|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| McComb W.D. Ч Physics of Fluid Turbulence |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 -model 107Ч109 -model 107Ч109
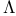 vortices 422Ч424 vortices 422Ч424
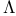 vortices, evidence from numerical simulation 427 vortices, evidence from numerical simulation 427
Absolute equilibrium ensembles 166
ALHDI, abridged LHDI See Lagrangian-history direct-interaction theories
Almost-Markovian models 335. See also Near-Markovian models
Apparent coefficient of viscosity for a non-Newtonian fluid 495
Apparent coefficient of viscosity for turbulent flow 8
Asymptotic series 147
Averaging methods, bulk mean velocity 4
Averaging methods, conditional average 413
Averaging methods, ensemble average 39
Averaging methods, global average 368
Averaging methods, partial average 367
Averaging methods, phase average 425
Averaging methods, shell-averaged energy spectrum 115
Averaging methods, spatial average, rolling average in LES 388
Averaging methods, time averages 5Ч6
Averaging methods, zone average 411Ч412
BBGKY hierarchy 159
BBGKY-type treatment of turbulence 159Ч160
Bernoulli distribution See Binomial distribution
Binomial distribution 529
Blasius empirical formula for wall shear stress in boundary layers 18. See also Wall shear stress
Blasius empirical formula for wall shear stress in flow through ducts 118
Blasius empirical formula for wall shear stress, extension to non-Newtonian fluids 499
Boltzmann equation 161
Bookkeeping parameter  145 191 206 226 232Ч233 246 292 301 304 359 145 191 206 226 232Ч233 246 292 301 304 359
Boundary-layer approximation 2
Boundary-layer thickness 12
Boundary-layer thickness, associated Reynolds number 12
Boundary-layer, constant-stress layer 14
Boundary-layer, equations of motion 13
Boundary-layer, turbulent buffer layer 15
Boundary-layer, turbulent inner layer length scale 15
Boundary-layer, turbulent inner layer velocity scale 15
Boundary-layer, turbulent inner layer, outer layer 14
Boundary-layer, turbulent length and velocity scales 14
Boundary-layer, turbulent viscous sublayer 15
Brown Ч Roshko vortices See Coherent structures
Bursts See Turbulent bursts
Central limit theorem 531
Centroid and relative coordinate system for two-point correlations 43
Chaos 428Ч430
Closure problem 6Ч7
Closure problem, most general form 42
Coherent structures 109. See also Turbulent bursts Phase Intermittency
Coherent structures, Brown Ч Roshko roll vortices in the mixing layer 109Ч110 407Ч409
Coherent structures, in free shear flows 410
Coherent structures, quasi-periodic, non-deterministic 109
Coherent structures, turbulent slugs and puffs in pipe flow 414Ч415
Coherent structures, turbulent spots in boundary layers 413Ч414
Coherent structures, vortex pairing versus vortex tearing 110 428
Coherent structures, wave packets and turbulent spots 430
Continuity equation 2
Convolution of two functions 538
Correlation coefficient See also Lagrangian autocorrelation and Correlation coefficient
Correlation coefficient for fluctuating velocities near a solid surface 21
Correlation coefficient, experimental value in flow through a pipe 28
Correlation coefficient, general two-point form 44
Correlation coefficient, transverse and longitudinal correlation coefficients 50Ч51
Cumulants of a distribution 530
Degrees of freedom in isotropic turbulence 113Ч114
Degrees of freedom in isotropic turbulence, Fourier modes as 381
Degrees of freedom in isotropic turbulence, reduction of 365
Degrees of freedom in isotropic turbulence, relationship to Taylor Ч Reynolds number 381Ч382
Deviatoric stress tensor, Newtonian fluid 3 524
Deviatoric stress tensor, non-Newtonian fluid 495Ч497
Diagrams (in perturbation theory) 147
Diagrams (in perturbation theory) for DIA as a second-order closure 221Ч222
Diagrams (in perturbation theory) for perturbation expansion of Navier Ч Stokes equation 213Ч223
Diagrams (in perturbation theory) for perturbation expansion of Navier Ч Stokes equation, class A diagrams 217Ч218
Diagrams (in perturbation theory) for perturbation expansion of Navier Ч Stokes equation, class B diagrams 218Ч221
Diagrams (in perturbation theory), application to electron gas 204Ч205
Diagrams (in perturbation theory), disconnected graphs, reducibly connected graphs and irreducibly connected graphs 198
Diagrams (in perturbation theory), Feynman-type diagrams 186
Diagrams (in perturbation theory), introduction to the graphical method 196Ч201
Diagrams (in perturbation theory), partial summation 188Ч190
Diffusion See Diffusion by continuous movements Turbulent
Diffusion by continuous movements: Taylor's analysis 437Ч441
