|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Bube R.H. Ч Photoconductivity of Solids |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Absorption of oxygen, chemical 195
Absorption spectra 43 131 231
Absorption spectra, compensated acceptors in II Ч VI compounds 163
Absorption spectra, crystal vibrations 217Ч219
Absorption spectra, excitation-induced 354Ч356
Absorption spectra, excited states of impurities in Si 141Ч145
Absorption spectra, exciton 226Ч228
Absorption spectra, free-carrier 210 211 215Ч217
Absorption spectra, infrared 199 210 211
Absorption transitions 42Ч45 211Ч228
Acceptor imperfections 42
Acceptor imperfections, characteristic ionization energies in II Ч VI compounds 169Ч171
Acceptor imperfections, compensated, and sensitivity 161 162 171Ч174
Acceptor imperfections, levels in II Ч VI compounds 162Ч171
Allochromatic (imperfection) photoconductivity 6
Amorphous materials 10 420
Amphoteric impurities 147
Amplification factor 333
Atomic battery 382
Attempt-to-escape frequency 50 51 293
Auger recombination 304 323 324
Band gap, controversy in PbS-like compounds 236 237
Band gap, controversy in PbS-like compounds, crystal binding 33 34
Band gap, controversy in PbS-like compounds, dependence on impurity concentration in InSb 247 248
Band gap, controversy in PbS-like compounds, determination of 229Ч235
Band gap, controversy in PbS-like compounds, grouping of compounds according to 232 235
Band gap, controversy in PbS-like compounds, pressure dependence 238Ч242
Band gap, controversy in PbS-like compounds, temperature dependence 237Ч240
Band gap, controversy in PbS-like compounds, values of 233 234
Band structure of Ge and Si 199Ч201
Barriers 57 357Ч364 376
Barriers, exhaustion 111
Barriers, interparticle 81 82 92
Barriers, metal-semiconductor 81 111Ч118
Barriers, modulation of 82 83 358Ч362
Barriers, surface 111 115
Binding, chemical, band gap 32Ч38
Binding, chemical, band gap, covalent 12
Binding, chemical, band gap, determination of 12 13
Binding, chemical, band gap, electronegativity 14 15 16
Binding, chemical, band gap, ionic 12
Binding, chemical, band gap, metallic 12
Binding, chemical, band gap, mobility 34Ч38
Binding, chemical, band gap, semiconducting 15 16
Binding, chemical, band gap, strength of 25 26
Boltzmann distribution 47
Bombardment damage 181
Bombardment-induced conductivity 402Ч404
Bragg reflection law 27 28
Bridgman Ч Stockbarger technique 103
Brillouin zones 27 28
Capture cross sections (see УCross section captureФ)
Capture probabilities 304
Capture transitions 42 45 46
chemical potential 47
Conduction band 31
Conductivity type, change of 181Ч187
Conductivity type, change of with increasing light intensity 156Ч158
Conductivity type, change of, attending relations 175Ч178
Conductivity, electric 30 32
Conductivity, electric, dark 130
Conductivity, electric, dependence on impurity ionization energy 159Ч162
Conductivity, electric, Fermi-level analysis 49Ч55
Contact potential 399Ч402 415
Continuity equations 326
Controlled imperfection 187
Controlled valency 183 192
Conversion of radiant energy 380Ч382
Conwell Ч Weisskopf relation 258
Cross section, capture 50Ч55 61 62
Cross section, capture, ratio for sensitizing centers 345
Cross section, capture, temperature dependence 73 314
Cross section, capture, vacancies 62
Crystal counters 402 457
Crystal growth techniques, gradient freezing 104
Crystal growth techniques, gradient freezing, pulling from melt 102 103
Crystal growth techniques, gradient freezing, slow cooling of melt 103Ч105
Crystal growth techniques, gradient freezing, solution 105
Crystal growth techniques, gradient freezing, tip fusion 103
Crystal growth techniques, gradient freezing, vapor phase 98Ч101
Crystal growth techniques, gradient freezing, zone melting 105Ч108
Crystals, nearly perfect 11
Crystals, nearly perfect, perfect 10
Cyclotron resonance 199 204Ч210
Czochralski technique 102
Damage, bombardment 181
Decay 274 276Ч292 425
