Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Stewart I.W. — The Static and Dynamic Continuum Theory of Liquid Crystals: A Mathematical Introduction
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: The Static and Dynamic Continuum Theory of Liquid Crystals: A Mathematical IntroductionАвтор: Stewart I.W. Аннотация: Stewart (Math, U. of Strathclyde, Glasgow) prepared this text for graduate students of applied mathematics, theoretical physics, and engineering. Introductory material sets the scene for later chapters which cover, in turn, the features and applications of the static theory and dynamic theory of nematics, including extensive derivations as a way to communicate to readers how to apply the results from continuum theory to practical problems. The final chapter, an introduction to the theory of smectic C liquid crystals, does not give as many detailed computations; as the author explains, "smectic liquid crystals have some uniquely different mathematical problems..." and detailed coverage is beyond the scope of this volume.
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Издание: 1st editionГод издания: 2004Количество страниц: 360Добавлена в каталог: 20.09.2009Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Kronecker delta 10 Lagrange multipliers 37 250 Lagrange multipliers, comments on SmC 266-267 Layer compression constant see smectic layer compression constant LCD see liquid crystal displays Lehmann, O. 2 Leslie angle see flow alignment angle Leslie coefficients 146 Leslie viscosities 146 151 Leslie viscosities, in terms of Miesowicz viscosities 158 Leslie viscosities, restrictions 146 Light scattering 236-246 Light scattering, displacements of director in 238 Light scattering, domination by slow modes 243 246 Light scattering, effective viscosities 245 Light scattering, experimental set-up 237 Light scattering, fast modes 242 Light scattering, governing dynamic equations 241- 242 Light scattering, in an electric field 246 Light scattering, in smectics, references to 300 306 Light scattering, in-plane mode 237 241 Light scattering, integrated intensities 245 246 Light scattering, line defects in SmA and SmC 268 272 Light scattering, line widths 245 246 Light scattering, Lorentzian lines 245 Light scattering, orientational fluctuations 236 Light scattering, out-of-plane mode 237 242 Light scattering, periodic disturbances 238 Light scattering, power spectrum 244 Light scattering, response functions 244 Light scattering, slow modes 242 Line singularities see disclinations line Line width (in light scattering) 245 Liposomes 268 Liquid crystal displays 8 72 101 108 109 Liquid crystals 1 Liquid crystals, classification of 2 Local angular velocity 134 Lorentzian lines 245 Lyotropic liquid crystals 2 6 Magnetic anisotropy 29 31 329 Magnetic anisotropy, conversion rule 31 Magnetic anisotropy, measurements of in nematics see Table D.3 Magnetic anisotropy, negative 30 Magnetic coherence length 68 69 71 122 Magnetic energy density 30 32 Magnetic fields 26 28-31 258-259 Magnetic induction 29 Magnetic potential 42 168 219 225 Magnetic torque 42 Magnetisation 28 29 32 42 149 Magnitude of a vector 11 Mandelstam's condition 232 Material time derivative 135 325 Maximum distortion angle 79 85 Maxwell equations 28 31 89 90 MBBA 4 64 67 159 164-166 169- 171 175 187 228 232 233 236 330 Measurements of see Table D.3 Melting point 2 Mesogenic 2 Mesomorphic phases 2 Mesophases 2 Miesowicz viscosities 155 156 158 Miesowicz viscosities, in terms of Leslie viscosities 158 Miesowicz viscosities, principal 155 156 Misalignment 84 Molecular length 4 Moving domain wall 317 Natural boundary condition 47 54 Natural orientation 14 Negative magnetic anisotropy 30 Nematic energy 20 21 Nematic energy, one-constant approximation 