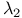"Bump" heights 107 109
"Bump" heights, asymmetry in 192
"Bumps", induced 191
"Bumps", induced, confocal 21
"Bumps", spontaneous emission 195 (Fig.)
"Cross relaxation" 155
"Ear" heights 107 109
"Mirror image" hole 119 120
"Soft" collisions 152
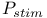 , exact calculation compared with additive approximation 124—125 , exact calculation compared with additive approximation 124—125
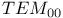 mode 34 mode 34
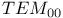 mode, square aperture 19 mode, square aperture 19
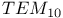 mode 34 mode 34
Abella 67
Absolute frequency shifts 153
Absorber profiles 170
Absorption bands, molecular 172
Absorption coefficient 74 167
Absorption coefficient, dithering the 176 176
Absorption Lorentz widths 178
Absorption profile, holes burnt in 167 (Fig.)
Absorption resonance 177
Absorption, expression for Doppler-broadened line 81
Accelerating ions 158
Accelerating ions, line shape for radiating 159 (Fig.)
Additive approximation 120
Additive approximation, comparison of exact calculation of 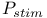 with 124—125 with 124—125
Algorithm, N modes 141
Amplifying transition, refractive index of 92 (Fig.)
Amplitude and phase 18
Amplitude expansion coefficients 41 42
Amplitude expansion coefficients, equations for 58
Amplitude gain, non-symmetric function 44
Amplitude response function 39
Anti-resonant term 70
Antropov 160
Aperture displacement 49
Aperture displacement, generalized 55
Aperture, circular confocal 23
Aperture, rectangular 11 12 39
Approximate Semi-Empirical Form for Power Broadening 146
Approximations in Boyd and Gordon Theory 27
Arakeljan 46
Arrathoon 150
Asymmetry 133
Asymmetry in "bump" height 192
Asymmetry in spontaneous emission "bumps" 195 (Fig.)
Austen 46
Ballik 104n 130 156 158 160
Barger 173 177 178 181
Barker 174
Basov 173 181
Beam profile, transmitted 56
Beat frequency spectrum 88 (Fig.)
Beat splitting, power dependent 90 (Fig.)
Beating effects 17
Beating effects, due to mixing of higher-order modes 16 (Fig.)
Beiser 28 29 48
Bending of confocal equivalent cavities 27—29
Bennett 15 21 29 33 37 41 44 51 68 90 94n 105 106 107 109 117 118 120 143 149 150 155 156 157 158 160 161 162 163 171n 172 174 176 187 189 191
Berman 151
Beterov 155 156 173
Binary spatial switching 46
Birky 109 191
Bloch 69
bode 94n
Bonczyk 109 130 154 191
BOND 104n
Borenstein 158
Born 81
boundary conditions 6
Boyd 21 22 23 25 26 27 30 31
Boyd and Gordon Theory, approximations in 27 88
Boyne 166
Brewster angle windows 34
Broadening, cross section for 153
Broadening, neon-helium 157
Broadening, neon-neon 157
Brown 68
Cavity length, "dithering" the 162 176
Cavity mode loss per transit 13 16 19 23
Cavity mode problem, perturbation expansion method in 49
Cavity phase shift 91
Cavity Q approximation 85
Cavity width 84 85
Cavity, confocal equivalent 27
Cavity, conventional 6
Chebotayev 36 109 155 173 174 175 176 181 183 184 186 187 189 191 196 203
Circular confocal aperture 23
Circular disc 19 (Fig.)
Circular mirror 23 (Fig.)
Collision broadening 149
Collisions, elastic 151
Collisions, phase-changing 152
Comparison with Lamb Theory 143 144 145
Computer solution of two-mode tuning characteristics 137—139
Confluent hyper-geometric functions 24
Confocal cavities, conjugate 56 (Fig.)
