|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Young M. — Optics and Lasers: Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
"Len" 2.2.1 2.2.2 5.5.6
"Len" equation 2.2.2 2.2.4 12.2.1
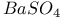 (diffuser) 4.1.5 (diffuser) 4.1.5
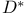 4.3.3 4.3.3
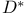 of various detectors (graph) 4.3.3 of various detectors (graph) 4.3.3
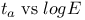 curve 7.1 curve 7.1
70-70 excitation condition 10.3.4 11.1
Abbe theory of microscopy 1 7.2.1 7.4.4
Aberration 1 2.2.2 2.2.12 2.2.13
Aberration, chromatic 2.2.12 7.4.1 7.4.3 12.2.1
Aberration, Problem 2.10 3.5 5.5.6 7.1.2 7.3.7
Aberration, spherical Problem 2.10 2.2.13 3.5
Aberration, wavefront 5.5.6
Aberration-limited lenses 3.8.1
Absorber 8.1.1
Absorptance 4.2.1
Absorption 2.1.2 8 8.2.1
Absorption coefficient 8.1.1
Acceptor level 4.3.1
Accommodation 3.1
Achromatic eyepiece 2.2.4
Acousto-optic beam deflection 9.4.4
Acousto-optic light modulator 9.4.4
Acousto-optics 9.4.4
Active device 12.1
Adaptation 3.1
Aerial image, luminance of 4.1.8
Airy disk 3.8 5.7.1 5.7.3 7.1.1 7.2.5 7.3.1 8.3.3
Aliasing 7.4.4
Aluminum 9.1.7
Aluminum oxide 8.4.1
Amplification of light 8.1 8.1.1
Amplitude 5.1
Amplitude hologram see “Hologram”
Amplitude transmittance see “Transmittance”
Analyzer see “Polarizer”
Angle of incidence 2.1.1 see “Refraction”
Angle of refraction see “Refraction”
Angular frequency 5.1
Angular spectrum 7.3.7
Anisotropic crystal see “Birefringence”
Antihalation dye 3.2.1
Antireflection coating 6.4.1
Aperture stop 3.2 3.7.1 3.7.3
Aperture stop, of camera 3.2
Aperture, filling the 3.3
Aphakia Problem 3.2
Aplanatic system 7.3.1
Apodization 7.3.3
Apodization, Problem 7.8
Arc lamp 4.2.1
Arrayed waveguide grating, Problem 12.7
Astigmatism 2.2.12 3.1
Atmosphere 4.2.1
Attenuation (in optical fibers) 11.1 11.2
Attenuation, measurement of 11.2.1
Avalanche photodiode 4.3.1
Aversion response 8.5
Axial mode see “Mode”
Babinet's principle 5.5.5
Back focal length 2.2.7
Backscatter 11.4
Balance ratio 7.1.3
Band gap 4.2.3 4.3.1
Band, energy 4.2.3 4.2.4 4.3.1 8.2 8.4.3
Bandwidth, electrical, of detector 4.3.3
Bandwidth, electrical, of fiber 10.1 11.1 11.3.2 11.3.4 11.3.5
Bandwidth, electrical, of fiber, measurement of 11.3.4
Bandwidth, electrical, of integrated-optical device 12.1 12.1.6
Barlow lens Problem 2.5
Beam divergence 5.5.4 8.4.8 see “Divergence”
Beam divergence of Gaussian beam 8.3.3
Beam radius 8.3.2
Beam splitter 6.4.1
Beam waist 8.3.3
Beam-optics launch 11.1.1 11.2.1
Bel 11.2.1
Bend in waveguide 10.3.5
Bending loss 10.3.5
benzene 9.4.5
Beryllia, beryllium 8.4.6 8.5
Bessel function 7.3.1 10.2.6
Bifocal 3.1
Binoculars 3.7.1 3.7.3
Birefringence 9.2.1
Birefringence, field-induced 9.4.1
Blackbody 4.2 4.2.1 4.2.2 4.2.3 9.2
Blackbody radiator see “Blackbody”
Blackbody, emissivity of 4.2.1
Blackbody, radiant emittance of 4.2.1 4.2.3
Blackbody, spectra of 4.2.1
Blazing 6.1.1 12.2.4
Bleaching of hologram 7.1.3
Bohr picture of atom 4.2.3
Bolometer 4.3.2
Boltzmann's constant 4.3.3
Borescope 3.7.3
Boresight 3.7.3
Bound ray 10.3.3
Bragg condition 7.1.4 9.4.4 12.1.4 12.1.5
Bragg diffraction 9.4.4
