Internal beats 21 (Fig.) 90 91
Inverse Lamb dip 171
Inversion density, effective 110
Ion lasers, noble gas 158
Ion temperatures 160
Ion temperatures in argon ion laser 161 (Fig.)
Ion-ion scattering, small angle 161
Ions, accelerating 158
Isotope effect 130
Isotope effect, oscillator frequency 132
Isotope effect, power tuning 132
Isotope effect, single-mode 129
Jacobs 35
Jaseja 130 (Table)
Javan 21 104n 109 117 130 154 162 174 175 191 196
Javan, Bennett and Herriott 46
Johnson 36
Karlov 46
Kazantsev 175 184 185 186
Keller 181
Kindlmann 149 (Fig.) 150
Kisliuk 36
Kleinman 36
Kleppner 67n
Knutson 109 155 156 157 187 189 191 205
Kogelnick 21 27n 30 31 35 88
Kolomnikov 36
Kramers 94n
Kramers — Kronig relations 83 94 98 104
Kronig 94n
Kurnit 67
Lamb 69 89 104n 106 117 118 120 121 143 145 151 158 175
Lamb dip 38 63 106 127 178
Lamb dip, inverse 171
Lamb dip, simple derivation of 117
Lamb theory 63 143 144 145
Laser see also "Helium-neon laser"
Laser pulses, mode-locked 149
Laser,  46 46
Laser, argon ion 37
Laser, frequency equation 93
Laser, helium 33 46 88 90
Laser, homogeneously broadened 99 100 101
Laser, inhomogeneously broadened 105
Laser, magnetostrictively tuned 90
Laser, oscilation frequency for 100
Laser, theoretical width of oscillation 89
Lasers, internally scanned 45
LaTourette 35 36 181
Lee 171 174 175 176
Letokhov 173 181 184
Levenson 181 203
Li 9 10 12 13 21 30 31 32
Lifetimes, excited state 5 149
Lifetimes, measurement of radiative 149
Lindholm 154
Line asymmetries 153
Line broadening 150
Line broadening in the argon ion laser 160
Line narrowing 89 152
Line shape for a radiating accelerating ion 159 (Fig.)
Line symmetry 157
Lisitzin 155 173 174 175 176 183 184 186 196
Locking effect 144
Longitudinal mode, isolation of 34
Lorentz broadening parameters for neon laser lines 157 (Fig.)
Lorentz width 8 155
Lorentz width, absorber 172
Lorentz width, absorption in methane 178
Lorentz width, intensity dependent 107
Lorentz width, power-broadened 147
Lorentz width, zero-field 150
Lorentzian limit 104
Lorentzian line, phase shift for 98
Lorentzian line, shape 73
Lorentzian natural width 73
Lorentzian profiles 81 (Fig.)
Lorentzian shaped holes 106 107
Magnetostrictively tuned laser 90
Maxwellian velocity distribution 80
McCall 67
McFarlane 117 118
Mercer 150 158 160
Methane, absorption 177
Methane, lines 173 177
Mikhnenko 155
Mirror locations 35
Mirrors, infinite strip 47
Mirrors, infinite strip plane parallel 14
Mirrors, plane circular 19
Mirrors, plane parallel 14 23
Mirrors, square aperture plane parallel 53
Mitchell 79 81
Mixed state 66
Mixed state, wave function 66
Mode appearance order 141
Mode competition 145
Mode coupling 53
Mode density 7 34
Mode discrimination 8 35
Mode distribution, oscillating 89 (Fig.)
Mode isolation 6 8
Mode isolation through saturable absorption 174 (Fig.)
Mode isolation, longitudinal 34
Mode locking effects 46
Mode locking, transverse 45
Mode mixing, cavity effects 45
Mode pulling effects 62 91
Mode pushing 91
Mode selection 34
Mode spacing 7
Mode suppression 170
Mode suppression with saturable absorbers 171
Mode suppression, technique 36 (Fig.)
Mode symmetry, effects in scanning lasers 52 53
Mode-locked laser pulses 149
Modes for continuous apertures 38
Modes, "walk-off" 9
Modes, diffraction loss for plane parallel and confocal 19 (Fig.) 23
Modes, dominant 19 (Fig.)
Modes, dominant confocal 23 26
Modes, dominant even symmetry 43 (Fig.)
Modes, even symmetric 19
Modes, higher-order 15 16
Modes, infinite strip 18
Modes, loss contours for curved mirror infinite strip 31 (Fig.)
Modes, non-symmetric 43 (Fig.) 43
Modes, odd-symmetric 19 43
Modes, self-reproducing 13 41 42
Molecular absorption bands 172
Morse 25
Multi-mode laser 84
Myers 28 29 47
N-modes with same polarization 140
N-modes, algorithm 141
N-modes, gain saturation equations for 140
N-modes, matrix equations for 140 141
N-modes, method of machine solution for 141
N-modes, ordering 141
N-modes, oscillation frequencies for 140
N-modes, phase shift coefficients for 141
Natural width 5 7
Negative feedback stabilization 163
Neon laser lines, parameters for 157 (Fig.)
Neon, hole burning at 6328 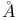 in 189 (Fig.) in 189 (Fig.)
Neon-helium broadening 157
Neon-neon broadening 157
Net probability, of absorption (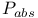 ) 70 73 ) 70 73
Net probability, of stimulated emission (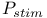 ) 71 72 ) 71 72
Noble gas ion lasers 158
| Normalization integral, spectral response of 79
Optical pumping, gain dithering by 166
Optimum coupling 33
Orthogonality, non-Hermitian 14
Oscillation frequencies for N-modes 140
Oscillation frequency near line center 120
Oscillation frequency, threshold 104
Oscillator dispersion characteristics 163 (Fig.)
