. II 368 500 Cut (of a parse tree) 140Ч141 CYCLE 39 Cycle-free grammar 150 280 302Ч303 307 D-chart 79Ч82 958 Dag 39Ч40 42Ч45 116 547Ч549 552 763Ч765 854Ч863 865Ч866 959 Dangling else 202Ч204 data flow 937Ч960 Davis, M. 36 de Bakker, J.W. 878 De Morgan's laws 12 De Remer, F.L. 399 512 578 645 665 Debugging 662 Decidable problem see "Problem" Defining equations (for context-free languages) 159Ч163 Definition (statement of a program) 909 Denning, P.J. 426 709 Depth (in a graph) 43 Derivation 86 98 Derivation tree see "Parse tree" Derivative (of a regular expression) 136 Derived graph 940Ч941 Descendant 39 Deterministic finite automaton 116 255 see Deterministic finite transducer 226Ч227 see Deterministic language see "Deterministic pushdown automaton" Deterministic pushdown automaton 184Ч192 201Ч202 208Ч210 251 344 398 446 448 466Ч469 684Ч686 695 701 708Ч709 711 712 717 Deterministic pushdown transducer 229 251 271Ч275 341 395 443 446 730Ч736 756 Deterministic recognizer 95 see "Deterministic "Deterministic "Recognizer" Deterministic two-stack parser 488 492Ч493 500 Dewar, R.B.K. 77 Diagnostics see "Error correction" Difference (of sets) 4 Differentiation 760Ч763 Dijkstra, E.W. 79 Direct access table 791Ч792 Direct chaining 808 Direct dominator see "Dominator" Direct lexical analysis 61Ч62 258Ч281 Directed acyclic graph see "Dag" Directed graph see "Graph directed" Disjoint sets 4 Distance (in a graph) 47Ч50 Distinguishable states 124Ч128 593 654Ч657 Distributive law 23 868 Domain 6 10 Dominator 915Ч917 923Ч924 934 939 959 Domolki's algorithm 312Ч313 452 Don't care entry [in an LR(k) table] 581Ч582 643 see DPDA see "Deterministic pushdown automaton" DPDT see "Deterministic pushdown transducer" Dyck language 209 e see "Empty string" e-free first (EFF) 381Ч382 392 398 e-free grammar 147Ч149 280 302Ч303 397 e-move 168 190 e-production 92 147Ч149 362 674Ч680 686Ч688 690 Earley's algorithm 73 281 320Ч321 397Ч398 Earley, J. 332 578 645 EDGE 37 Eickel, J. 455 Eight queens problem 309 Elementary operation 317 319 326 395 Emptiness problem 130Ч132 144Ч145 483 Empty set 2 Empty string 15 Endmarker 94 271 341 404 469 484 698 701 707 716 Engeler, E. 58 English, structure of 55Ч56 78 Englund, D.E. 936 960 Entrance (of an interval) 947 Entry (of a block) 912 Equivalence class see "Equivalence relation" Equivalence of LR(k) table sets 585Ч588 590Ч596 601 617 625 652Ч683 Equivalence of parsers 560 562Ч563 580Ч581 see "Exact Equivalence of programs 909 936 Equivalence of straight-line blocks 848 891 Equivalence problem 130Ч132 201 237 362 684Ч686 709 936 Equivalence relation 6Ч7 12Ч13 126 133Ч134 Equivalence topological see "Equivalence of straight-line blocks" Equivalence under algebraic laws 868Ч869 Erase state 691 693 708 Error correction/recovery 59 72Ч74 77 367 394 399 426 546 586 615 644 781 937 Error indication 583 Essential blank (of a precedence matrix) 556 Euclid's Algorithm 26Ч27 36 910 Evans, A. 455 512 Evey, R.J. 166 192 Exact equivalence (of parsers) 555Ч559 562 585 Exit (of an interval) 947 Extended precedence grammar 410Ч415 424Ч425 429 451 717 Extended pushdown automaton 173Ч175 185Ч186 Extended pushdown transducer 269 Extended regular expression 253Ч258 extensible language 58 501Ч504 Feldman, J.A. 77 455 Fetch function (of a recognizer) 94 FIN 135 207 Final configuration 95 113 169 175 224 228 339 583 648 Final state 113 168 224 Finite ambiguity 332 Finite automaton 112Ч121 124Ч128 255Ч261 397 see Finite control 95 443 see Finite set 11 14 Finite transducer 223Ч227 235 237Ч240 242 250 252 254Ч255 258 722 first 300 335Ч336 357Ч359 Fischer, M.J. 102 426 719 843 Fischer, P.C. 36 Flipping (of statements) 853Ч859 861Ч863 Flow chart 79Ч82 see Flow graph 907 913Ч914 Floyd, R.W. 52 77 166 211 314 426 455 563 878 906 Floyd-Evans productions 443Ч448 452 564Ч579 FOLLOW 343 425 616 640 Formal Semantic Language 455 FORTRAN 252 501 912 958 Frailey, D.J. 906 Freeman, D.N. 77 263 Frequency profile 912 Frontier (of a parse tree) 140 Function 10 14 Futrelle, R.P. 237 Galler, B.A. 58 Gear, C.W. 936 gen 945Ч955 Generalized syntax-directed translation scheme 758Ч765 782Ч783 Generalized top-down parsing language 469Ч485 748Ч753 Gentleman, W.M. 61 Gill, A. 138 Ginsburg, S. 102Ч103 138 166 211 237 Ginzburg, A. 138 GNF see "Greibach normal form" Gotlieb, C.C. 314 goto 386Ч390 392 598 616
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



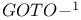
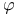 -inaccessible set of LR(k) tables
-inaccessible set of LR(k) tables