|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Neumann J.V. Ч Theory of Self-Reproducing Automata |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Nervous system, complexity of 37
Nervous system, languages of 15
Nervous system, probabilistic logics and 15
Neuron fatigue 48Ч49
Neuron response 100
Neuron stimulus 100
Neurons 77 99Ч101
Neurons, excited 44
Neurons, quiescent 44
Non-Euclidean spaces 103
Non-linear partial differential equations 2 19 33Ч34 97
Non-linear partial differential equations of self-reproduction 97 106
Nyquist, H. 61
Optimally and minimality 91Ч92
Ordinary stimulus 110Ч111
Ordinary transmission states  107 134Ч136 107 134Ч136
Ordinary transmission states  as connecting lines 135Ч130 as connecting lines 135Ч130
Ordinary transmission states  , logical-neural functions and 134 , logical-neural functions and 134
Output direction 135
Parallel processing 7 22 23 157Ч158 261
Parametron 16
Periodic pulser  162Ч170 238 292 162Ч170 238 292
Periodic pulser  , alternate periodic pulser , alternate periodic pulser  174 174
Periodic pulser  , characteristic of 163 , characteristic of 163
Periodic pulser  , construction of 163Ч175 , construction of 163Ч175
Periodic pulser  , corruption of by interference 169Ч170 , corruption of by interference 169Ч170
Periodic pulser  , dimensions of 168Ч164 170Ч171 , dimensions of 168Ч164 170Ч171
Periodic pulser  , external characteristics summarized 174Ч175 , external characteristics summarized 174Ч175
Periodic pulser  , operation illustrated 162Ч163 , operation illustrated 162Ч163
Periodic pulser  , order of 168 , order of 168
Periodic pulser  , phasing for 173Ч174 , phasing for 173Ч174
Periodic pulser  , rules for avoiding corruption (final version) 172 , rules for avoiding corruption (final version) 172
Periodic pulser  , rules for avoiding corruption (initial version) 169Ч170 , rules for avoiding corruption (initial version) 169Ч170
Periodic pulser  , special periodic palser , special periodic palser  , shown defective and altered 174 , shown defective and altered 174
Periodic pulser  , special periodic pulser , special periodic pulser  163 167 227 163 167 227
Periodic pulser  , start mechanism of 164 , start mechanism of 164
Periodic pulser  , stop mechanism of 165Ч166 , stop mechanism of 165Ч166
Periodic pulser  , timing considerations corrected 172Ч173 , timing considerations corrected 172Ч173
Periodic pulser  , timing considerations for 168Ч169 170Ч171 , timing considerations for 168Ч169 170Ч171
Periodic repetition 158
Pitts, W. 9 43 77 100 101
Prepositional functions 100Ч101
Primary (constructing) automaton 82 111 116 271 288 289
Probabilistic logics 20 26 58Ч63 99
Probability theory 99
ProgrammerТs language 14Ч15
Programming 12Ч15
Pulser  150Ч162 292 150Ч162 292
Pulser  , behavior described 159 , behavior described 159
Pulser  , characteristic of 159 , characteristic of 159
Pulser  , construction of 159Ч161 , construction of 159Ч161
Pulser  , dimensions of 159Ч161 , dimensions of 159Ч161
Pulser  , external characteristics summarised 162 , external characteristics summarised 162
Pulser  , order of 159 , order of 159
Pulser  , timing for 160Ч161 , timing for 160Ч161
Quadratic lattice 132
quantum mechanics 59 62
Quiescence, total 104
Quiescent states 99 103 106Ч107
Rajchman, J.A. 12
Read-write mechanisms 114Ч116
Read-write-erase control unit  226 227 246Ч250 251 259 293 226 227 246Ч250 251 259 293
Read-write-erase control unit  , control organs , control organs  of 229Ч230 of 229Ч230
Read-write-erase control unit  , dimensions of 242Ч243 , dimensions of 242Ч243
Read-write-erase control unit  , function of 246Ч247 , function of 246Ч247
Read-write-erase unit  226Ч227 230Ч281 237Ч243 261 269 293 226Ч227 230Ч281 237Ч243 261 269 293