Diffusion by continuous movements: Taylor's analysis for long diffusion times 440
Diffusion by continuous movements: Taylor's analysis for short diffusion times 440
Diffusion by continuous movements: Taylor's analysis, equivalence to the diffusion problem in Eulerian coordinates 460Ч461
Diffusion by continuous movements: Taylor's analysis, extension to discrete particles 452
Diffusion by continuous movements: Taylor's analysis, extension to discrete particles, Tchen's analysis 454Ч456
Diffusion by continuous movements: Taylor's analysis, extension to discrete particles, Дcrossing trajectoriesУ 456
Diffusion by continuous movements: Taylor's analysis, extension to shear flows 456Ч458
Diffusion by continuous movements: Taylor's analysis, extension to three dimensions 441
Diffusion by continuous movements: Taylor's analysis, turbulent diffusion coefficient 440Ч441
Direct interaction (in DIA) 338
Direct interaction approximation (DIA) 225Ч241. See also LHDIA ALHDIA Renormalized
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), application to axisymmetric turbulence 334
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), application to inhomogeneous turbulence 331Ч338
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), calculation of freely decaying turbulence 316Ч328
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), conservation of energy 236
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), equation for response function 234
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), equation for the correlation function 234
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), idealised convection problem 273
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), inertial-range 3/2 power law 237
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), infinitesimal response tensor 226
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), mean response tensor 227
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), physical realizability 241
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), spurious convection effects 269Ч274
Direct interaction approximation (DIA), violation of random Galilean invariance 276
Dissipation rate 9 524 526
Dissipation rate for decaying turbulence 313
Dissipation rate, estimate for pipe flow 117
Dissipation rate, fluctuations in 104 328
Dissipation rate, local dissipation rate 108
Dissipation rate, measured distribution in flow through a pipe 29Ч31
Dissipation rate, relationship to energy spectrum of isotropic turbulence 66
Dissipation rate, relationship to the Taylor microscale for isotropic turbulence 52
Dissipation spectrum 84
Dissipation spectrum for decaying turbulence 313
Drag 132. See also Friction drag
Drag reduction by additives 130
Drag reduction by additives, additive degradation 134
Drag reduction by additives, comparison of macroscopic fibres with microscopic polymers 520Ч521
Drag reduction by additives, definition 131
Drag reduction by additives, effect on heat and mass transfer 518Ч519
Drag reduction by additives, effect on turbulent diffusion 519Ч520
Drag reduction by additives, heterogeneous drag reduction 511
Drag reduction by additives, homogeneous drag reduction 511
Drag reduction by additives, in fibre suspensions 133 140Ч141
Drag reduction by additives, in polymer solutions 133Ч140
Drag reduction by additives, maximum drag reduction asymptote 140
Drag reduction by additives, natural occurrence 133
Drag reduction by additives, threshold (onset) effect 136Ч139
Drag reduction, by flexible walls 498. See also Drag reduction by additives
Drag reduction, in heated boundary layers 498
Drag, form drag 132
Drag-reducing fibre suspensions, frequency of turbulent bursts 521
Drag-reducing fibre suspensions, intensities, correlations and spectrum 514Ч517
Drag-reducing fibre suspensions, mean velocity distributions 512Ч514
Drag-reducing fibre-polymer suspensions 517Ч518
Drag-reducing polymer solutions, effect on free turbulence 511Ч512
Drag-reducing polymer solutions, effect on turbulent structure 505Ч506
Drag-reducing polymer solutions, frequency of bursts 509 521
Drag-reducing polymer solutions, importance of the region near the wall 509Ч511
Drag-reducing polymer solutions, mean velocity distributions 506Ч507
Drag-reducing polymer solutions, spectra and correlations 509
Drag-reducing polymer solutions, turbulent intensities and Reynolds stress 508Ч509
Drag-reducing polymer solutions, ultimate mean velocity profile 507
Early turbulence See Non-Newtonian fluids
Eddy diffusivity 464. See also Turbulent diffusion in an Eulerian frame Diffusion
Eddy turnover time 315
Eddy-viscosity hypothesis 20. See also Subgrid models