23 Nematic liquid crystals 3 7-8 Nematic viscosities 151 154-159 Nematic viscosities, canonical set 158 Nematic viscosities, measurements of see Table D.3 Nematic viscosities, physical interpretation 154 Nematic viscosities, restrictions 146 Newtonian fluid 157 170 176 177 180 212 213 Newtonian viscosity 170 176-177 180 213 No-slip boundary condition 150 167 Non - Newtonian fluid 177 Non - Newtonian properties in nematics 177 Non-contemporaneous variations 34 Non-flow-aligning 166 Non-flow-aligning, instability in oscillatory shear 196 Normal stress 139 Normal stress differences 177 Notation and conventions 9-12 35 Null Lagrangian 38-39 Objective 136 Objectivity see principle of material frame-indifference Oersted (Oe) 32 One-constant approximation 22-23 79 81 110 Orientational fluctuations 236 Orthogonal vectors 11 Oscillatory shear flow 187-197 Oscillatory shear flow, flow-aligning nematics 191 Oscillatory shear flow, non-flow-aligning nematics 191 Oscillatory shear flow, stability and instability 191-197 Oseen, C.W. 7 Out-of-plane mode 237 Out-of-plane surface tilt angle in SmC 275 280 PAA 4 7 67 159 165 166 171 175 216 217 228 330 Parabolic cyclides 272-275 Parabolic cyclides, Cartesian equation for 273 Parabolic cyclides, cross-sections of 274 Parabolic cyclides, illustrations 272 274 Parabolic cyclides, parametrisation of 273 Parodi relation 146 151 Patents 108 Penetration length in smectics 284- 286 Permeability of free space 29 329 Permeation in smectics 319 Permittivity of free space 27 329 Perpendicular disclinations 118 Physical components 198 Physical components, in cylindrical coordinates 325-327 Pieranski - Guyon instability 166 Pitch, cholesteric 5 23 24 Pitch, SmC* 307 308 Planar alignment 47 Planar alignment, in SmC 302 Plane of shear 155 163 Point defect 115 127 Point defect at a surface or interface 127-131 Point form 139 Poiseuille flow 209-217 Poiseuille flow, anisotropic fluid 210-213 Poiseuille flow, between coaxial cylinders 217 Poiseuille flow, isotropic viscoelastic fluid 217 Poiseuille flow, nematic liquid crystal 213-217 Polar fluids 134 140 Polarisation vector 236 Polariser 102 Polymorphism 7 Power 33 Power spectrum 244 Pressure gradient 209 Pretilt 82 85 109 Pretilt at the boundaries 82-84 Pretilt, advantage of 84 Principle of material frame-indifference 136 Principle of virtual work 33 35 259 Proper orthogonal matrix 15 136 Rapini - Papoular weak anchoring en-ergy 49 Rate of strain tensor 133 135 151 293 326 Rate of viscous dissipation 141-143 145 Rate of work hypothesis 140 Reaction time 221 Reduced viscosity 223 Reformulation of dynamic equations 153- 154 Reformulation of equilibrium equations 50-56 Reformulation of equilibrium equations, boundary conditions 53 Reformulation of equilibrium equations, bulk equations 51 Reformulation of equilibrium equations, in SmC 265 Regional angular velocity 134 Reinitzer, F. 2 Relative angular velocity 133 134 Relative shear velocity 187 Relaxation time 222 Response functions 244 Response time 316 Response time in SmC* 316-317 Reynolds number 188 189 Reynolds' transport theorem 139 141 324 Rigid body motion 143 Rise time 221 Ritschke, A. 4 Rod-like molecules 2-3 Rotating magnetic field 171 Rotational viscosity 157 158 Rotational viscosity, direct measurement of 175 Saddle-splay 21 38 Scalar product 11 Scalar triple product 11 Scaling properties 185-187 217 Scattered beam 236 Scattering angle 236 Scattering plane 236 Scattering vector 236 SCE13 312 SCE3 312 Schadt 101 108 Scheurle, B. 4 Secondary flow 170 Secondary flow component 170 Secondary flow, cellular 209 See cholesteric liquid crystals chiral smectic C see SmC* Shear 155 Shear flow 162 176-187 Shear flow, between parallel plates 182-185 Shear flow, in bookshelf SmC 305-306 Shear flow, in planar