|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| McComb W.D. Ч Physics of Fluid Turbulence |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Large eddy simulation (LES), in configuration space 120
Large eddy simulation (LES), in wavenumber space 118Ч120 390Ч391
Large eddy simulation (LES), Leonard stress 122
Large eddy simulation (LES), resolved scales 121
Large eddy simulation (LES), shear flows 387Ч388
Large eddy simulation (LES), Smagorinsky model 122
Large eddy simulation (LES), subgrid scales 121
Laser anemometer 92
Laser anemometer, differential Doppler mode 95
Laser anemometer, frequency shifting 95
Laser anemometer, optical background 545Ч549
Laser anemometer, Дlaw of the wallУ See Mean velocity
Lattice gas models 402
Length scales see Taylor microscale Integral Kolmogorov Inner-layer Boundary
Liouville equation for an inviscid fluid 166
Liouville equation for turbulence 242 258 264
Liouville equation in statistical mechanics 157
Liouville equation, time-dependent for turbulence 263
Local energy-transfer (LET) theory 300Ч307
Local energy-transfer (LET) theory, application to the computation of total energy decay in 3D turbulence 337
Local energy-transfer (LET) theory, comparison with DIA 306Ч307
Local energy-transfer (LET) theory, computation for decaying turbulence 319Ч328
Local energy-transfer (LET) theory, equation for the pair correlation 305
Local energy-transfer (LET) theory, generalized covariance equation 305
Local energy-transfer (LET) theory, response equation for the propagator 306
Local energy-transfer (LET) theory, statistical form of the basic hypothesis 302Ч303
Local energy-transfer (LET) theory, velocity-field propagator 301
Log-normal distribution of the dissipation rate 105
Log-normal distribution of the dissipation rate, comparison with experimental results 106Ч107
Logarithmic mean velocity distribution 16Ч17
Markov process 162
Markov process, Brownian motion 162 163Ч165
Markov process, Chapman Ч Kolmogorov equation 162Ч163
Markov process, Fokker Ч Planck equation 163Ч164
Markov process, Langevin equation 163Ч164
Markov process, master equation 162Ч163
Markov process, relative diffusion 451
Markov process, scalar transport 475
Master equation See Markov process
Maximal randomness (in DIA) 338
Maxwell model See non-Newtonian fluids
Mean field theory 347 349
Mean motion effects see turbulent diffusion of particles
Mean velocity, axial and transverse distributions in a free jet 31Ч32
Mean velocity, ensemble average 39
Mean velocity, equations for 7Ч8
Mean velocity, experimental distributions in duct flows 25Ч27
Mean velocity, linear law 17
Mean velocity, mean (bulk) 4
Mean velocity, time averaged 5Ч6
Mean velocity, universal distribution near a solid surface 16Ч17
Mean velocity, Дlaw of the wallУ 16
Microscale of time, Eulerian differential scale 54
Mixing-length model 20Ч22
Mixing-length model, applied to a free jet 22Ч24
Mixing-length model, relevance of the bursting process 431
Mixing-length, free jet 23
Mixing-length, wall region 21
Mode coupling 146 247
Modified EFP theories 290Ч300. See also Edwards Ч Fokker Ч Planck theory
Modified EFP theories, local energy-transfer equations 298Ч300
Modified EFP theories, maximal entropy principle 290Ч294
Modified EFP theories, response function determined by local energy balance 294Ч298
Molecular dynamics simulation 402
Moments (of the velocity field), many-point, many-time hierarchy 41
Moments (of the velocity field), relation to cumulants 529Ч530
Moments (of the velocity field), single-point, single-time 8
Moments (of the velocity field), two-point, two-time 9
Momentum integral equation (Von Karman form) 17
Navier Ч Stokes equation 3
Navier Ч Stokes equation as used for direct numerical simulation 114
Navier Ч Stokes equation in filtered form for large-eddy simulation 122
Navier Ч Stokes equation, solenoidal (divergenceless) form 36 39
Navier Ч Stokes equation, solenoidal form in wavenumber space 55Ч56
Near-Markovian model closures See also Markov process
Near-Markovian model closures, quasi-normal Markovian approximations 307Ч308
Near-Markovian model closures, test-field model 309
Near-Markovian model closures, test-field model, computation for decaying turbulence 317Ч319
