|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Adler S.L. Ч Quantum theory as emergent phenomenon |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
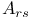 , defined 48 , defined 48
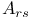 , generalized choice of 51 , generalized choice of 51
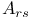 , simplest choice of 49 51 161 , simplest choice of 49 51 161
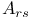 , time-reversal invariance condition on 50Ч51 , time-reversal invariance condition on 50Ч51
 defined 30 defined 30
 15 16 130 140 157 15 16 130 140 157
 , decomposition of general matrix with respect to 101Ч102 , decomposition of general matrix with respect to 101Ч102
 , reduction of Hilbert space modulo 100Ч105 , reduction of Hilbert space modulo 100Ч105
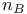 , ,  defined as numbers of bosonic, fermionic canonical coordinates 27 defined as numbers of bosonic, fermionic canonical coordinates 27
 and and  defined 122 defined 122
 matrices for Dirac equation (see also Dirac) matrices for Dirac equation (see also Dirac)
 matrices for Dirac equation, representation covananl identities for 202Ч203 matrices for Dirac equation, representation covananl identities for 202Ч203
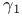 , matrices for УMФ model 70Ч71 , matrices for УMФ model 70Ч71
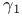 , matrices for УMФ model, identities for 203 , matrices for УMФ model, identities for 203
 14Ч20 39 42Ч52 54Ч55 60 62 117 14Ч20 39 42Ч52 54Ч55 60 62 117
 , anti-self-adjoint 15 45 117 , anti-self-adjoint 15 45 117
 , average in canonical ensemble 84Ч85 129 , average in canonical ensemble 84Ч85 129
 , average in unitary fixed ensemble 105 129 157 , average in unitary fixed ensemble 105 129 157
 , conservation discovered by Millard x 19 43 , conservation discovered by Millard x 19 43
 , construction of global unitary generators from 45 , construction of global unitary generators from 45
 , current for 54Ч55 60 66 69 , current for 54Ч55 60 66 69
 , dependence on non-commulative parts of phase space variables 48 , dependence on non-commulative parts of phase space variables 48
 , equipartition of 16 19 117 133 , equipartition of 16 19 117 133
 , fermionic part of 49 , fermionic part of 49
 , fluctuations of 17 129 146Ч147 154 158 , fluctuations of 17 129 146Ч147 154 158
 , invariance properties of 47 , invariance properties of 47
 , Noether formulation 44 54 55 , Noether formulation 44 54 55
 , Poincare invariance of 47 136Ч137 , Poincare invariance of 47 136Ч137
 , rate of growth with system size 146Ч147 , rate of growth with system size 146Ч147
 , self-adjoint component of 15 48Ч52 83 159Ч160 162 , self-adjoint component of 15 48Ч52 83 159Ч160 162
 , supersymmetric Yang Ч Mills model expression 69 141Ч143 , supersymmetric Yang Ч Mills model expression 69 141Ч143
 , time-reversal properties of 50Ч52 , time-reversal properties of 50Ч52
 , traceless 45 , traceless 45
 , WessЧZumino model expression 66 , WessЧZumino model expression 66
 , УMФ model expression 71 , УMФ model expression 71
Adjoint, assigmenl of fermionic variables 40Ч41 44 45 48Ч52
Adjoint, condition on fermionic trace Hamiltonian 40Ч41
Adjoint, properties of operator derivative 26
Adjoint, rule for products 23 193Ч194
Anticommutation relations, canonical of quantum theory 14 34Ч38 75 147
Anticommutation relations, canonical, effective or emergent 12 16 76 117 133 137Ч138 141 144 147
Anticommutation relations, canonical, local structure of 10 190
Anticommutation relations, canonical, not assumed 21 75
Anticommutator, notation defined as {X, F) 14 24
Approximations leading to quantum theory (see Quantum theory approximations)
Averages,  defined 88 defined 88
Averages,  defined 83Ч84 defined 83Ч84
Averages,  and and  defined 119 defined 119
Averages, over unitary fixed ensemble 108 111Ч112
Ax-Kochen approach (see Quantum theory)
Axial gauge, defined 93Ч94
Axial gauge, trace Hamiltonian 95
B-mesons 178Ч179