Read-write-erase unit  , construction of 287Ч243 , construction of 287Ч243
Read-write-erase unit  , dimensions of 241 , dimensions of 241
Recognizer  ) 189Ч190 ) 189Ч190
Recognizing device 175 (see also УRecognizerФ)
recursive functions 26
Redundancy 60
Refractoriness 90 (see also УFatigueФ)
Refractory period 48 96
Regularity 105
Reliability 22 23 24Ч25 67 70Ч73
Reliable systems and unreliable components 19 70Ч71
Responding organ  181 215 181 215
Reverse process 107 111 140Ч342 272
Reverse process, need for 143
Richard paradox 123Ч124
Richard paradox and self-reproduction 122Ч123
Richard, J. 123
Rigid binary tape 83
Rigid member 8i
Rigid timing 157
Russell, B. 125
Scientific method 3
Secondary (constructed) automaton 111 271 288
Secondary (constructed) automaton, algorithm for constructing and starting 276
Secondary (constructed) automaton, algorithm for constructing and starting revised 283Ч285
Secondary (constructed) automaton, complete description of initial conditions for 117
Secondary (constructed) automaton, construction of 272 280Ч285 290Ч291
Secondary (constructed) automaton, dimensions of 116Ч117
Secondary (constructed) automaton, initial state of 117 127Ч128
Secondary (constructed) automaton, parametric form plan of 112Ч113
Secondary (constructed) automaton, plan of 111Ч112
Secondary (constructed) automaton, positioning of 120Ч127 129
Secondary (constructed) automaton, starting stimulus for 12S
Secondary (constructed) automaton, universal type of plan of 116Ч118
Self-reference and self-reproduction 125Ч126
Self-reproducing cellular automaton 294Ч296
Self-reproduction 19Ч21 78Ч86 92 95 106 289Ч291 292
Self-reproduction in a cellular structure 291Ч296
Self-reproduction, a priori argument against 79 118 121
Self-reproduction, cellular model of 93Ч95
Self-reproduction, circumvention of a priori argument against 118Ч119
Self-reproduction, conflicts and collisions of progeny 130
Self-reproduction, continuous model of 93 95 97Ч99 105Ч106 2S8
Self-reproduction, differential equations of 97 106
Self-reproduction, excitation-threshold-fatigue model of 93 95 96
Self-reproduction, kinematic model of 80Ч87 93Ч94 287Ч288
Self-reproduction, physiological aspects of for automats 129Ч131
Self-reproduction, probabilistic model of 93
Self-reproduction, sequential 128Ч129
Self-reproduction, single-action 128Ч129
sequencing 111Ч112
| Serial processing 22 23
Shannon, C.E. 27 59Ч61
Sharpless, T.K. 6
Simulation 14Ч15
SIZE 64Ч65
Special stimuli 110Ч111 288
Special stimuli, origination of 141Ч142
Special transmission states  107 107
Speed 65Ч66
Split 139
SSEC 66
State organ  267Ч269 267Ч269
State transition rule, derived for confluent states 136Ч138
State transition rule, derived for ordinary transmission states 136Ч138
State transition rule, derived for sensitized states 144Ч146
State transition rule, derived for special transmission states 140
State transition rule, illustrated 151Ч156
State transition rule, modifications required by reverse process 140Ч141
State transition rule, modified for confluent states 147Ч148
State transition rule, rigorous description of 148Ч150
State transition rule, verbal summary 150Ч161
States see УConfluent statesФ УOrdinary УSpecial УUnexcitabic
States of cell alar automaton, verbal summary 150Ч151
States, active 103
States, duality of ordinary and special 143Ч143
States, excitable 107 109 288
States, excited 99
States, INITIAL 108 264
States, sensitized 107 145
Static-dynamic converter 281Ч283
Stationarity 103
Step in phase k in period s 158
Step m period s 158
Stimalus organ 81
Stimuli producer 81
Stop at step l 158
storage devices 7 10 41
Storage devices, acoustic delay line 8 67Ч53
