|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| David O.Tall — Advanced Mathematical Thinking |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Hanna, G. 23 54—61 162 254
Hardy, T. 19
Harel, G. 12 31 37 63 82—93 142 255
Hart, K.M. 8
Hausdorff, F. 43 89
Heid, K. 237 238
Heller, J.L. 118
Helplessness 152
Henle, J.M. 172
Hermite, C. 13 253
Hersh, R. 44 146 149
Hess, P. 201 203
Heuristics 132 137 220
Hierarchy of concepts 256
Hilbert, D. 5 146 149 162 200 208
Hippocrates of Chios 159
Historical texts 138
History of analysis 168
Hodgson, B.R. 235
Hoffman, K.M. 29
Homotopy group 106
Horizontal growth of knowledge 83
Hubbard, J.H. 193 239
Humanistic mathematics movement 149
Hyperreal numbers 163
Illumination 50
Inbar, S. 147
Inconsistencies in comparing infinite quantities 204
Inconsistencies, raising students' awareness of 206—207
Induction, mathematical 38
Infinitely large and infinitely small 160—161
Infinitely small 160 168
Infinitesimal 6 160 161 198 199
Infinitesimal as 'banned' by Weierstrass 168
Infinitesimal as a carrier of paradoxes 169
Infinitesimal as an abreviation of an expression 169
Infinitesimal as defined by Cauchy 160
Infinitesimal in minds of mathematicians 162
Infinitesimal in non-standard analysis 162 168
Infinitesimal of Leibniz 161
Infinitesimal, decline in face of the limit notion 169
Infinitesimal, metaphysical haze 171
Infinitist 156
infinity 110 125 156 196 199—214
Infinity, actual 199 200
Infinity, actual, accepted by Galileo etc 200
Infinity, actual, rejected by Aristotle 200
Infinity, actual, rejected by Poincare 200
Infinity, actual, student experiences 202
Infinity, actual, student understanding 209—213
Infinity, cardinal 199 201 203
Infinity, comparing infinite quantities 199 203—205
Infinity, comparison between two infinite sets 199
Infinity, measuring 202 203
Infinity, non-standard 199
Infinity, ordinal 199
Infinity, potential 199 200 202
Infinity, student conceptions 201—205
Infinity, student difficulties 161
Infinity, teaching the Cantorian theory 199
Infinity, theoretical conceptions 200—201
INRC group 102
Institutionalization 135
Instrumental understanding 48
integral 85 151 167 176
Integral as a continuous linear form 175
Integral as a function 92
Integral as a process of measure 175 190
Integral as an inverse to differentiation 191
Integral as area under a curve 191
Integral as encapsulation and interiorization 105
Integral, Riemann 227
Integral, student conceptions 175
Integration 107 147 173 174
Integration in terms of the primitive 173
Integration in terms of the Riemann sum 173
Integration operation 82
Integration, algorithms 174
Intellectual development 100
Intelligent behaviour 131
Interiorization 103 104 106 113 143
Interiorization of a statement 115
Interiorization of actions 100 101 107 111 113 117
Intermediate Value Theorem 163 257
International Commission for Mathematical Instruction 170
Intuiting 40 41
Intuition 13—14 40 125 132 154
Intuition in mathematical creativity 47
Intuition in research using the computer 231
Intuition of actual infinity 201
Intuition of infinity 199—214
Intuition of infinity, origins in student experience 207
Intuition of infinity, via experiences of comparative size 202
Intuition, criteria for comparing infinite quantities 203—205
Intuition, developed with computer graphics 232
Intuition, primary 14
Intuition, primary, effects on thinking processes 207
Intuition, secondary 14 203 205
Intuitionism 55
Intuitionist school 54
Irrationality of 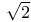 217 217
ISETL 242 244—248
Isomorphism 119
Isomorphism between vector spaces 82
Iterated limit 86
Iteration 114
Jacobian matrix 173 180 186
Janvier, C. 147
jargon 109
Jeeves, J. 15
Jensen, R. 144
Jordan's Theorem 146
Jordan, M. 48
Jurgens, H. 29
Jurin, J. 161
Kane, M.J. 141
Kantscluetsch, H. 38
Kaput, J.J. 31 39 41 63 82—93 255
Karplus, R. 147
Keisler, H.J. 172 238
Kepler, J. 10
King 151
Kitcher, P. 56
Klein, F. 14 17
Kleinberg, E.M. 172
Kleiner, I. 146
Kline, M. 141
Kline, W. 141
Kocak, H. 193 232
Kolata, G. 233
Kronecker, L. 4 5
Krutetskii, V.A. 146
L'Hospital, Marquis de 168
Laborde, C. 225
Lagrange, analysis without limits or infinitesimals 169
Lagrange, J.L. 161 163
Lakatos, I. 35 56
Lander, L.J. 232
Lane, K.D. 235
Laurent, H. 171
Learning difficulties in algebra 144
Learning theories and their deficiencies 142—144
Legrand, M. 19 137 191 216
Lehman, D.R. 141