Bragg reflection 7.1.4 12.1 12.1.5 12.2.4
Brewster window 8.4.4 9.1.2
Brewster's angle 1 8.4.1 8.4.4 9.1.2 9.1.3
Brewster's Law 9.1.3
Bright-adapted eye 3.1 4.1.2 8.5
Brightness 1 see also “Luminance”
Brightness temperature 4.2.2
Buckshot 8.1.1
Cadmium sulfide 4.3.1 4.3.3
Calcite 9.2.1 9.2.3
Camera 1 3.2 3.8.1 4.1.7
Camera, lens 2.2.12
Camera, pinhole 5.5.4
Camera, theoretical resolution limit of 3.8.1 see
Candela 4.1.2
Carbon arc 4.2.1
Carbon-dioxide laser see “Laser”
Cardinal point 2.2.7 see also “Principal point” “Focal
Cataract Problem 3.2 8.5
Cavity 8 8.1 8.3.1—4
Cavity lifetime 8.2.3
Cavity, concentric 8.3.4
Cavity, confocal 8.3.2 8.3.4
Cavity, hemispherical 8.3.4 8.4.4
Cavity, plane-parallel 8.3.1 8.3.4
Cement 9.2.3
Center of perspective Problem 3.6
Change of sign 2.2.3
Channel waveguide 1 12.1.1 see
Character recognition 7.2.6
Characteristic curve 3.2.2 see also “D vs 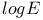 curve” curve”
Charge-Coupled Device 7.4.1 7.4.4 7.4.5 see
Chemical-vapor deposition 12.2.5
chromatic aberration 2.2.12 7.4.1 7.4.3 12.2.1
Chromatic dispersion see “Dispersion”
Chromatic resolving power of diffraction grating 6.1.2
Chromatic resolving power of Fabry — Perot interferometer 6.3.1
Chromium oxide 8.4.1
Circle of confusion 3.2.4
Cladding (of waveguide) 10.1
Cladding mode 11.1.3
Cladding-mode stripper 11.1.3 11.3.4
Classes of lasers 8.5
Close-up photography 3.2.4
Coherence 1 3.8.4 5.3.1 5.6 6.2 7.3.1 7.3.2 8.3.5
Coherence area 5.6.2 5.6.4 8.3.5
Coherence length 5.6.1 6.2 8.3.5
Coherence length, for second-harmonic generation 9.3.1
Coherence length, in optical communications 11.3.5
| Coherence time 5.6.1
Coherence, degree of 6.2
Coherence, of laser sources 8.3.5
Coherence, of microscope illumination 5.6.4
Coherence, of multimode laser 8.3.5
Coherence, of single-mode laser 5.6.3 8.3.5
Coherence, of thermal sources 5.6.3 6.2
Coherence, partial 3.8.4 5.6 7.4.5
Coherence, spatial 5.6.2
Coherence, temporal 5.6.1
Coherent background 7.1
Coherent light 5.6 7.3.1 7.3.3
Coherent light, resolution in 5.7.2 5.7.3
Coherent transfer function 7.3.6 7.3.7
Color slide 3.2.1
color temperature 4.2.2
Color vision 3.1
Coma 2.2.12
Comparator 3.4
Complementary screen 5.5.5
Complete set 10.2 10.4.2
Complex conjugate 5.1.2
Complex-exponential function 5.1.2
Compound microscope see “Microscope”
Computer 7.4.1 9.2.6
Computer processing 7.4.2
Concave 2.2.5
Condenser enlarger 3.3
Condenser, microscope 3.8.4 see
Condensing lens 3.3 5.6.4
Condensing lens and coherence 5.6.4
Condensing lens, numerical aperture of 5.6.4
Conduction electron 4.2.4
cones 3.1
Confocal Fabry — Perot interferometer 6.3.3 see also “Interferometer”
Confocal microscope see “Scanning confocal microscope”
Conjugate points 2.2.2
Conjugates 2.2.2
Connector (optical fiber) 1 10.4
Connector, multimode 10.4.1
Connector, single-mode 10.4.2
Conservation of radiance 4.1.8
Constant deviation Problem 2.1
Constructive interference see “Interference”
Continuum 4.2.3
contrast 3.2.2 7.4.1
Contrast enhancement 7.2.4
Contrast index 3.2.2
Converging-beam optical processor 7.2.7
Convex surface 2.2.5
Convolution 7.2.6 7.3.1 7.3.2 7.4.1 7.4.3 7.4.5
Convolution kernel 7.4.3
Convolution theorem 7.4.3
