|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Adler S.L. Ч Quantum theory as emergent phenomenon |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Poincare group invariance generators 56Ч57 134
Poincare group invariance of Wightman functions 206
Poincare group invariance, graded 64 72Ч73
Poisson algebra 30
Poisson bracket, classical 10 195Ч196
Poisson bracket, generalized 13 21 130 199Ч200
Poisson bracket, generalized, defined and properties, of 29Ч32
Poisson bracket, generalized, of trace generators 46Ч47 57 64 67 70 134
Poisson bracket, generalized, of trace supersymmetry generators 64 67 70 72 201
Poisson bracket, Jacobi identity for 19 194Ч198
Quantum field theory 8 9 11Ч13 15Ч17 39 46 118 125 128 131 135 151 191
Quantum theory, approximations/assumptions leading to 128Ч147 157 191
Quantum theory, Ax-Kochen approach 6 8
Quantum theory, Bohmian approach 6Ч8
Quantum theory, Copenhagen interpretation 5 6
Quantum theory, emergent 16 128Ч155
Quantum theory, histories approach 6 7
Quantum theory, many worlds approach 6 8
Quantum theory, measurement problem in 2Ч6 9 10 19 190
Quantum theory, probabilistic interpretation 5Ч7 10 151 156Ч189
Quantum theory, relation to trace dynamics 12Ч13
Quantum theory, statistical interpretation 5
Quantum Zeno effect 177
R, R+1 indices of phase space variables, defined 105
R, R+1 indices of phase space variables, exception to shift invariance of restricted measure 119Ч120 130 135
Rabi oscillation of frequency 177 179
Reduction (of stale vector) 5 7 8 10 17 19 154 156Ч190
Reduction (of stale vector), rale of 17 175Ч189
Representation covanant gamma matnx identities 202Ч203
Sample space 5Ч7 10
Scale invanance 11 58 131 190Ч191
Schroedinger equation 17
Schroedinger equation, nonlinear deterministic 18
Schroedinger equation, stochastic (see Stochastic Schroedinger equation)
Schroedinger picture 12 118 147Ч151 156Ч189
SchurТs lemma 108
Slem Ч Gerlach expenmenl 3Ч5 153 184
Source terms  16 31 88 118Ч119 124 127 129Ч130 132 139 144 157 16 31 88 118Ч119 124 127 129Ч130 132 139 144 157
Source terms  with vanishing classical parts 132 with vanishing classical parts 132
Spin structure 56
Stnng theory 11 70 190
Stochastic Schroedinger equation 13 17 18 49 156Ч190
Stochastic Schroedinger equation, accretion model for energy vanance 181Ч185
Stochastic Schroedinger equation, continuous spontaneous localization (CSL) 17 156Ч157 168Ч169 173Ч175 185-189
Stochastic Schroedinger equation, energy-driven 17 156Ч157 169 173Ч185
Stochastic Schroedinger equation, environmental effects on 181Ч185
Stochastic Schroedinger equation, Lorenlz noninvariance 169Ч170
Stochastic Schroedinger equation, phenomenological constraints on 156 175Ч189
Stochastic Schroedinger equation, reduction rate formulas 174Ч175 180 188
Stochastic Schroedinger equation, simulation methods for 180
Stochasticity parameter,  defined 188 defined 188
Stochasticity parameter,  defined 174 defined 174
Stochasticity parameter, M defined 175
Sum rule for 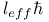 142 146 142 146
Superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) 178
Supergravity 15 73Ч74
Superluminal propagation 18 154 155 165 168
Superspace 64 72Ч74
Supersymmetry and supersymmetric 11 15 17 141Ч142 146 190Ч191
Supersymmetry and supersymmetric, algebra closure 67 70 72Ч73
Supersymmetry and supersymmetric, gamma matrix identities for 201Ч203
Supersymmetry and supersymmetric, local 15 64 73Ч74