Storage devices, cathode ray tube 68
Storage devices, electrostatic 11Ч12
Storage devices, film 75
Storage devices, magnetic tape 75
Storage devices, punched cards 75
Storage devices, punched tape 74
Storage devices, vacuum tubes 7Ч8 67
Strict logics 59
Structure 104Ч106
Subharmonic generator 16Ч17
Survival 72 73
Synthesis 75Ч86
Szilard, L. 59 50 61
Tape and tape control components 201
Tape, indefinitely extendible 92 202Ч203 289
Tape-copying operation 295
Tarski, A. 55
Taub, A. 1
Temporal reference frame 108
Tessellation model see УCellular structureФ
Thatoher, J. 279 280 290 291
Theory of games 21
Thermodynamic-based logics 62Ч63
Thermodynamics 19 26 28 59Ч63 66 91
Threshold 97Ч98
Threshold neurons 96
Threshold switches 9
Timing loop  115 180 213Ч214 228 238 246 293 115 180 213Ч214 228 238 246 293
Timing loop  , function of 213 215 , function of 213 215
Timing loop  , lengthening of 216Ч218 , lengthening of 216Ч218
Timing loop  , shortening of 221Ч222 , shortening of 221Ч222
Timing loop  , timing considerations for 213Ч214 , timing considerations for 213Ч214
Tissues 77
Total numerical material produced in a process 39
Transfer area  227 252Ч253 293 227 252Ч253 293
Transition rule 132 134
Transmission states  135 (see also УOrdinary transmission statesФ УSpecial 135 (see also УOrdinary transmission statesФ УSpecial
Triple-return counter  170Ч187 215 227 238 292 170Ч187 215 227 238 292
Triple-return counter  , behavior described 180 , behavior described 180
Triple-return counter  , coding and decoding considerations for 184Ч185 , coding and decoding considerations for 184Ч185
Triple-return counter  , construction of 181Ч185 , construction of 181Ч185
Triple-return counter  , corruption considerations for 186 , corruption considerations for 186
Triple-return counter  , dimensions of 179 185Ч186 , dimensions of 179 185Ч186
Triple-return counter  , function of 180 , function of 180
Triple-return counter  , function of in , function of in  234 234
Triple-return counter  , primary and secondary input-output pairs in 131 , primary and secondary input-output pairs in 131
Triple-return counter  , timing considerations for 181 185Ч187 , timing considerations for 181 185Ч187
Turing machine 25 45 49Ч53 54 74Ч75 107 114Ч115 289 293
Turing machine, abstract 52
Turing machine, automatic programming and 14Ч15
Turing machine, circle-free 62 124
Turing machine, circular 52 124
Turing machine, concrete 51Ч52 124
Turing, A. 14 25 43 49 52 83 92 99 122 204
Type theory 51 63Ч65 125
Ulam, S.M. 1 2 3 5 6 28 94 95 102
Unexcitable state  107 109 139Ч140 288 107 109 139Ч140 288
Universal computing machine 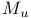 270Ч271 285Ч286 294 270Ч271 285Ч286 294
Universal construction, affected by interference problem for  260Ч261 260Ч261
Universal constructor  271Ч286 289Ч291 294 УConstructing 271Ч286 289Ч291 294 УConstructing
Universal constructor  , general construction procedure 272 , general construction procedure 272
Universal constructor  , modified to , modified to  295 295
Universal Turing machine 50Ч51 52 56 83 288
Universal Turing machine, designed in cellular structure 266Ч270
Universal Turing machine, operation of in cellular space 268Ч269
Vanuxem Lectures 95Ч96
Visual pattern 46Ч47 53Ч54
Volume 66
von Neumann, Mrs. K. 1 94
von NeumannТs five main questions 92 292
Wang, H. 291
Wiener, N. 22 27 00 01
Wigington, R.L. 16
Wilkes, M.V. 9
Williams, F.C. 12
Wire-crossing 180 183 190 191Ч192 261Ч264
Wright, J. 43
УCopyingФ, use of descriptions vs. originals in self-reproduction 84 121Ч122
УGarden-of-EdenФ configuration 291
УStructure of the vacuumФ 102Ч106 109
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте








 of
of 
 )
)