Leibniz, G.W. 10 91 161 168 169
Leibniz, G.W., definition of tangent 174
Leibniz, G.W., notation for calculus 170
Leinhardt, G. 148
Lempert, R.O. 141
Leron, U. 19 41 216 220 221 223
| Levels of understanding 143
Lewin, P. 82 143
LIMIT 106 125 134 154
Limit absence in Greek mathematics 160
Limit as a barrier 155
Limit as a concept 156
Limit as a formal definition 153
Limit as a procept 255
Limit as a process 156
Limit as being impassible 154
Limit as the basis for calculus 168
Limit in epsilon-delta terms 162
Limit in integration 105
Limit in the derivative concept 17
Limit is it attained? 161—162
Limit of a function 84 85 167
Limit of a sequence 73 78 167 177
Limit of a series 166
Limit of a staircase 163
Limit of polygons as a circle 159
Limit of secants 76
Limit, colloquial meaning 154
Limit, conceptual difficulty 178 188
Limit, conflicts in 134 176
Limit, defined as unencapsulated process 163
Limit, double 86
Limit, dynamic 155
Limit, generic 10 162 164
Limit, given by operations 153
Limit, iterated 86
Limit, metaphysical aspect 161
Limit, mixed 155
Limit, monotonic 155
Limit, obstacles in history 159
Limit, static 155
Limit, stationary 155
Limits 153—166
Linear function as conceptual entity 90
Linear functional 109 150
Linear transformation 150
Lisp 242
Local approximation 170
Local straightuess 136 187 238
Logic schema 111—113
Logical thinking 103
Logicism 55 56
Logicist school 54
Logico-mathematical thinking 100
LOGO 242
Lorenz, E. 232
MacLane, S. 50 82 141
Major, R. 150
Manin, Y. 59
Maple 235 236
Martin, G. 201 203
Maslow, A.H. 58
Masochism 232
Mason, A. 27 32 146
Mason, J. 18 20 25 37 41 138
Mathematica 28 236 242
Mathematical content 128
Mathematical gazette 171
Mathematical induction 102 106 109 110—113 120 123 139 See
Mathematical induction as a process 110
Mathematical induction, encapsulated as an object 110
Mathematical minds 4 63
Mathematical phobics 148
Mathematical practice 56
Mathematical Reviews 59
Mathematical theory structure of 46
Matrix 82 84 91 104
McCloakey, M. 205
Mean value theorem 218
Meaning of calculus concepts 237
Measure theory 167
Melamed, U. 201 214
Menis, Y. 241
Mental reconstruction 9
Meta-mathematical instruction 138
Meta-mathematical knowledge 131 138
Meta-mathematical reflection 136—138
Meta-mathematics 138
Metaphysical aspect of limit 161
Metaphysics of infinity 169
Method of exhaustion 168
Metric for aesthetics 151
Misconceptions 27 236
Misconceptions about "getting close", "growing large", etc 156
Misconceptions in learning about limits 164
Misconceptions of a function 74
Misconceptions of a limit of a sequence 79
Misconceptions of a tangent 76
Misconceptions of a variable 145
Modelling 34
Models of learning 142
modus ponens 113
Monadic number 221
Moore, R.L. 137
Movshovitz-Hadar, N. 216—218
Muir, A. 42
Multiple embodiment 141
Multiple embodiment, (picture, graph, formula) 189
Multiplication as addition of additions 100
Mundy, J. 147
Munroe, M.E. 86
Mutstion, mathematical 49
Nelson, E. 172
Nering 92
Newton, I. 56 160 168 169
Nicholas of Cusa 10
Nisbett, R.E. 141
Non-standard analysis 6 172 187 196—198 202
Non-Standard Analysis (Robinson) 172
Non-standard analysis, its weak impact on education 172—198
Notation 88 148—151 152
Notation as substitute for a concept 88 93
Notation in forming conceptual entities 88—91 93
Notation system 89
Notation to encapsulate entities 90
Notation to name a concept 89
Notation, elaborated 88 91 93
Notation, f(x) for a function 149
Notation, graphical 90
Notation, tacit 88 93
NUMBER 100 106
Number as concept 253
Number as process 253
Number, cardinal 200 202
Number, cardinal number of set of reals 212
Number, hyperreal 202
Number, infinite measuring 202
Number, monadic 221
Number, ordinal 200
Number, triadic 221
Numerical analysis 241
Numerical methods, used to solve problems 131
Object 102 106
Object-pivot in structural proof 221
Object-valued operator 83 87 93
Obstacle 9—11 166 175
Obstacle in learning calculus/analysis 196
Obstacle to construction of formal concepts 195
Obstacle, cognitive 11 21 165
Obstacle, conceptual 133 153
Obstacle, didactical 158
Obstacle, epistemological 103 134 158 162
Obstacle, epistemological, didactically transmitted 163—164
Obstacle, epistemological, important characteristics 158
Obstacle, epistemological, inability to overcome 165
Obstacle, genetic 158
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте