|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Neumann J.V. Ч Theory of Self-Reproducing Automata |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
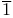 vs. vs. 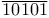 discriminator 187Ч189 209 292 discriminator 187Ч189 209 292
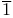 vs. vs. 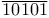 discriminator, behavior described 187 discriminator, behavior described 187
 vs. vs.  discriminator, construction of 188Ч189 discriminator, construction of 188Ч189
 vs. vs.  discriminator, dimensions of 188Ч189 discriminator, dimensions of 188Ч189
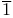 vs. vs. 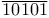 discriminator, function of 187 discriminator, function of 187
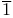 vs. vs. 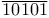 discriminator, timing considerations for 188Ч189 discriminator, timing considerations for 188Ч189
29-state finite automaton cell 94 106Ч108
Acoustic delay line see УStorage devicesФ
Analog computers 21 22 36Ч38 68Ч70 98
Area 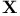 227 252Ч253 293 227 252Ч253 293
Area 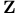 227 253 293 227 253 293
Area 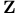 , construction of 256Ч257 , construction of 256Ч257
Automata see УComputersФ УFinite УInfinite
Automata theory 10 17Ч28
Automata theory, biology and 21
Automata theory, communication and control engineering and 21
Automata theory, continuous mathematics and 25Ч27 97
Automata theory, mathematical logic and 10 19 25 43Ч45 47Ч48 49Ч56
Automata theory, thermodynamics and 28
Automata, artificial 21Ч25 (see also УComputersФ)
Automata, complex 20 32 79
Automata, complexity of 30Ч37
Automata, complicated 20
Automata, constructed see УSecondary (constructed) automatonФ
Automata, constructing see УPrimary (constructing) automatonФ
Automata, construction aspects of 92 et passim
Automata, efficiency of 37Ч39 91Ч92
Automata, formalistic study of 91 102
Automata, human nervous system and 9Ч10 43Ч49
Automata, logical aspects of 92 et passim
Automata, natural 21Ч25 64
Automata, non-constructible 291
Automata, probabilistic 99
Automata, self-reproducing 19 21 294Ч296
Automata, single-cell 111
Automatic programming 5 14Ч15
Automaton milieu 72Ч73
Axiomatic method 43Ч44 76
balance 28 40Ч41 63
base two 114
behavior 270
Bigelow, J. 12 105
Birkhoff, G. 2 34 59
Bitwise implication 175
Black Box 45
Boltzmann, L. 26 59 60Ч61
BoltzmannТs constant 66
Boolean algebra 100
Booth, A.D. 16
Brainerd, J.G. 6
Brillouin, L. 68
Burks, A.W. 6 12 37 43 126 262 270 271 291
Calculation chain 24
Cellular automata see УCellular structureФ УInfinite
Cellular model, description of 106Ч106
Cellular structure 94 103Ч106 288
Cellular structure, construction-universality of 92 116
Cellular structure, logical universality of 265Ч271
Cellular structure, tape unit in 26 293
Cellular structure, tape-reading method in 283
Cellular structure, von NeumannТs 29-state 291Ч292
Church, A. 261Ч262
Codd, E.F. 280
Coded channel 180 190Ч200 227 228 239Ч243 252 293
Coded channel, behavior described 190Ч191 227
Coded channel, capacity of in  239Ч241 239Ч241
Coded channel, construction of 192Ч194
Coded channel, corruption problems in 191 196Ч198
Coded channel, cyclicity in 198Ч200
Coded channel, dimensions of 195 242Ч243
Coded channel, function of 190 191Ч192
Coded channel, main channel of 193
Coded channel, rule for avoiding corruption in 198
Coded channel, timing considerations for 195Ч196
Coincidence organ 81
Collision in single reproduction, avoidance of 120Ч121
Combinatorics 62
Communication channel 60
complexity 22 23 54 58 65Ч73 79Ч80 118
Complexity, reliability and 23
Complication 47Ч48 54Ч73 78Ч80
Complication, complexity and 79Ч80
Complication, degeneration and 79Ч80
Component size 20
Computation 24 270
Computation, quantity of 26
Computation, size and reliability related 26
Computation, speed of 37Ч41
Computer components and efficiency 22 66Ч67 72Ч73
Computers 32 35Ч41 75 УAutomataФ УDigital
Computers, applications of iu science 33Ч34
Computers, circuits of 15Ч17
Computers, efficiency of 28
Computers, heuristic use of 3Ч5 33Ч35
Computers, human nervous system and 9Ч10 43Ч49
Computers, mixed synchronous, asynchronous 8
Confluent states  107 136Ч139 147 107 136Ч139 147
Confluent states  and the and the  neuron 130Ч137 138 neuron 130Ч137 138
Confluent states  and the + neuron 136 and the + neuron 136
Connecting loop  115 180 208 210Ч213 228 238 246 293 115 180 208 210Ч213 228 238 246 293
Connecting loop  , lengthening of 216 218Ч220 , lengthening of 216 218Ч220
Connecting loop  , preliminary description of behavior of 210Ч213 , preliminary description of behavior of 210Ч213
Connecting loop  , shortening of 222Ч224 , shortening of 222Ч224
Connecting organ 80
Constructibility 92 156 292
Constructing arm 271Ч270
Constructing arm, design of 272Ч276
Constructing arm, double path procedure 273Ч277