Oscillator frequency with saturable absorber 170
Oscillator frequency, isotope effect 132
Output coupling 33
Output coupling, power 33
Packard 60
Perturbation expansion, method in cavity mode problem 49
Phase dispersion function 145
Phase interruption rates 75
Phase shift coefficient for N modes 141
Phase shift coefficient for pure Gaussian 103
Phase shifts 170
Phase shifts for Doppler broadened limit 103
Phase shifts for gain and absorber 168
Phase shifts for Lorentzian line 98
Phase shifts, cavity 19 (Fig.) 22 28 93
Phase shifts, due to a hole 119
Phase shifts, single-pass 93
Phase-changing collisions 152
Pole 28 29 47
Pollack 22 144 145 146 154
Population densities, effective zero-field 75
Population inversion distribution, hole in 107
Positronium 69n
Positronium, resonance experiments 68
Power broadening 74 146
Power broadening, approximate semi-empirical form for 146
Power dependent beat splitting 90 (Fig.)
Power tuning characteristic 127
Power tuning curve, in the single mode for the two-isotope case 133 (Fig.)
Power tuning curve, isotope effect 132
Power tuning curve, with a saturable absorber 172 (Fig.)
Power-broadened Lorentz width 147
Pressure shifts 154
Probability, flow of 69
Probability, interpretation 64
Projections, spatial Fourier 145
Prokhorov 8 46
Pulsation effects 144
Pulsation terms 144
Q approximation, of cavity 85
Rabinowitz 35 181
Radiating accelerating ion, line shape for 159 (Fig.)
Radiative lifetimes, measurement of 149
Ramsey 67 67n
Ramsey, double field technique of 67n
Rautian 121 123 158 175 196
Rectangular aperture 11 12
Rectangular reflection aperture 39
Refractive index of amplifying transition 92 (Fig.)
Relative excitation 144
Relative phase shift 27 28
Resonance frequencies, Doppler shifted 82
Resonance technique, double field 67
Resonance, absorption 177
Resonance, cavity 139 (Fig.)
Resonance, standing wave 8
Resonance, with phase interruption 68
Resonant interactions 153
Resonator, generating confocal 35
Resonator, split confocal equivalent 29
Rigrod 33 34 35 36
Running waves, gain coefficient for 74
Running waves, hole burning by 178
Sanders 69
Saturable absorber, frequency of oscillator with 170
Saturable absorber, gain curves in 186 (Fig.)
Saturable absorber, gain with 175 (Fig.)
Saturable absorber, hole depths in single-mode with 169
Saturable absorber, mode suppression with 171
Saturable absorber, power tuning curve with 172 (Fig.)
Saturable absorber, self-stabilization by 181
Saturable absorber, threshold hysteresis effects with 184—186
Saturable absorption, mode isolation through 174 (Fig.)
Saturated absorption 178
Saturated gain 178
Scanning cavities, existence of self-reproducing modes in 48
Scanning cavities, problem of 48
Scanning Fabry — Perot analysis 155 (Fig.)
Scanning lasers 29 48
Scanning lasers, computed beam profiles 54
Scanning lasers, computed relative intensity profile in 55
Scanning lasers, computer solutions for 56
Scanning lasers, mode symmetry effects in 52 53
Scanning, confocal problem 55
Scanning, confocal problem, periodic binary type 47 (Fig.)
Scanning, continuous 52
Scanning, continuous, periodic transverse 46
Schawlow 8 9 181
Schoefer 174
Schrodinger equations 64 65
Schrodinger equations for two-frequency case 122
Schwarz 155 191
Schweitzer 109 191
Scully 89
Sealer 150
Self-stabilization effect 182
Self-stabilization effect, by saturable absorbers 181 183
Servo-loop stabilization 176
Shahin 181
Shank 155 191
Shimizu 181
Shimoda 146 162
Single-mode, equations 125
Single-mode, gain saturation in 168
Single-mode, gas laser 131 (Fig.)
Single-mode, hole burning model in 131 (Fig.)
Single-mode, hole depths in 169
Single-mode, hysteresis effect 128 (Fig.)
Single-mode, isotope effect in 129
Single-mode, power tuning curves in 133 (Fig.)
Single-mode, saturable absorber 166—171
Single-mode, tuning curves 37 (Fig.)
Single-mode, tuning dip 118 (Fig.)
Skolnick 171 176
Slepian 22
Small angle ion ion scattering 161
Small signal gain 170
smith 36 46 154 155 156
Sobel'man 121 123 158
SOCHOR 37
Soncini 46
Spatial Fourier projections 145
Spatial switching, binary 46
Spectral purity 89
Spectral response, normalization integral 79
Split confocal equivalent resonator 29
Spontaneous emission bumps, assymmetry in 195 (Fig.)
Spontaneous emission profiles, analysis of 155 (Fig.)
Spot width 26
Square aperture 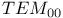 mode 19 mode 19
Stabilization by gain modulation 163 164 165
Stabilization, negative feedback 163
Stabilization, reciprocal mutual 177 (Fig.)
Standing wave effects 105
Standing wave resonance condition 8
Strong wave weak wave tuning dips 178—181
Surdutovich 175
Surface of constant phase 26 27 28
Surface of constant phase, condition for 27
Surface of constant phase, radius of curvature 27
Svelto 46
Swept transverse aperture 47
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



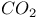
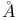 in
in 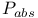 )
) 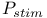 )
) 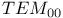 mode
mode