Near-Markovian model closures, test-field model, prediction of the Kolmogorov constant 318
Newton's law (as a definition of the coefficient of viscosity) 3
Newton's law (as a definition of the coefficient of viscosity), non-linear terms, conservative nature of 66 526
Newton's law (as a definition of the coefficient of viscosity), non-linear terms, conservative nature of, for second-order closure approximation 236
Non-Newtonian fluids 494
Non-Newtonian fluids, apparent viscosity 495
Non-Newtonian fluids, early turbulence 500Ч501
Non-Newtonian fluids, effect on isotropic turbulence, experimental assessment 503Ч505
Non-Newtonian fluids, effect on isotropic turbulence, theoretical assessment 501Ч503
Non-Newtonian fluids, friction factors 500
Non-Newtonian fluids, power-law fluid 495
Non-Newtonian fluids, rheological models 496
Non-Newtonian fluids, shear thinning 495
Non-Newtonian fluids, structural turbulence 500Ч1
Non-Newtonian fluids, viscoelastic 495
Numerical simulation of turbulence See Full simulation Large-eddy
Obukhov Ч Corrsin constant 474
Oldroyd model See Non-Newtonian fluids
Pair correlation (of velocities), zero-order 213
Pao's spectral correlation for isotropic turbulence 84
Passive scalar convection 460. See also Turbulent diffusion Diffusion Scalar
Phase space 154
Phase space, velocity in 156
Pitot tube 89
Poisson equation for the electron gas 202
Poisson equation for the pressure in a fluid 37
Prandtl number See also Heat and mass transfer
Prandtl number, eddy (turbulent) form 464
Prandtl number, molecular form 462
Prandtl Ч Karman empirical formula for flow through ducts 19. See also Wall shear stress
Probability distribution functions 155
Probability distribution functions, ensemble for 155
Probability distribution functions, JV-particle 156
Probability distribution functions, non-Gaussian nature for turbulence 165Ч166
Probability distribution functions, non-Gaussian nature for turbulence, in the inviscid case 167
Probability distribution functions, one-point 155
Probability distribution functions, two-point 155
Production of turbulence 28
Production of turbulence, experimental value in duct flows 30Ч31
Propagators and time evolution 184Ч185
Propagators, equivalence to Green function 186
Propagators, Fourier-transform 208
Propagators, renormalized, for the Navier Ч Stokes equation 217Ч218
Propagators, zero-order, for the Navier Ч Stokes equation 207
Proper orthogonal decomposition 430
Pseudo-spectral method 116
Quasi-normality hypothesis 78
Quasi-normality hypothesis, equation for the spectral density 81
Quasi-normality hypothesis, failure due to evolution of negative spectra 81
Quasi-particle approach 141 14
Quasi-stationarity, of decaying turbulence 314Ч315
Rate of strain tensor 496
Reduced probability distribution functions 158
Reduced probability distribution functions, distribution vector 159
Relative diffusion 449Ч452
Relative diffusion, extension to three dimensions 452
Relative diffusion, Richardson's law 451
Renormalization 141 143
Renormalization group (RG) 148Ч149
Renormalization group (RG) and upper critical dimension 349
Renormalization group (RG), application to randomly stirred fluid motion 350Ч351
Renormalization group (RG), application to sub-grid-scale modelling of turbulence 351Ч353
Renormalization group (RG), applied to critical phenomena 346
Renormalization group (RG), epsilon expansion 349
Renormalization group (RG), fixed point 148 348
Renormalization group (RG), Forster Ч Nelson Ч Stephen theory, calculation of the effective viscosity 357Ч359
Renormalization group (RG), Forster Ч Nelson Ч Stephen theory, crossover value of  362 362
Renormalization group (RG), Forster Ч Nelson Ч Stephen theory, recursion relations 359Ч361
Renormalization group (RG), iterative averaging 364
Renormalization group (RG), iterative averaging, conditional (partial) average 367
Renormalization group (RG), iterative averaging, effective dissipation wavenumber 367
Renormalization group (RG), iterative averaging, equations for effective viscosity 377
| Renormalization group (RG), iterative averaging, fixed point 377
Renormalization group (RG), iterative averaging, global averaging 368
Renormalization group (RG), iterative averaging, Markovian approximation 375