Eddy-viscosity hypothesis, Boussinesq form 128
Eddy-viscosity hypothesis, Heisenberg-type 76 430
Eddy-viscosity hypothesis, Kolmogorov Ч Prandtl form 127
| Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory 241Ч257. See also Modified EFP theories
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, comparison with DIA 253Ч255
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck equation 245Ч248
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, energy-balance equation 252
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, expansion for the probability distribution of velocities 248Ч250
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, exponential time-dependencies 254
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, infinite value of Kolmogorov spectral constant 269
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, limit of infinite Reynolds number 255Ч257
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, Liouville equation 242
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, main hypothesis 248
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, response equation 253
Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory, turbulent ensemble 243
Effective coefficient of viscosity 8 295
Energy balance equation for fluctuating velocities 9Ч11
Energy balance equation for fluctuating velocities in wavenumber space 65Ч67
Energy balance for velocity fluctuations as computed for isotropic turbulence in wavenumber space 84Ч86
Energy balance for velocity fluctuations as measured in flow through a pipe 28Ч31
Energy cascade in wavenumber space 65 69Ч70
Energy spectrum, governing equation 66
Energy spectrum, measured one-dimensional spectra 81Ч83
Energy spectrum, one-dimensional form 61Ч63
Energy spectrum, Pao's empirical correlation 84
Energy spectrum, with respect to wavenumber 61
Energy transfer spectrum 84
Entropy, elimination of infra-red divergence 294
Entropy, maximum entropy principle for the intermittency exponent 109
Entropy, maximum entropy principle for the turbulence distribution function 290Ч294
Eulerian coordinate frame 436
Fine-structure intermittency 100. See also Structure functions Intermittent Intermittency
Fine-structure intermittency, cross over from intermittent scaling to Kolmogorov scaling 331
Fine-structure intermittency, Kolmogorov energy spectrum with intermittency correction 328
Flatness factor of a distribution 530
Flatness factor of the probability distribution of the longitudinal velocity difference 103
Fourier series 536
Fourier transform pair 537
Free-surface intermittency, conditional average 413
Free-surface intermittency, zone average 411Ч412
Friction drag, calculation for a boundary layer 17
Friction drag, empirical formulae, see wall shear stress friction (or drag) coefficient (external flows) 18
Friction drag, friction factor (internal flows) 19
Friction velocity 15
Full simulation (of turbulence) See also Large-eddy simulation (LES)
Full simulation (of turbulence), isotropic turbulence 382
Full simulation (of turbulence), Kolmogorov spectrum 384
Full simulation (of turbulence), Monte Carlo methods 401
Full simulation (of turbulence), shear flows 384Ч387
Functional formalisms 167Ч176
Functional formalisms of Hopf 174Ч176
Functional formalisms of Lewis and Kraichnan 167 169Ч174
Functional formalisms, comparison with quantum field theory 176
Functionals, characteristic 168Ч70
Functionals, probability distribution 167
Functionals, standard notation for 156
Galilean invariance 534
Galilean invariance, invariance of single-time moments 275
Galilean invariance, noninvariance of two-time moments 275Ч276
Galilean invariance, postulate of random Galilean invariance 274Ч276 340Ч342
Gaussian distribution 529
Green's function 539
Grid-generated turbulence 49
Heat and mass transfer 460Ч471. See also Turbulent diffusion Diffusion
Heat and mass transfer, application of DIA 469
Heat and mass transfer, experimental measurements in pipes and jets 470Ч471
Heat and mass transfer, experimental values of turbulent diffusities 471
Heat and mass transfer, Fick's law 461
Heat and mass transfer, Fourier's law 461
Heat and mass transfer, single-point balance equations 465Ч467
Heat and mass transfer, statistical formulation 463Ч464
Heat and mass transfer, two-point balance equations 467Ч470
Heisenberg effective viscosity theory 76Ч77
Heisenberg effective viscosity theory, basic hypothesis 76
Heisenberg effective viscosity theory, eddy viscosity 77
Homogeneous turbulence 47
Homogeneous turbulence, local homogeneity 101
Homogeneous turbulence, velocity-field moments 56Ч59
Hot-wire anemometer 89
Hot-wire anemometer, constant-current operation 90