aligned SmC 302-305 Shear flow, key equations 180 Shear flow, near a boundary 180-182 Shear flow, oscillatory 187-197 Shear plane see plane of shear Shear stress 139 156 182 184 SI units 31 329 Sign convention for spontaneous polarisation 307 Simple flow alignment 162 Simple shear flow in SmC 301-306 Simple shear flow, steady solutions 164 Slow modes (in light scattering) 242 SMA 5 6 249 256 267 268 272 281 284 297 319 SmA elastic energy 256 SMC 5 6 9 249 267 268 SmC constraints 248-249 SmC elastic constants 251 SmC elastic constants, inequalities 255-256 SmC elastic constants, measurements and estimates 257 SmC elastic constants, Orsay notation 252 SmC elastic constants, physical interpretation 253 SmC elastic energy 250-258 320 SmC Freedericksz transition 275-281 SmC viscosities 296-301 SmC viscosities, classification of 297-299 SmC viscosities, measurements of in DOBCP 301 SmC viscosities, physical considerations 301 SmC viscosities, restrictions 299-300 SmC 258 SmC 296 SmC* 6 9 247 308 306-319 SmC* elastic energy density 310 SmC* electric energy density 311 SmC* material parameters 312 SmC* viscosities, identification with SmC viscosities 312 SmC* viscosities, measurements of in ZLI-3234, ZLI-3488, ZLI-3489 301 SmC, in-plane surface twist angle 275 276 279 SmC, mathematical description 249 SmC, out-of-plane surface tilt angle 275 280 Smectic A see SmA Smectic C see SmC Smectic C liquid crystals see SmC Smectic cone angle 6 248 249 257 312 Smectic interlayer distance 6 248 249 284 Smectic layer compression 281-291 319 Smectic layer compression constant 281 284 Smectic layer dilation 282 319 Smectic layer thickness 6 Smectic layer undulations, reference to SmC experiment 283 Smectic layer undulations, references to SmA experiments 282 Smectic liquid crystals 5 Smectic tilt angle see smectic cone angle Soliton-like solution 317 Specific driving force 212 213 215 Specific volume, measurements of in nematics see Table D.3 speed of light 329 Spherical solution 43 44 Spin tensor 135 Splay 15 16 21 Splay geometry 73 Splay viscosity 158 228 Splay, measurement of 77 Spontaneous polarisation 248 307 308 Spontaneous polarisation, contribution to SmC* energy 310 Spontaneous polarisation, sign convention for 307 SSFLC device 308 313 316 Stability 196 Stability and instability 165 191 196 Static theory of SmC 248-281 Static theory of SmC* 312-313 STN 101 Strength of a disclination 111 Stress tensor 37 139 151 Stress tensor, normal stress 139 Stress tensor, normal stress differences 177 Stress tensor, physical interpretation of 139 Stress tensor, shear stress 139 Stress vector 139 Strong anchoring see anchoring strong Suffix notation see index notation Summation convention 9 10 Supertwisted nematic device 101 Surface at an interface 123 Surface force 138 139 Surface moment 138 139 Surface tension 120 122 123 329 Surface tension, measurements of in nematics see Table D.3 Surface tilt angle in SmC 275 280 Surface traction 174 206 Surface twist angle in SmC 275 276 279 Surface viscosity 150 Switch-off time 218 222 Switch-off time, in bookshelf SmC 280 Switch-off time, in twisted nematic device 223 Switch-on time 218 221 224 228 234 Switch-on time, in bend geometry, 235 Switch-on time, in bend geometry, 236 Switch-on time, in bookshelf SmC 280 Switch-on time, in splay geometry, 228 Switch-on time, in splay geometry, 229 Switch-on time, in twisted nematic device 223 Switch-on time, reduction of (via backflow) 228 236 Switching 72 223 228 308 317 Tables, conversion from Gaussian cgs to SI 329 Tables, fundamental constants 329 Tables, material constants for nematics 330
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



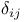
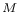 , elastic energy
, elastic energy 