Renormalization group (RG), iterative averaging, mean field approximation 372 373
Renormalization group (RG), perturbation expansion of the Navier Ч Stokes equation 355Ч357
Renormalization, effect on growth of number of terms in perturbation series 339
Renormalization, effective mass of conduction electrons 143
Renormalization, line renormalization 222
Renormalization, partial summation 188Ч189
Renormalization, screened potential 143 202Ч203
Renormalization, vertex renormalization 222
Renormalized perturbation theory 144
Renormalized perturbation theory and the turbulence closure problem 184
Renormalized perturbation theory, application to Navier-Stokes equation 205Ч212
Renormalized perturbation theory, direct-interaction approximation DIA 144
Renormalized perturbation theory, equilibrium system with weak interactions 190Ч205
Renormalized perturbation theory, perturbation series 146
Renormalized perturbation theory, primitive expansion 208Ч212
Renormalized perturbation theory, renormalized perturbation series 147
Resistance to flow see Wall shear stress
Reversion of power series 240Ч241 289
Reynolds averaging 7 40
Reynolds equation (for the mean velocity in duct flows) 19
Reynolds number for boundary layer on a flat plate 12
Reynolds number for decaying turbulence 31Ч31
Reynolds number for dissipation range of wavenumbers 69
Reynolds number for non-Newtonian fluids 498
Reynolds number for pipe flow 4
Reynolds number, based on Taylor Microscale (Taylor Ч Reynolds number) 82
Reynolds stress 8
Reynolds stress, closure approximation 336
Reynolds stress, experimental distribution in duct flows 28
Reynolds stress, governing equation 10
Reynolds stress, in a free jet 32
Reynolds stress, total shear stress tensor 8
Reynolds's analogy 464
Richardson's law See Relative diffusion
SBLHDI, SBALHDI See Lagrangian-history direct-interaction theories
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence 471
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, application of RPTs 478Ч479
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, Batchelor wavenumber 475
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, Batchelor's model for the viscous ranges of wavenumbers 477Ч478
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, diffusion cut-off wavenumber 474
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, inertial-convective range of wavenumbers 474
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, inertial-diffusive range of wavenumbers 475
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, numerical simulation 479
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, scalar transfer spectrum 473
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, spectral covariance 472
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, spectrum of scalar variance 473
Scalar transport in homogeneous turbulence, summary of spectral forms 478
Schmidt number See also Heat and mass transfer
Schmidt number, eddy (turbulent) form 464
Schmidt number, molecular form 462
Self-consistent field (SCF) theory 257Ч265
Self-consistent field (SCF) theory, comparison with EFP theory 262
Self-consistent field (SCF) theory, Liouville equation 258
Self-consistent field (SCF) theory, perturbation expansion 261
Self-consistent field (SCF) theory, self-consistency criterion 260
Self-consistent field (SCF) theory, single-mode distribution 259
Self-consistent field (SCF) theory, single-mode operator 259
Self-consistent field (SCF) theory, theory of Balescu and Senatorski 264
Self-consistent field (SCF) theory, theory of Phythian 264Ч5
Self-consistent field (SCF) theory, time-dependent Liouville equation 262
Skewness of probability distribution 530
Skewness of probability distribution for decaying turbulence 314
Skewness of probability distribution of the longitudinal velocity difference 102
Skewness of probability distribution, independence of Reynolds number 384
Skewness of probability distribution, theoretical predictions of 319
Smagorinsky model see Subgrid models
Stationary turbulence 53
Stationary turbulence under the action of external stirring forces 71Ч72
Statistical formulation, many-point form 39Ч42
Statistical formulation, many-time moments in wavenumber space 63Ч64