Constructing arm, head of 274
Constructing arm, operation of 274Ч276
Constructing arm, single path procedure 272Ч273 277
Constructing unit  205Ч208 238 293 205Ч208 238 293
Constructing unit  , design of 279Ч280 295 , design of 279Ч280 295
Constructing unit  , function of 201Ч202 , function of 201Ч202
Constructing unit  , input-output connections 232Ч233 , input-output connections 232Ч233
Constructing unit 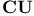 , interconnections with , interconnections with  205Ч206 228Ч229 232Ч233 205Ч206 228Ч229 232Ч233
Constructing unit 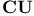 , postulates for 207 , postulates for 207
Constructing unit 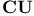 , schematic description of 206Ч207 , schematic description of 206Ч207
Constructing unit 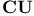 , viewed as special type of finite automaton 286 , viewed as special type of finite automaton 286
Construction 101Ч132 288
Construction universality 92 110
Construction universality of cellular structure 286 202
Construction, geometry and kinematics of 101Ч102
Constructive method 91Ч92
Control organ 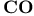 227Ч228 229 230 245 227Ч228 229 230 245
Control organ 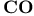 , delay adjustments in 244Ч245 , delay adjustments in 244Ч245
Control organ 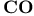 , operation of 230 , operation of 230
Conversion of freely timed sequences to rigidly timed ones see УStatic-dynamic converterФ
Crossing lines and paths see УWire-crossingФ
Crossing organ 262Ч253
Crossing organ, dock sequences in 202
Crossing organ, used to solve interference problem for  263Ч204 263Ч204
Crystal 108
Crystal lattice 104
Crystalline regularity 93 94
Crystalline structure 132
Crystalline symmetry 103Ч104
Cutting organ 81
Decision machine 52
Decoding organ 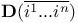 175Ч179 175Ч179
Decoding organ 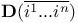 , behavior described 175 , behavior described 175
Decoding organ 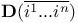 , characteristic of 176 , characteristic of 176
Decoding organ 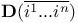 , construction of 175Ч179 , construction of 175Ч179
Decoding organ 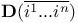 , dimensions of 176Ч177 178 , dimensions of 176Ч177 178
Decoding organ 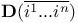 , order of 176 , order of 176
Decoding organ 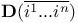 , timing considerations for 176 177 178Ч179. , timing considerations for 176 177 178Ч179.
Degenerative processes 62
Delay area 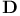 246 246
Delay area  , dimensions of 260 , dimensions of 260
Delay area  227 241Ч242 243 227 241Ч242 243
| Delay area  , construction of 256Ч257 , construction of 256Ч257
Delay area  , delay considerations and 257Ч258 293 , delay considerations and 257Ч258 293
Delay line see УStorage devicesФ
Delay paths 146
Delay paths, odd 146Ч147
Delays, single 147
Delays, single, through confluent states 147
Descriptive statement  for numerical parameters 112Ч113 for numerical parameters 112Ч113
Differential equations of self-reproduction 97 106
Diffusion processes 97Ч98
Digital computers 21 22 35 36 69Ч70 98
Digital organ 69Ч70
Digitization 61Ч62
Dimensionality 104Ч105
Direct process 107 111 142Ч145 272
Direct process, need for control by fixed stimulus sequences 143Ч145
Directed process 135
Distal notation 48
Double line trick 138
Eccles, J.C. 97
Eckert, J.P. 6 8
EDSAC 9
EDVAC 9Ч11 19 i58 261
Efficiency 28 40 48 67 93
Elementary parts 77
Energy and information 66Ч67
ENIAC 6Ч10 19 37 48 65
entropy 59Ч63 67
Entscheidungsproblem 49 204
Error detection and correction 24Ч25 73
Error-detecting and -correcting codes 61
Estrin, G. 12
Evolution 79 92Ч93 99 131
Excitation 44 97Ч98
Failure 58 70Ч73
Fatigue 44 96 97Ч98
Finite automata 108 114Ч115 267 286
Finite automata, embedded in cellular structure 267Ч268 293
Flip-flop 174
Flow diagram 13Ч14 84
Free timing 157
Fusing organ 81
Gene-function 130
Goedel number 55
Goedel, K. 25 53 55Ч56 125 126
GoedelТs theorems 47 51 53Ч56
GoedelТs undecidable formula and self-reproducing automata 126
Goldstine, H.H. 4 6 12 37 95 105 279
Gorman, J.E. 262
Goto, K. 16 17
Growth 109 110
Growth functions 139Ч142
Halting problem 52Ч53 124Ч126
Halting problem, undecidability of and RichardТs paradox 125Ч126
Hamming, R.W. 61
Hartley, R.V.L. 59 61
Heuristic use of computers 3Ч5 33 35
Hixon Symposium 53 81
Holland, J.H. 99 262 270
Homogeneity 72 103Ч106
Homogeneity, functional or intrinsic 103Ч104 106 288
Homogeneity, total 104
Homogeneous medium 103
Hydrodynamics 2Ч3 34
Hydrodynamics, computers and 3
Idealized computing elements and computer design 9Ч10
Idealized excitation-threshold-fatigue neuron 96
Idealized neurons 44 ff. 287
Idealized switch-delay elements 25
Infinite cellular automata 108 et passim
Infinite cellular automata, spatial and temporal relations 132Ч134 152
