Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Fröman N., Fröman P.O. — JWKB approximation: contributions to the theory
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: JWKB approximation: contributions to the theoryАвторы: Fröman N., Fröman P.O. Аннотация: The book contains a rigorous treatment of the one-dimensional JWBK-approximation. Using the ideas introduced by Zwaan and Kemble as a starting point we develop a method for examining the properties of the JWKB-approximation which is powerful also in intricate and complicated applications. In the first place we have had quantal problems in mind and hence, in the main part of the book, we assume the coefficients of the differential equation considered to be real on the real axis. This assumption simplifies the treatment. There are, however, important applications, for instance in the theory of electromagnetic waves, where the reality condition is not fulfilled. It should therefore be pointed out that the general theory in chapters 3, 4, and 7, is not subject to the above mentioned restriction and that the method can be worked out also when the coefficients are complex.
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 1965Количество страниц: 138Добавлена в каталог: 06.12.2009Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
a-coefficients see also “a-vector” a-coefficients, definition of 15 a-coefficients, differential equations for 15 a-coefficients, limiting properties of 29 92 103—105 115—116 a-vector see also “a-coefflcients” a-vector, definition of 16 a-vector, differential equation for 16 a-vector, integral equation for 16 Anti-Stokes' line 60 Asymptotic approximation method 1 Asymptotic phase 125—130 Asymptotic phase, exact expressions for 126 128 Basic Estimates 26—27 Bethe 132 Birkhoff 3 4 Bohm 7 97 Brillouin 1 Carlini 1 Classical turning point 34 Classical turning point, in the generalized sense 34 80 Classically allowed region 34 Classically allowed region, in the generalized sense 34 80 Classically forbidden region 34 Classically forbidden region, in the generalized sense 34 80 Connection formulae 1—3 6—8 83—89 97 Connection formulae, derivation of 83—86 Connection formulae, one-directional (one-sided) nature of 2 6—8 40 46 86—89 97 Current density 7 91 Epsilon, 13 Estimates of the F-matrix chapters 4 6 7 F-functions, definition of 20 F-matrix, basic estimates of 26—27 F-matrix, definition of 16 F-matrix, determinant of 17—18 F-matrix, differential equation for 17 F-matrix, estimates of see “Estimates of the F-matrix” F-matrix, integral equation for 17 F-matrix, inversion of 18 F-matrix, limiting properties of 27—29 92 103 F-matrix, multiplication rule for 21 F-matrix, series for 16 18—20 F-matrix, symmetry properties of 30—33 F-vector, definition of 20 Feshbach 7 GANs 1 Generalized classical turning point 34 80 good 94 Green 1 Harmonic oscillator, linear 109 Harmonic oscillator, three-dimensional 120—125 Heading 1 3 4 7 88 97 Hecht 14 Hydrogen-like ion 117—120 131—132 Jeffreys, B.S. 1 94 Jeffreys, H. 1 2 7 88 97 JWKB-approximation 1—2 JWKB-approximation, first order 11 JWKB-approximation, modified 4 110 JWKB-approximation, second order 10 JWKB-method see “JWKB-approximation” Kemble 3—5 8 15 86 90 91 94 112 Kramers 1 112 Langer 2 6 86 88 97 112 113 130 131 133 134 Liouville 1 Liouville — Green approximation 1 Loewdin 14 Mayer 14 Merzbacher 7 51 97 Messiah 86 Miller 94 Morse 7 Mu-integral, 26 O-symbol 2—3 45—46 Olver 3 23—25 27 35 Pauli 7 Phase-integral method 1 Potential barrier, overdense 34 43—51 Potential barrier, parabolic 51 59 91 94 99 Potential barrier, underdense 34 51—59 Potential well 102 Probability current 91 Quantization condition 105—109 115—116 Quantization condition, exact 106 108 116 Quantization condition, semi-classical 4 9 108—109 116 117 119 121—125 Reflection coefficient, approximate expressions for 94 101 Reflection coefficient, exact expressions for 93 99—100 Salpeter 132 Schiff 86 Schwarzian derivative 14 Seifert 2 Semi-classical quantization condition see “Quantization condition” Stokes' constants 4 Stokes' line 60 Stokes' phenomenon 5 6 12 23 74 Symmetry relations 5 30—33 Transition point 34 Transmission coefficient, approximate expressions for 90—91 94 101 Transmission coefficient, exact expressions for 93 99—100 Turning point see “Classical turning point” w(z), definition of 13 Wave function, exact expression for 20 Wentzel 1 WKB-method 1 Zwaan 3
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



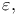 definition of
definition of  -integral, definition of
-integral, definition of