Becchi Ч Rouet Ч Stora Ч Tyutin (BRST) invariance 94 98Ч100 112 114 208Ч211
Becchi Ч Rouet Ч Stora Ч Tyutin (BRST) invariance, nilpotence of 99 209 211
Bell inequalities 6 7 17 119 151Ч155
Bilinear fermionic structure 40Ч41
Bohmian approach (see Quantum theory)
Boldface, defined to indicate trace quantities 24
Bom rule 5 6 8 13 17 151 154 156 169Ч174
Boson oi bosonic, commutators in  14 16 14 16
Boson oi bosonic, creation and annihilation operators 148
Boson oi bosonic, type (even grade) defined 22Ч23
Boson-fermion balance 12 17 20 118 139 142 144Ч147 154
Brownian motion 13 17 154 156Ч192
Canonical, algebra not trace class 133
Canonical, ensemble 12 15Ч17 20 38 76 81Ч88 123
Canonical, quantization 10 13 19 75 190
Canonical, transformations 46Ч47 76Ч80 133 135 200
Chain rule (see Leibniz rule)
Charmed meson decay 180
Classical mechanics 12 13 198Ч200
Clustering and energy-driven stochastic equation 182
Clustering and unitary fixing 105
Clustering in deriving canonical from microcanonical ensemble 90 137
Clustering of Wightman functions 137 208
Commutation relations of quantum theory 14 34Ч38 75 147
Commutation relations, canonical effective or emergent 12 16 76 117 133 137Ч138 141 144 147 153
Commutation relations, local slraclure of 10 190
Commutation relations, nol assumed 21 75
Commutator, notation defined as [X, F] 14 24
Completeness relation 150 157Ч158
Conformal invariance 11 58
Conserved quantities (see Trace dynamics)
Conserved quantities for continuum spacetime theories 52Ч58
Conserved quantities, global unitary invariance of 43 101
Conserved quantities, operator  42Ч52 (see also 42Ч52 (see also  ) )
Conserved quantities, symmetry under interchange of  with with  62Ч63 62Ч63
Conserved quantities, trace fermion number N 39Ч42
Conserved quantities, trace Hamiltonian H 29
Conventions for melnc, summation, Grassmann quantities 193Ч194
Copenhagen interpretation (see Quantum theory)
Correlation, function g(x) defined 168
Correlation, length  defined 186 defined 186
Correlations, in canonical ensemble 87 93
Cosmological blackbody radiation 82 169
Cosmological constant 11 131 191
Cosmology of early universe 190
Covariant derivative 68 204Ч205
Current algebra 46
Cyclic identities (see Trace)
Cyclic identities, bilinear 22
Cyclic identities, trilinear 23
Dark matter, energy 191
De Witt-Faddeev-Popov, determinant 95 97 208 209
De Witt-Faddeev-Popov, method 94 106 109Ч111
Decoherence 4 5
Degenerate manifold 172 173
Density matrix 167 170 172
Density matrix for mixed state 172
Derivative  (see also Trace Operator (see also Trace Operator
Derivative  , defined 24 , defined 24
Derivative  , properties of 24 26 , properties of 24 26
Dirac, fermion 15 39 58Ч60 63
Dirac, gamma matrices 53 63 73 201Ч203
Dynamical variables, УfastФ and УslowФ parts of 128 140Ч141 191
Effective projection in field equations 191
Effective projection in Ч Podolsky Ч Rosen experiments 10
Effective projection, defined 101
Effective projection, four-vector 56Ч57
Effective projection, operator tensor 61
Effective projection, trace tensor 15 55Ч57 60Ч61 131 190-191
Ensemble, Canonical (see Canonical Ensemble
Ensemble, microcanonical (see Microcanonical ensemble)
entropy 15 76 85 87 90Ч91
Epsilon symbol  defined 78 defined 78
Epsilon symbol  , , 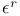 , or , or  defined 24Ч25 28 122 defined 24Ч25 28 122
Equilbnum ensemble (see Canonical Ensemble
Equilibrium distribution  81Ч82 81Ч82
Equilibrium distribution  , averages over defined 83Ч84 88 , averages over defined 83Ч84 88
Equilibrium distribution  , fluctuations of conserved quantities in 87 93 , fluctuations of conserved quantities in 87 93
Equilibrium distribution  , parameters of 83 128 145 , parameters of 83 128 145
Equilibrium distribution  , residual unitary invariance of 103 , residual unitary invariance of 103
Equilibrium distribution  , unitary fixed 108 , unitary fixed 108
Equilibrium distribution  , vector notation for parameters of 89 , vector notation for parameters of 89
Equipartition 16 19 81 117Ч118 133 190