information 18 20 67 60Ч03 66 67 78
Information theory 19 27 42 60Ч68
Inhibitory organ 81
Initial cell assignment 108 152 291
Initially quiescent automata 264 291
Input direction 135
Isotrophy 106 100 288
JONIAC 12
Kemeny, J. 96Ч96
Keynes, J.M. 59
Kinematics 101
Kleene, S.C. 43 101 123 125
Language, complete epistemological description of 55
Laplace, P.S. 58
Lee, C.Y. 290
Linear array  112Ч116 202Ч204 259 293 112Ч116 202Ч204 259 293
Linear array  , altering , altering 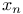 in 210Ч212 224Ч226 in 210Ч212 224Ч226
Linear array  , described 203 , described 203
Linear array  , function of 203 , function of 203
Linear array  , function of , function of 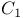 and and 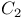 in lengthening and shortening on 214Ч216 in lengthening and shortening on 214Ч216
Linear array  , lengthening on 216Ч220 , lengthening on 216Ч220
Linear array  , moving its connection with MC 214Ч226 , moving its connection with MC 214Ч226
Linear array  , operations on summarized 209Ч210 , operations on summarized 209Ч210
Linear array  , read-write sequence of operations on 209Ч210 , read-write sequence of operations on 209Ч210
Linear array 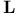 , shortening on 220Ч224 , shortening on 220Ч224
Linear array 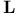 , use of for non-numerical (universal) parametrization 110 , use of for non-numerical (universal) parametrization 110
Logic, formal 42Ч43
Logical depth 24
logical operators 42 99Ч101 111
logical organization 20 22 23Ч24
Logical universality 92 265Ч271 287 292
Machine language 14Ч15
Machine-man interaction 5
Main channel of coded channel 193
Maser 10
Mathematical logic 10 19 25 43Ч45 47Ч66
Mauchly, J. 6
MaxwellТs Demon 60 61
McCulloch Ч Pitta neuron nets 43Ч49 75 80
McCulloch, W. 9 43 77 100 101
McNaughton, R. 270
Memory 39Ч41 67Ч68 101 203
Memory control unit  115 201Ч202 205Ч206 226Ч250 261Ч262 293 et 115 201Ч202 205Ч206 226Ч250 261Ч262 293 et
Memory control unit  , , 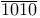 as no-response characteristic 209 as no-response characteristic 209
Memory control unit  , constructing devices in 264Ч265 , constructing devices in 264Ч265
Memory control unit  , control organ , control organ 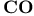 in 243Ч246 in 243Ч246
Memory control unit  , corruption considerations 253Ч255 , corruption considerations 253Ч255
Memory control unit  , delays in control processes in 254Ч259 , delays in control processes in 254Ч259
Memory control unit  , design modifications of 267 264Ч265 , design modifications of 267 264Ч265
Memory control unit  , dimensions of 244 , dimensions of 244
Memory control unit  , dimensions of areas , dimensions of areas 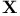 , , 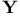 , , 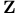 , , 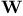 263 263
Memory control unit  , function of 205Ч206 231Ч238 , function of 205Ч206 231Ч238
Memory control unit  , interconnections with CU 205Ч206 228Ч229 282Ч233 , interconnections with CU 205Ч206 228Ч229 282Ч233
Memory control unit  , modus operandi on , modus operandi on  207Ч210 207Ч210
Memory control unit  , operation of 228Ч229 , operation of 228Ч229
Memory control unit  , organization of 226Ч228 , organization of 226Ч228
Memory control unit  , postulates for 207 , postulates for 207
Memory control unit  , redesign using double path procedure for reading , redesign using double path procedure for reading  277Ч279 277Ч279
Memory control unit  , solution of interference problem in 269Ч264 , solution of interference problem in 269Ч264
Memory, access to 40Ч41
Memory, capacity of 40Ч41 68
Memory, hierarchical 23Ч24 41
Memory, human 39 48Ч49
Memory, unlimited 113Ч114
Memory, virtual 68
Mixed analog-digital systems 22 27
Monte Carlo method 6
Moore, E.F. 94 291
Morgenstern, O. 2 59
Morphogenesis 99
Moter organ 80
Muntyan, M. 279
Muscle organ 77 80 31Ч82
Mutation 87 130
Myhill, J. 291
Natural selection 131
Negation, synthesis of 138
Neighbors, immediate 133
Nervous system 9Ч10 39 42Ч48 64
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 vs.
vs.  discriminator
discriminator 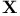
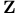


 neuron
neuron 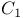
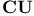
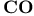
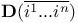
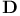
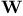
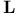 for numerical parameters
for numerical parameters 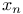 in
in 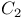 in lengthening and shortening on
in lengthening and shortening on 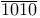 as no-response characteristic
as no-response characteristic 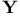 ,
,