Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Randall J.T. — The Diffraction of X-rays and Electrons By Amorphous Solids, Liquids, and Gases
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: The Diffraction of X-rays and Electrons By Amorphous Solids, Liquids, and GasesАвтор: Randall J.T. Аннотация: For the purposes of structural investigations the various forms of matter may conveniently be divided into four classes,namely, crystalline solids, amorphous solids, liquids, and gases. Following on the work of W. L.Bragg in the years 1912 and 1913 knowledge of the arrangements of atoms and molecules in the crystalline state has increased continually at a very rapid rate.The first investigations on the diffraction of X-rays by amorphous solids and liquids were published by Debye and Scherrer in 1916, but it is only comparatively recently that anything like a proper understanding of the results has been obtained. The theories which have been proposed to explain the experimental results are all ultimately. concerned with the degree of structure in the substances, and the working out of the ideas has depended to a large extent on the results of X-ray crystallography. For example, in order to determine the degree of atomic arrangement that may be assigned to a piece of silica glass or a drop of water, the structures of cristobalite and ice must be accurately known.Between the truly crystalline solid and the amorphous solid there exists a vast region of microcrystalline substances of great chemical and biological importance;of these, carbon blacks, cellulose, stretched rubber, and the proteins may be mentioned.In addition there are the substances which may be microcrystalline in one direction only;this description applies to a large number of surface layers, from those due to chemical action with the underlying substance to the two-dimensional crystal in the form of a gas layer. The method of electron一diffraction is ideally suited to the investigation of structure in such cages as these.Finally, the same method, as well as that of X-ray diffraction,may be used to study the structure of single gaseous molecules.
Язык: Рубрика: Физика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Издание: 1st editionГод издания: 1934Количество страниц: 290Добавлена в каталог: 30.08.2009Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
17 262 83—84 Acetone, distance between carbon atoms in 97 Acetyl halides 101 Acetylene, structure of molecule 95 Adam, surface layers 3 156 224 Adsorbed gases and carbon structure 195 Adsorbed gases on nickel, diffraction of electrons by 241 Alanine residues 215 Alcohols, liquid, Stewart and Morrow's results 156 Alcohols, liquid, Warren's interpretation 157 Alg 209 Aliphatic compounds, distance between carbon atoms in 92 224 Alkali metals, 84 Alkali metals, aggregation in vapour phase 132 Alkali metals, diffraction of X-rays by liquid 129—135 Allis and Morse, quantum theory of Ramsauer effect 89 Aluminium, cold-drawn wire 14 Aluminium, liquid 133 Amaldi, diffraction of X-rays by water 137 Amorphous solids 2 28 173 Amorphous solids, theory of diffraction of X-rays by 178 Andrade, viscosity of liquids 165 Andress, cellulose structure 204 Antimony sesquioxide glass 177 Argon, gas, scattering of X-rays by 54 Argon, liquid, scattering of X-rays by 128 Arnot, scattering of slow electrons by atoms 77 80 85 Aromatic compounds, distance between carbon atoms in 93 Asahara, amorphous carbons 190 Astbury, and Marwick, cellulose structure 205 Astbury, and Street, structure of hair and wool 215 Astbury, Fundamentals of Fibre Structure 200 Astbury, Fundamentals of Fibre Structure, investigations on muscle 221 Astbury, Fundamentals of Fibre Structure, views on gelatin 221 Astbury, structure of hair and wool 3 Atomic and ionic radii, tables of 264 Atomic arrangement in crystals 22 Barnes, structure of ice 139 Beilby, aggregation and flow of solids 244 Benzene, liquid 159—161 Benzene, solid 26 161 Benzene, vapour 92 Bernal, and Crowfoot, liquid crystals 253 258 Bernal, and Fowler, structure of ice and water 140 et seq. Bernal, and Fowler, theory of ionic solution 150 Bernal, crystal structure of amino-acids 222 Bernal, crystal structure of graphite 188 Bethe, refraction of electron waves 239 Bewilogua, diffraction of X-rays by chlorine - substituted methanes 71—73 Bismuth, liquid 134 Bismuth, melting of 252 Bismuth, sesquioxide, vitreous 177 Blatchford, diffraction of X-rays by liquid sulphur 135 Boas and Rupp, diffraction of electrons by passive and pure iron 241 Bohm, X-ray examination of muscle 221 Bone, constitution of coal 196 Boric anhydride, vitreous 177 Born, and K 260 Born, calculation of crystal spacings and energies 27 Born, lattice dynamics 260 Born, theory of scattering of electrons by gases 81 Boron trichloride