Confocal cavities, flat field conjugate 29
Confocal cavity 39
Confocal cavity, analysis 21
Confocal cavity, relationship of variables 22
Confocal coordinates, generalized 25
Confocal equivalent cavity 27 28 30 35
Confocal equivalent cavity, bending of 27
Confocal equivalent cavity, existence of modes 30
Confocal equivalent cavity, lens 29
Confocal expansion matrix 55
Confocal mode, field variation 25
Confocal mode, one-dimensional 54
Confocal modes, intensity distribution 26
Confocal modes, relative intensity 26 (Fig.)
Confocal resonance condition 22
Confocal resonator, generating 35
Confocal scanning problem 55
Confocal variable, generalized 24
Conjugate confocal cavities 56 (Fig.)
Conte 145
Conventional cavities 6
Cordover 109 130 154 191
Cross section for broadening 153
Curvature, radii of 35
Curved mirror infinite strip modes, loss contours for 31 (Fig.)
Deutsch 68
Dicke 8 152
Dierssen 60
Diffraction integral 10 14
Diffraction integral, one-dimensional 13
Diffraction loss 19 (Fig.)
Diffraction loss for plane parallel and confocal modes 23 (Fig.)
Dipole-dipole interactions 151 153
Displaced apertures, expansion problem in 50
Dithering of cavity length 162 176
Dithering, discharge current 165
Dithering, gain 162
Dithering, gain, by optical pumping 166
Dithering, the absorption coefficient 176 176
Doppler broadened gain absorption coefficients 79
Doppler broadened limit 115 120 131
Doppler broadened limit, phase shift for 103
Doppler broadened line, absorption expression for 81
Doppler broadened line, small gain coefficient at center of 80
Doppler limit 120
Doppler linewidth 6
Doppler profile 139 (Fig.)
Doppler shifted resonance frequencies 82
Doppler width 80
Doppler-free spectroscopy 203
Dumping mirror 33
Eigenvalue, of Gaussian gain aperture 44 (Fig.)
| Eigenvalue, problem 14
Einstein 62
Einstein A coefficient 69 76 76n
Elastic collisions 151
Elastic phase interruption 69
Elastic scattering, "large angle" 151
Electric dipole, matrix element of 70
Electric dipole, transition 70
Elliott 123n
Energy loss, fluctuations in (per transit) 14
Energy loss, total fraction per pass 33
Etalon, intra-cavity 36
Excitation, relative 144
Excited state lifetimes 149 (Fig.)
Expansion coefficients 49
Expansion matrix, confocal 55
Expansion problem in displaced apertures 50
Exponential gain, effects of 148
Fabry — Perot 38 88
Fabry — Perot analysis 156 189 195
Fabry — Perot cavities and mode density 34
Fabry — Perot interferometers 8 9
Fabry — Perot scanning 155 (Fig.)
Faddeyeva 81 82 83 145
Feld 174 175 196
Feldman 196
Feshbach 25
Field distribution 18 (Fig.) 25
Flammer 22 23
Flat-field conjugate confocal cavity 29
Fluctuations in energy loss per transit 14
Folded cavities 27—29
Foley 154
Fork 88 144 145 146 154
Fourier projections, spatial 145
Fourier transforms 95
Fourier transforms, cavity width by 84
Fox 9 10 12 13 21 30 31 32
Fox and Li modes 9 10 10 12 19 48 88
Fox and Li modes, symmetry 14
Frequency equation for general laser 93
Frequency locking effect 144
Frequency shifts, absolute 153
Frequency stabilization 162 165 171 177
Frequency tuning characteristic 127
Frequency, of oscillator 170
Fresnel number 13 30
Fresnel number, effective 30
Fried 145
Functions, confluent hyper-geometric 24
Functions, tabulated by Faddeyeva and Terent'ev 83
Gain absorption coefficients, Doppler-broadened 79
Gain apertures 41
Gain apertures, eigenvalues of Gaussian 44 (Fig.)