Hot-wire anemometer, King's law 90
Hydrodynamic stability 406 433
Inertial subrange of wavenumbers 71
Inertial transfer coefficients 541
Infra-red divergence 269
Infra-red divergence, freedom from of LET 325
Input term See Work done by external forces
Integral length scales, for decaying turbulence 313Ч314
Integral length scales, general tensor form 45
Integral length scales, longitudinal scale 52
Integral time scale, Eulerian form 45
Integral time scale, Lagrangian form 438Ч439 453
Intermittency See Coherent structures Fine-structure Free-surface
Intermittency exponent  106 109 328Ч329 106 109 328Ч329
Intermittency factor 103 411 415
Intermittency function 411
Intermittent dissipation rate 104
Isotropic turbulence 48
Isotropic turbulence, isotropic spectrum tensor 59Ч61
Isotropic turbulence, isotropic two-point correlation 50
Isotropic turbulence, local isotropy 49 101
Isotropic turbulence, local isotropy and the application of Kolmogorov hypotheses to shear flows 73
Iterative averaging See Renormalization group
Karman Ч Howarth equation 502
Kinetic energy of fluid motion in general 9
Kinetic energy of fluid motion in turbulence 10
Kinetic energy of fluid motion of fluctuating velocities 11
Kolmogorov constant (in the energy spectrum) 70
Kolmogorov constant (in the energy spectrum), ALHDI prediction 325
Kolmogorov constant (in the energy spectrum), measured values 83Ч84
Kolmogorov constant (in the energy spectrum), relationship between three-dimensional and one-dimensional forms 83
Kolmogorov constant (in the energy spectrum), SBALHDI prediction 327
Kolmogorov constant (in the energy spectrum), values from numerical simulation 384 387 401
Kolmogorov constant (in the energy spectrum), variation from one class of flow to another 330
Kolmogorov dissipation length scale 68
Kolmogorov dissipation velocity scale 68
Kolmogorov dissipation wavenumber 69
Kolmogorov energy spectrum 70
Kolmogorov energy spectrum, intermittency corrections 328
Kolmogorov energy spectrum, spectral density 71
Kolmogorov Ч Obukhov log-normality hypothesis 105Ч107 328
Kolmogorov's first and second hypotheses 70
Kolmogorov's first and second hypotheses, application to scalar transport 474Ч478
Kolmogorov's first and second hypotheses, investigation by Champagne 329
Kolmogorov's first and second hypotheses, weaker forms 330
Kolmogorov's third hypothesis 105Ч106
Lagrangian autocorrelation 438
Lagrangian autocorrelation of discrete particles 453
Lagrangian coordinates for scalar diffusion 436Ч437
Lagrangian coordinates in LHDI theory 278
Lagrangian correlation coefficient 438Ч439
Lagrangian correlation coefficient, conjecture of Hay and Pasquill 444Ч446
Lagrangian correlation coefficient, conjecture of Hay and Pasquill, Corrsin's independence hypothesis 446Ч447
Lagrangian correlation coefficient, of discrete particles 453
Lagrangian correlation coefficient, problem of relation to Eulerian coordinates 441Ч447
Lagrangian integral time scale 438Ч439
Lagrangian integral time scale of discrete particles 453
Lagrangian statistical quantities experimental measurements 447Ч448
Lagrangian statistical quantities experimental measurements, from numerical simulations 448Ч449
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories 277Ч290
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories, abridged LHDI theory 286Ч288
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories, compatibility with the Kolmogorov inertial-range spectrum 286
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories, computation for decaying turbulence 324Ч328
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories, DIA adapted to Lagrangian-history coordinates 282Ч286
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories, Lagrangian coordinates 278
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories, Lagrangian-history formulation of the equations of motion 278Ч281
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories, Lagrangian-history formulation of the equations of motion, generalized velocity, solenoidal part and curl-free part 279
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories, random Galilean invariance 285Ч286 325
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories, statistical formulation: moments of the generalized velocity field 281Ч282
Lagrangian-history direct-interaction (LHDI) theories, strain-based LHDI and ALHDI 284Ч290
Langevin equation generalized to turbulence 309 351.
Large eddy simulation (LES) 118 381.
Large eddy simulation (LES), Heisenberg-type effective viscosity 119
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -model
-model 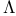 vortices
vortices 