Equipartition in classical statistical mechanics 117Ч118
Euler-Lagrange equations for continuum theory 52
Euler-Lagrange equations for Dirac fermion 205Ч206
EulerТs theorem 41
EulerТs theorem, expectation E[ ] of density matrix 167Ч168 176
EulerТs theorem, expectation E[ ] of probabilities 176Ч177
EulerТs theorem, expectation E[ ] of variance 171Ч172
EulerТs theorem, expectation E[ ], defined 167
Extensive generators 134
Fermion or fermionic, adjoint convention 20 23 193Ч194
Fermion or fermionic, adjoint properties of canonical variables 40Ч41 44 48Ч52 117 148 159
Fermion or fermionic, anticommutators in  14 16 14 16
Fermion or fermionic, creation, annihilation operators  defined 136 147Ч148 defined 136 147Ч148
Fermion or fermionic, introduction inlo theory 20
| Fermion or fermionic, structure of trace Hamiltonian and Lagrangian 39 42
Fermion or fermionic, trace charge or number 39 42 54 60 62 66 69 129
Fermion or fermionic, trace current 53Ч54 59Ч60 66 69
Fermion or fermionic, type (odd grade) defined 22
Field strength 68 204
Fierz identities 202
figure 2 12Ч14 138
Fluctuation(s) in amplified currents 183Ч184
Fluctuation(s) in conserved quantities 87 93
Fluctuation(s) in energy 181Ч185
Fluctuation(s) in spacetime geometry 185
Fluctuation(s), accretion induced 181Ч184
Fluctuation(s), corrections to Ward identities 17 18 127 156Ч170 190
Four-vector notation 52
Fullerene diffraction 188
GamblerТs ruin 172
Gauge invanance 204 206 210
Gauge, axial 93Ч96
Gauge, Coulomb 94
Gauge, fixing 16 93Ч100 104 108
Gauge, nontemporal 94 96
Gauge, potential 68
Gauge, properties of conserved quantities 97
General relativity 11
Generalized Poisson bracket (see Poisson bracket)
Generalized quantum dynamics 19 (see also Trace dynamics)
Ghost fermions 94 97Ч100 112Ч116 208-211
Global unitary invariance 13 20 190
Global unitary invariance of ensemble averages of trace polynomials 107
Global unitary invariance of generators 47 136
Global unitary invariance of matrix models 12 45 76 135 169
Global unitary invariance of trace Hamiltonian and/or Lagrangian 12 14 43 47 48 83
Global unitary invariance, breaking by canonical ensemble 16 20 85 100Ч102
Global unitary invariance, BRST invariance for fixing 208Ч211
Global unitary invariance, effect of fixing on Ward identities 116
Global unitary invariance, fixing of 16 20 61 103Ч116 191
Global unitary invariance, Noether charge  for 45 54Ч55 for 45 54Ч55
Global unitary invariance, Noether current or theorem for 54 55
Global unitary invariance, trace generators for 45
Golden Rule 180
Grade (see Grassmann algebra)
Grassmann algebra or quantities 13 20Ч24 193Ч194 206 208Ч209
Grassmann algebra or quantities, adjoint convention 23 193Ч194
Grassmann algebra or quantities, even and odd grade sectors 22Ч23 193
Grassmann algebra or quantities, integrals over 77 193
Gravitation 11 131 180 185 191
Gravitino 73
Hamilton equations for 28 31 198
Hamilton equations for generic trace dynamics 28 31
Hamilton equations, formal integration of 32
Hamilton equations, use to show conservation of  43Ч44 43Ч44
Hamiltonian (see Effective Hamiltonian or trace)
Hamiltonian form of 19 (see also Trace Hamiltonian)
Hamiltonian form of, irreducible 105
Hamiltonian form of, operator gauge invanance in 68 93Ч100 204 206
Hamiltonian form of, supersymmetric models with 64Ч74
Hamiltonian form of, symplectic geometry of 30 198Ч200
Hamiltonian form of, tangent vector field 198Ч199
Hamiltonian, phase flow 200
Hamiltonian, rest mass dominated 160 173 185
Hamiltonian, vector field 199
Heisenberg picture or evolution 12 14 16 17 118 130Ч131 135 147 149 158 163
Heisenberg picture or evolution, contrasted with trace dynamics 21 32Ч38
Heisenberg picture or evolution, lime integrated form 131Ч132 135
Heisenberg uncertainty relations 138
Hidden variables 6 17 119 152Ч155
Hierarchy of mass or energy scales 128 143 191
Hierarchy of matrix structures 12 13 138
Hilbert space 12
Hilbert space, complex 2 21Ч22 194
Hilbert space, quatemionic 2 19 194
Hilbert space, real 2 191 194
Hilbert space, reduction modulo  100Ч105 100Ч105