Decay range analysis 330Ч335
Decay rate, increased 288Ч290
Decay rate, increased, electric fields 292
Decay rate, increased, purification 302
Decay time 69 71
Decay, transients 290 291
defects 39 129 178Ч196
Defects formation 179
Defects, alkali halides 179 180
Defects, CdS, CdSe, CdTe 187Ч192
Defects, Ge, Si 181
Defects, MgO, BaO 193 194
Defects, PbS, PbSe, PbTe 181Ч187
Defects, ZnO, 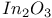 , , 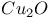 194Ч196 194Ч196
Defects, ZnS 192 193
Demarcation level 65 276 312 335
Demarcation level, steady-state Fermi level 66 67
Dember effect 2 377 384Ч386 425
Density of states, effective 48 202
Detailed balance equation 51
Diamagnetic splitting of bands 248
Diffusion constant 268
diffusion length 268 423Ч425
Direct transitions 44 45 212Ч214
Dislocations 259 315Ч318
Donors 42
Donors, characteristic ionization energies in II Ч VI compounds 169Ч171
Drude Ч Zener equation 215
Dyes 408 410Ч416
Edge emission 46 321 322
Effective density of states 48 202
effective mass 29 30
Effective mass, angular dependence 206Ч208
Effective mass, determination of 204Ч211 248Ч250
Effective mass, longitudinal and transverse 199 202
Effective mass, negative 210
Effective mass, negative, scalar 198
Effective mass, negative, tensor 30
Effective mass, negative, values of 209
Electrode contacts 110Ч128
Electrode contacts, CdS crystals 118Ч120
Electrode contacts, metal-semiconductor 110Ч120
Electrode contacts, neutral 85 113 127 332
Electrode contacts, ohmic 113Ч128
Electrofax 429 430
Electroluminescence 124 321
Electron-voltaic effect 382
Electronegativity 14 15
electrophotography 127 429 430
Emission spectra 131 165 223
Emission spectra, conduction 31
Emission spectra, density of states 46Ч48
Emission spectra, effective density of states 48 202
Emission spectra, occupation of states 46Ч49
Emission spectra, real crystals 198Ч203
Emission spectra, valence 31
energy bands 24
Energy levels, electron in potential well 21
Energy levels, electron in potential well, electrons in nearly perfect crystals 39Ч42
Energy levels, electron in potential well, electrons in perfect crystals 22Ч30
Energy levels, electron in potential well, free electron 20
Energy levels, electron in potential well, harmonic oscillator 20
Energy levels, electron in potential well, imperfection 130
| Energy levels, electron in potential well, impurities in Ge and Si 135Ч158
Energy levels, electron in potential well, impurities in II Ч VI compounds 158Ч170
Energy-level schemes for imperfections, CdS 353 371Ч374
Gain, photoconductivity 7 60
Gain, photoconductivity, homogeneous photoconductors 76 77
Gain, photoconductivity, maximum 126Ч128 406
Gain, photoconductivity, npn junction 80
Ge surface 399 400
Ge surface, demarcation levels 66 67 312 335 346
Ge surface, doubly charged impurity in Ge 155
Ge surface, Equal-energy surfaces, ellipsoidal 199
Ge surface, equilibrium 53
Ge surface, Excitation spectra 131 164 168Ч170 230
Ge surface, Excitation transitions 42Ч45 211Ч215 219-225
Ge surface, Excitons 38 39 211 223 225Ч228
Ge surface, Extinction coefficient 235
Ge surface, Extraction, field 375
Ge surface, F centers 5 179 180
Ge surface, Fermi function 47
Ge surface, Fermi level 49Ч55
Ge surface, Fermi level, analysis of conductivity 49Ч55
Ge surface, Franck Ч Condon principle 132 144
Ge surface, Frerichs technique 99
Ge surface, PbS 365 366
Ge surface, quasi 53
Ge surface, spherical 198
Ge surface, steady state 53 312 335
Ge surface, valence bands in Ge and Si 200 201
Ge surface, ZnS 371Ч374
Glow curves 131 296 300 301
Growth of photoconductivity 274 276Ч292
Growth of photoconductivity, S-shape 285Ч287
Growth of photoconductivity, transients 290 291
Hall angle 261
Hall constant 177 260
Hall effect 1 131 210 259Ч263 363 364
Hall effect, measurement of 263
Hall mobility 264
Hall mobility, relation to microscopic mobility 261 264
Hall potential 260
Historical survey 1
hole 32
Hydrocarbons 408Ч410