Statistical formulation, single-point form 7Ч11
Statistical formulation, single-time moments in wavenumber space 64Ч65
Structural turbulence see Non-Newtonian flows
Structure functions 102 328
Sub-ensemble Eulerian correlation coefficient 447
Subgrid models See also Large-eddy simulation Eddy
Subgrid models, application of RG 397Ч399
Subgrid models, application of RPT 391Ч397
Subgrid models, assessment of subgrid models 388Ч389
Subgrid models, Smagorinsky model 122
Taylor hypothesis of Дfrozen convectionУ 62
Taylor microscale 51Ч52
Taylor microscale for decaying turbulence 313Ч314
Taylor Ч Green vortex 400
Taylor Ч Reynolds number See Reynolds number
Taylor's analysis of turbulent diffusion See Diffusion by continuous movements and Relative diffusion
Tchen's analysis See Diffusion by continuous movements
Test problems in isotropic turbulence 176Ч181
Test problems in isotropic turbulence, free decay 177
Test problems in isotropic turbulence, stationary turbulence 179
Test problems in isotropic turbulence, stationary turbulence, cross-correlation of stirring force with the velocity field 181
Test problems in isotropic turbulence, stationary turbulence, random stirring forces 180
Test-field model See Near-Markovian model closures
Thin shear layer See Boundary layer approximation
Time scales See Eddy turnover time Integral Lagrangian Lagrangian Taylor
Time series analysis 98
Time series analysis, aliasing errors 99
Tollmien Ч Schlicting waves 430
Transfer spectrum See Energy transfer spectrum Scalar
Transition from laminar to turbulent flows 406
Transitional structures See Coherent structures
Transport power 236 296
Transport power for decaying turbulence 313
Turbulence models, 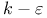 model 128 model 128
Turbulence models, algebraic stress models 128
Turbulence models, two-equation models 127
Turbulent bursts 110Ч112
Turbulent bursts, ejection-sweep cycle 112 417
Turbulent bursts, frequency of bursts 418Ч420
Turbulent bursts, frequency of bursts in drag-reducing fluids 509Ч521
Turbulent bursts, low-speed streaks 110Ч417
Turbulent bursts, production of turbulence 111
Turbulent bursts, streaky structure 418
Turbulent bursts, streaky structure and streamwise vortices 420Ч423
Turbulent diffusion coefficient 481Ч483. See also Diffusion by continuous movements
Turbulent diffusion in an Eulerian frame See Diffusion by continuous movements Heat Scalar
Turbulent diffusion of particles (in an Eulerian framework), finite-step diffusion coefficient 486
Turbulent diffusion of particles (in an Eulerian framework), governing equation 480Ч482
Turbulent diffusion of particles (in an Eulerian framework), mean motion effects 483 490
Turbulent diffusion of particles (in an Eulerian framework), measurements in turbulent flows 489Ч490
Turbulent diffusion of particles (in an Eulerian framework), perturbation treatment of finite inertia 488Ч489
Turbulent diffusion of particles (in an Eulerian framework), random walk models 484Ч487
Turbulent mixing 490Ч491
Turbulent mixing, diffusion limited 491
Turbulent spots See Coherent structures
Two-dimensional mean flows 1
Two-dimensional mean flows as a special case 12
Ultraviolet catastrophe 166
Unidirectional laminar flow 3
Unphysical oscillations in response function of DIA 317
Unphysical oscillations in response function of LET 324
Velocity field in wavenumber space 54
Velocity fluctuations in a free jet 32
Velocity fluctuations, experimental values for the r.m.s. distributions in duct flows 27Ч28
Viscosity, anomalous extensional viscosity in polymer solutions 135Ч136 497
Viscosity, dynamic viscosity 3
Viscosity, extensional viscosity 497
Viscosity, kinematic viscosity 3
Viscosity, molecular viscosity as a Дbare quantityУ 143 148
Viscous dissipation of energy See Dissipation rate
von Karman constant 21
von Karman constant, experimental value 26
Vortex pairing See Coherent structures
Vortex simulation of turbulence 402
Vortex stretching as an interpretation of turbulence 73Ч75
Vortex stretching as an interpretation of turbulence, relevance of numerical simulation 426
Vortex tearing See Coherent structures
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте




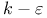 model
model