Supersymmetry and supersymmetric, supercurrent 11 190
Supersymmetry and supersymmetric, trace dynamics models 64 74
Supersymmetry and supersymmetric, Wess Ч Zumino model 15 64 67 201
Supersymmetry and supersymmetric, Yang Ч Mills model 15 64 67Ч70 76 93Ч100 141Ч142 201
Supersymmetry and supersymmetric, УMФtheory matrix model 15 64 70Ч72 203
| Support properties 17 128Ч129 139Ч144
Support properties, possible superconductive analog 143Ч144
Survival probability 177
Symplectic notation defined 30Ч31
Symplectic structures 198Ч200
T superscnpt used to denote transpose 51 59 65Ч66 70 193 206
Thermodynamics 13 15 156 190
Time-reversal transformation 50Ч52
Tr notation for trace 22
Trace dynamics 12Ч14 16Ч19 21-38
Trace dynamics, conserved operator C in 42Ч52
Trace dynamics, contrasted with unitary Heisenberg evolution 21 32Ч38
Trace dynamics, correspondence of operators with quantum field theory 135Ч136 147Ч148
Trace dynamics, Euler Ч Lagrange equations for 27Ч28
Trace dynamics, formal integration of equations of motion 32
Trace dynamics, generic conserved quantities in 13Ч15 39Ч63 82
Trace, action 27
Trace, angular momentum density 56Ч57
Trace, class 12 32 34 38 133 192
Trace, current 53Ч54 66 69
Trace, cyclic permutation under 12 13 21Ч25
Trace, dynamics (see Trace dynamics)
Trace, energy-momenlum four-vector (four-momentum) 56Ч57 66
Trace, energy-momenlum lensor 15 55Ч58 60Ч61
Trace, fermion number 14 39 42 59Ч60
Trace, generators 45Ч47 129
Trace, Hamiltonian decoupling 15 16 136 169
Trace, Hamiltonian defined 12 28
Trace, Hamiltonian properties 13 29 39 40 47 48 62Ч63
Trace, Hamiltonian, specific models 40 59 65 68 71 95
Trace, Lagrangian 12 15 16 27 52
Trace, Lagrangian densily 52 60 204
Trace, Lagrangian, specific models 40 48 58Ч59 64 65 67Ч68 70
Trace, notation Tr for 22
Trace, operator derivative of 18 21 24 26
Trace, Poincare generators 57 82 134
Trace, polynomial defined and properties of 24 26
Trace, real, in real and qualemionic Hilbert space 194
Trace, supercharge 64 67 70 72
Trace, supersymmetry current 64 67 70
Transition probabilities 17 177 179Ч180
Two-level (of stale) system 177Ч179
Unitary canonical generators 134 135
Unitary fixing 17 76 104Ч116 124 191 208Ч211
Unitary fixing, physical quantities independent of 137Ч138
Unitary invariance, global (see Global unitary)
Vacuum state 136 150 158 162Ч163 206
Vandermonde determinant 111Ч112
Variance 171 175 178 180 187Ч188
Von Neumann, measurement model 3 181
Von Neumann, recursion 184
Ward identity/identities 16 17 81 112 114Ч116 117Ч147 154 157 160
Ward identity/identities, effect of unitary fixing on 115Ч116
Ward identity/identities, restnctions on underlying theory implied by 139Ч147
Ward identity/identities, Уoff-shellФ extension 127 130 134Ч135
Weisskopf Ч Wigner theory 176Ч177
Weyl ordering 19 33Ч38 43 161
Weyl ordering, generating function for 33Ч34
White noise 165 169
Wightman functions 16 17 136Ч138 158 206Ч208
Wightman functions, cluster property of 137 208
Wightman functions, reconstruction of quantum field theory from 137 206Ч208
Wightman functions, spectral condition 20 137 207
Zeno effect (see quantum Zeno effect)
Уchemical potentialФ (see Equilibrium distribution parameters
УfaslФ parts of dynamical variables 128 140Ч141 191
УslowФ parts of dynamical variables 128 131 140Ч141 191
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте




 defined
defined  defined
defined