Idiochromatic (intrinsic) photoconductivity 6
II Ч VI compounds 160 345
Impact recombination 304 323 324
Imperfection photoconductivity, theory of, for semiconductors 132Ч135
Imperfections, crystal 11 38Ч42
Imperfections, crystal, effects on photoconductivity 129Ч132
Imperfections, crystal, recombination at 305Ч318
Impurity conduction 52 145 146
Impurity incorporation, dependence on atmosphere 189 190
Impurity incorporation, dependence on atmosphere, methods of 108 109
Impurity interaction 145 146
Impurity ionization energies, Ge 136
Impurity ionization energies, Ge, Si 137 144
Impurity ionization energies, Ge, thermal vs. optical 143 144
Index of refraction 235
Indirect transitions 212Ч215 219Ч225
Injection 8 124
Injection, induced radiation emission 139
Inversion layer 115
Ionization energies of holes from sensitizing centers 345
Junctions, preparation of 108 109
Klasens Ч Schoen model 373 374
Kyropoulos technique 102
Lambe Ч Klick model 373 374
Layer preparations, chemically-deposited 95
Layer preparations, chemically-deposited, electrolysis 95
Layer preparations, chemically-deposited, evaporated 95Ч97
Layer preparations, chemically-deposited, melted 98
Layer preparations, chemically-deposited, sintered 94 95
Lifetime 57
Lifetime, carrier density 131
Lifetime, excited 58
Lifetime, free 58
Lifetime, majoritv-carrier 59
Lifetime, measurements of 423Ч425
Lifetime, minority-carrier 58
Lifetime, pair 58
Lifetime, radiative recombination 319
Light amplifiers 431Ч433
Luminescence 46 321 367Ч375
Luminescence, centers 370
Luminescence, field modulation 374 375
Luminescence, transitions 370
Magneto-absorption, oscillatory 247Ч250
Magneto-optic effect 211 247Ч250
Magnetoresistance 199 203
Mass action, law of 184
Mixed crystals 250Ч254
Mobility 32 34 35 255Ч272
Mobility, ambipolar 265
Mobility, anomalies 199
Mobility, conductivity 263
Mobility, drift 263Ч268
Mobility, effective, barrier 57
Mobility, Hall 264
Mobility, microscopic 263
Mobility, photoconductivity 264 266
Mobility, types of 263 264
Mobility, values of 268Ч271
Mobility, values of temperature dependence 272
Mobility, Уa-cФ 267 279
Models of photoconductivity, analysis of a simple model 326Ч330
Models of photoconductivity, analysis of a simple model, two-center model 338Ч342
Multiply charged centers 137 406
Multiply charged centers, in Ge 146Ч158 258 346
Negative photoconductivity 404Ч406
Noise 59 60 406Ч408
Noise, black-body radiation 60
Noise, f noise 407
Noise, generation-recombination 407
Noise, Johnson or Nyquist 407 1
Noise, npn junctions 79 80 128 358
noise, signal-to-noise ratio 60 407
Optical quenching 174 348Ч354
Optically stimulated trap emptying 275 299
Organic photoconductors 408Ч415
Overshoot phenomena 290 291
Oxygen impurity effects 97 174Ч178 300 364Ч367
Paramagnetic susceptibility or resonance 276
Pauli exclusion principle 22
Pellet preparation 98
Phase transformations 417Ч420
Phonons 38
Phonons, energies in Ge and Si 213 214 222
Phonons, in recombination 304
Photocells 428 429
Photoconductivity performance 73 74
Photoconductivity varying as power of light intensity greater than unity 155 174 342Ч348
Photoconductivity, mechanism of, in PbS layers 356Ч367
Photoconductor systems, simple 74Ч87
Photoconductor systems, simple, homogeneous 75Ч77
Photoconductor systems, simple, non homogeneous 77Ч87
Photodielectric effect 2 3 276 420Ч423
Photoeffect, crystal 3
Photography, electrophotography 127 429 430
Photography, electrophotography, silver halide 415 416
Photomagnetoelectric (PME) effect 3 377 384Ч390 425
Photomagnetoelectric (PME) effect, longitudinal 390
Photomagnetoelectric (PME) effect, quadratic or transverse 390
Photon 38
Photoresponse 134 (see also УSensitivityФ)
Photosensitivity 130 (see also УSensitivityФ)
Photovoltaic effect 1 357 376Ч384 415 424 425
Photovoltaic effect, high voltage 382 383 418
Photovoltaic effect, lateral 383 384
Photovoltaic effect, surface 384
piezoresistance 199
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 ,
,