Core (of waveguide) 10.1
Core diameter, measurement of 11.5.5
Cornea 3.1 8.5
Corner cube see “Cube corner”
Cos2 fringes 5.2 5.3.1 5.6.1 5.6.2 6.2
Cosine-fourth law 4.1.7
Coupler 10.2.2 12.1.5
Coupler, butt 12.1.5
Coupler, directional 6.2.2 12.1.5
Coupler, end 12.1.5
Coupler, grating 10.2.3
Coupler, prism 10.2.2
Coupler, star 10.4.3
Coupler, tapered output 12.1.5 see
Coupling efficiency 10.2.2
Coupling length 10.2.2
Coupling loss 10.4 11.2.1
Cover slip 3.5
Critical angle 2.1.4 9.1.5 10.1
Critical illumination 3.4.8
Cross-correlation 7.2.6 7.4.3 7.4.5
Crystalline lens 3.1
Cube corner 2.1.5
Cutback method 11.2.1
Cutoff (of lens) 7.3.7
Cutoff (of optical waveguide) 10.2.6
Cutoff frequency 4.3.3 7.3.7
D vs 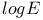 curve 3.3.2 curve 3.3.2
Damage (to eye) 8.5
Dark current 4.3.3
Dark noise 4.3.3
Dark resistance 4.3.1
Dark-adapted eye 3.1 8.5
Dark-field illumination, Problem 7.5
Dark-ground illumination, Problem 7.5
Dc term 7.2.2
Deblurring 7.3.4
Decibel 11.2.1
Dee star see “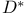 ” ”
Defocusing 3.2.4. 7.3.5
Degree of coherence 6.2 8.3.5
Delta parameter 10.3.1
density see “Optical density”
Depletion layer 4.3.1
Depth of field 3.2.4
Depth of focus 3.2.4
Depth of focus of Gaussian beam Problem 8.3
Depth of focus, Problem 5.12
Destructive interference see “Interference”
Detectivity see “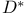 ” ”
Detector 4.3
Detector, 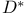 4.3.3 4.3.3
Detector, bolometer 4.3.2
Detector, CCD 7.4.1
Detector, cutoff frequency 4.3.3
Detector, noise equivalent power 4.3.3
Detector, noise in 4.3.3
Detector, photoconductive 4.3.1
Detector, photodiode 4.3.1
Detector, phototube 4.3.1
Detector, photovoltaic 4.3.1
Detector, pyroelectric 4.3.2
Detector, quantum 4.3 4.3.1
Detector, quantum efficiency of 4.3.3
Detector, radiation thermocouple 4.3.2
Detector, radiation thermopile 4.3.2
Detector, response time of 4.3.3
Detector, responsivity of 4.3.3
Detector, room temperature, 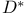 of (graph) 4.3.3 of (graph) 4.3.3
Detector, spectral sensitivity of 4.3.3
Detector, square law 5.1.1
Detector, thermal 4.3 4.3.2
Detector, thermistor 4.3.2
developer 3.2.1 3.2.2
Deviation, constant Problem 2.1
Deviation, Problem 2.1
DFB laser see “Laser distributed-feedback”
Diamond turning 12.2.3
Diaphragm 3.7.3
Dichroic crystal 9.2.4
Differentiated image 7.4.3
Diffraction 1 3.8 4.1.7 5 5.3.1 5.5 5.5.2 5.5.4 7.2.1
Diffraction efficiency see “Hologram”
Diffraction grating 1 5.5.2 5.7.3 6.1 7.1.1 7.1.2
Diffraction grating and Abbe theory 7.2.1
Diffraction grating in holography 7.1.1
Diffraction grating in waveguide 10.2.3 12.2.4
Diffraction grating, blazed 6.1.1
Diffraction grating, chromatic resolving power of 6.1.2
Diffraction grating, concave 6.1
Diffraction grating, holographic 6.1.1
Diffraction grating, phase 7.1.2
Diffraction grating, plane 6.1
Diffraction grating, reflection 6.1
Diffraction grating, sinusoidal 7.1.1
Diffraction lens 12.2.4
Diffraction order see “Order”
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 (diffuser)
(diffuser) 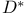
 curve
curve  curve”
curve”