histories (see Quantum theory)
Holography 142 185 192
Independent particle picture 163
Internal symmetries 134
Interpretation (see Quantum theory)
Intertwining identities 205
Ito calculus 164Ч167 171 176
K defined 85
K defined, role in effective projection 101Ч2 134 135
K-mesons 178Ч179
Klein Ч Gordon scalar 15 39 58Ч61
Kochen Ч Specker Iheorem 6 7 17 119 151Ч153
Lagrangian (see Trace Matrix
Legendre transformation 40
Leibniz rule (chain rule) for differentiation 25 30 120 125Ч126 131 166 195Ч196 199
Lie algebra of trace functionals 30 46 199
Liouville theorem 15 76Ч81 200
Locality as an emergent property 138
London rigidity 143
Lorentz (see also Poincare group invanance)
Lorentz, invanance of C 47 131 136Ч137
Lorentz, nomnvanance of stochastic reduction 169Ч170
Lorentz, noninvanance of canonical ensemble 82 136
Lorentz, trace 61 131 190
Lorentzian profile 177 179
Lueders rule 156 169 173
Many worlds (see Quantum theory)
Martingale 172 176Ч177
Master equation 167Ч168
Matrix 12 21Ч24
Matrix models 2 12 13 15 18 21Ч38 106 109 169 190
Matrix models, Lagrangian and Hamiltonian dynamics 21 27Ч28
Measure for classical phase space 118
Measure for matnx integration 15 76Ч81 90 95Ч97 103 106Ч107 210Ч211
Measure for matnx integration, canonical invanance of 77Ч80
Measure for matnx integration, global unitary invanance of 80Ч81 106Ч107
Measure for matnx integration, Haar 103Ч104
Measure for matnx integration, modified (unitary fixed) 101 103Ч116 119
Measure for matnx integration, permutation symmetry of 111Ч112
Measure for matnx integration, shift invanance of 81 115 119
Measurement, apparatus 2Ч6 9 10 152Ч153 156 160 162-163 181 184
Measurement, contextual dependence in 152
Measurement, problem (see Quantum theory)
Mechanics of matnx models 2 12 15 17 39 75
Meissner effect 143
Meromorphic function 13 24
Metric, convention 193
Metric, spacetime 191
microcanonical ensemble 16 19 76 88Ч93
Microcanonical ensemble, approximation by canonical ensemble 92
Microcanonical ensemble, Ward identities in 123
Mtegraiion measure (see Measure)
N defined as dimension of Hilbert space 22
N defined as dimension of Hilbert space, relation N=2K 85
N defined as trace fermion number 39 42 Trace
Noether theorem or charge 14 39 42Ч44 53Ч57
Noether theorem or charge for internal symmetry 53
Noether theorem or charge for Poincare invariant theory 55Ч58
Nonlocality 10Ч11 138 155 190 167Ч168
Number density  , defined 168 , defined 168
Number density  , mutual commutativity of 173Ч174 , mutual commutativity of 173Ч174
Orthonormality 151 158
Partition function,  defined 88 defined 88
Partition function, conditions for existence 86Ч87
Partition function, global unitary invanance of 107
Partition function, Z defined 86 106
Pauli spin matrices 51 101 177Ч178 201
Phase space vanables, classical and non-commutative parts of 47 48 138
Phase space vanables, indices R, R+1 defined 105
Phenomenology of continuous spontaneous localization reduction 185Ч189
Phenomenology of energy-driven reduction 175Ч185
Pi zero decay 180
Planck constant 15 16 83 85 102 117 193
Planck constant, sum rule involving 142 146
Planck mass, energy, or scale 11 13 128 144 180Ч183 185
Poincare group invariance 15 39 47 82Ч83 104 117 134Ч137
Poincare group invariance associated Noether charges and currents 55Ч58
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



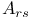 , defined
, defined  defined
defined 
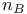 ,
,  defined as numbers of bosonic, fermionic canonical coordinates
defined as numbers of bosonic, fermionic canonical coordinates  and
and  defined
defined  matrices for Dirac equation
matrices for Dirac equation 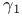 , matrices for УMФ model
, matrices for УMФ model 
 defined
defined  defined
defined  and
and  defined
defined  with
with 
 defined
defined 
 defined
defined  ,
, 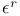 , or
, or  defined
defined 
 defined
defined  for
for  , defined
, defined  defined
defined