Gain apertures, Gaussian 40 41 42 43 44 60 61
Gain coefficient 102 167
Gain coefficient for running waves 74 111
Gain coefficient, differential power 110
Gain coefficient, high intensity 78
Gain coefficient, intensity-dependent 74
Gain coefficient, low intensity 77
Gain coefficient, small signal 75 80
Gain coefficient, total power 111
Gain curve in presence of saturable absorber 186 (Fig.)
Gain curve, hole in small signal 107
Gain hole, depth of 115 117 127
Gain hole, due to one running wave 112
Gain hole, expression for 113
Gain hole, width of 115
Gain in wing of a hole 178
Gain measurement, small signal 86 (Fig.)
Gain modulation 163
Gain profile 167 (Fig.) 170
Gain saturation 178
Gain saturation, equations for 140
Gain, with a saturable absorber 175 (Fig.)
Gaussian limit 104
Gaussian modes 24
Gaussian modes, aperture limit 59
Gaussian profiles 81 (Fig.)
Gaussian, phase shift coefficient for pure 103
Gaussian, phase shift for distribution of Lorentzians 101
Generalized confocal coordinates 25
Generalized confocal resonators 30
Generalized confocal variable 24
Generating confocal resonator 35
Geometrical phase shift 13
Goldenberg 67n
Gordon 21 22 23 25 26 27 30 88 89 94n
Gould 8
Green's function 10 (Fig.)
Griem 161
Griem's theory 161
Gyorffy 158
Haensch 155 156 181 191 196 203
Hahn 67
Hall 173 177 178 181
Hamiltonian, perturbing term in 64
Hargrove 144
Hartmann 67
Heitler 192
Helium-neon laser 130 (Table) 144 154 186
Helium-neon laser, 0.63 micron 173
Helium-neon laser, 1.15 micron 118 (Fig.) 187 191 195
Helium-neon laser, 3.39 micron 163 (Fig.) 171 172 173 187 191
Helium-neon laser, 6328 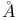 transition 156 (Fig.) 174 187 189 191 transition 156 (Fig.) 174 187 189 191
Hermite polynomials 24 25
Herriott 21 88
High loss, regions of high and low 32
High loss, singular regions of 30
Hole burning analysis, oscillation frequency from 118—119
Hole burning effects 105
Hole burning effects in three-level laser spectroscopy 186—197
Hole burning model 130 180 182
Hole burning model for two isotopes 131 (Fig.)
Hole burning model, by running waves 178
Hole burning model, in 6328 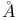 neon 189 (Fig.) neon 189 (Fig.)
Hole burning model, in a single-mode gas laser 131 (Fig.)
Hole depths 107
Hole depths in single-mode with saturable absorber 169
Hole depths, gain in wing of 178
Holes 109
Holes in the velocity distribution 189
Holes, burnt at 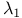 , observed at , observed at 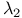 190 190
Holes, burnt in the gain and absorption profile 167 (Fig.)
Holes, present for two modes 134 (Fig.)
Holstein 75
Holt 109 146 191 192 195
Homogeneous broadening 79
Homogeneously broadened lasers 99 100 101
Homogeneously broadened lasers, oscillation frequency for 100
Hughes 69n
Huygens principle 12
Hyper-geometric functions, confluent 24
Hysteresis effects 125 132 134 139
Hysteresis effects in two-mode operation 138 (Fig.)
Hysteresis effects, single mode 128 (Fig.)
Hysteresis effects, threshold 184—186
Inelastic decay rates 69
Infinite strip modes 18
Infinite strip modes, loss contours for curved mirror 31 (Fig.)
Infinite strip, modes 18 51 47
Infinite strip, phase shift 20
Infinite strip, plane parallel mirrors 14
Infinite strip, uniform plane wave loss 19
Inhomogeneous broadening 79
Inhomogeneous broadening, threshold oscillation frequency for 104
Inhomogeneously broadened gas laser 105
Intensity dependent Lorentz width 107
Intensity gain 77
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



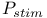 , exact calculation compared with additive approximation
, exact calculation compared with additive approximation 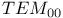 mode
mode 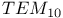 mode
mode 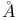 transition
transition 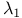 , observed at
, observed at