vapour 92 Boron trichloride vapour, amide 95 Bradley, structure of selenium 183 Bragg, and, Darby shire, diffraction of electrons by thin films 231 Bragg, focal conics in liquid crystals 259 Bragg, intensity of reflexion 19 Bragg, James and Bosanquet, intensity of X-ray reflexion from crystals 19 Bragg, Sir W. H., structure of ice 139 Bragg, structure of diamond 188 Bragg, structure of silicates 25 Bragg, W. L., Law of Reflexion 11 Braunbek, melting of polar compounds 260 Brill, and Pelzer, determination of particle size 38 42 Brill, determination of particle size 44 Brill, structure of natural silk 215 Brockway and Pauling, diffraction of electrons by carbon suboxide 99 Brockway and Pauling, diffraction of electrons by hexafluoride vapours 98 100 Brockway and Pauling, diffraction of electrons by methyl azide 99 100 Bromine, distance apart of atoms in 92 Bromoform, structure of 97 Bullard and Massey, scattering of slow electrons by atoms 78 Bullard and Massey, scattering of slow electrons by molecules 88 Cadmium, oxide film, diffraction of electrons by 231 232 Cadmium, pyrophosphate, vitreous 177 Cadmium, scattering of electrons by vapour 81 Cameron, investigations on particle size 44 Carbon dioxide, solid 23 Carbon dioxide, structure of molecule 74 Carbon disulphide, structure of molecule 75 92 100 Carbon suboxide, structure of molecule 99 Carbon tetrachloride, dipole moment of 72 Carbon tetrachloride, liquid 122—125 Carbon tetrachloride, vapour 65 91 93 100 Carbon, amorphous 190 Carbon, crystalline forms of 188 Carbon, effect of crystal size on hardness of 191 Carbon, effect of crystal size on spacings 192 Carbon, inner potential of graphite 245 Carbon, single, double, and triple bond distances in compounds of 92 95 Carbonyl compounds, molecular structure 99—100 Catalysis and electron-diffraction 241 Cates, oxidation of iron 241 Celluloid 211 Cellulose, acetates 211 Cellulose, nitrates 209—210 Cellulose, structure of 202 et seq. Chi 81 Chi 88 Chlorine molecule, structure of 76 Chlorine-substituted methanes 72—73 Chloroform, molecular structure of 72 Cholesteric liquid-crystals 254 Clark, amorphous carbons 193 Clark, on cellulose 211 Clark, on gutta-percha 214 Close-packing in liquids 118 134 Close-packing in polish-layers 245 Coal, nature of 196 Coal, X-ray investigations of 197 Collagen, X-ray pattern of 221 Compton, A. H., scattering of X-rays by single atoms 56—57 Coster and Prins, liquid mercury 135 Cotton see Cellulose Cotton-grass, X-ray pattern of 211 Cox, crystal-structure of benzene 160—161 Crystals, perfect and imperfect 18 Crystals, size, dependence of spacing on 48 Crystals, structure of 14—26 Cyanogen, structure of molecule 95 Cybotaxis 115 126 Cyclic compounds, structure of 92 95 159 Darbyshire and Dixit, investigation of polish 245 Davisson and Germer, adsorbed gases on nickel 241 Davisson and Germer, experiments on 232 et seq. Davisson and Germer, inner potential of nickel 239 Davisson and Germer, refraction effect 239 Davisson and Germer, wave-nature of electron 3 de Broglie, wave-nature of electron 76 79 227 Debye and Scherrer, diffraction of X-rays by carbons 190 Debye and Scherrer, diffraction of X-rays by liquids 106 Debye, diffraction of X-rays by- powdered crystals 13 14 Debye, gradation between scattering curves for liquids and gases 166 Debye, scattering of X-rays by gases 62 Debye, scattering of X-rays by liquids 121—124 Debye, structure of isomers 66 Dennison, data for ice 140 Dennison, vibrations in molecules 260 Di-iodobenzenes, molecular structure 98 Diacetylene, structure of 95 Dichlorobenzene, structure of ortho- and para-molecules 76 Dichloroethanes, structure of 71 Dichloroethylene, structure of isomers 70 96 Dichloropentane, free rotation in 96 Dipole moments of chlorine-substituted methanes 72 Distribution of particle size 47 Dornte, diffraction of electrons by vapours 96—97 99 Dupin, cyclides of 259 Durain 197 Dymond and Watson, scattering of electrons by gases 77 Ehrenfest, formula 64 Ehrenfest, scattering of X-rays 62 Ehrhardt, structure of isomeric dichloroethylenes 70—71 Electron-optics 246 Electrons, diffraction by gases and vapours 76 89 Electrons, diffraction by liquids 169 Electrons, diffraction by single crystals 238 Electrons, diffraction by surface layers 240 241 Electrons, diffraction by thin films 231 Electrons, radial distribution of in atoms 58 61 Electrons, wave-nature of 3 76 228 Elsasser, wave-nature of electron 229 Ethane, structure of 95 Ethyl ether, X-ray examination, near critical point 167 Ethyl iodide, C — I distance in 97 Ethyl para-azoxybenzoate liquid crystals 254 256 Ethylene, structure of 95 Ewald and C. Hermann, Strukturbericht 4 Fajans, ionic refractivities in solution 150 Farnsworth, diffraction of electrons by copper 238 Fatty acids, liquid 158 Fax 87—88 Fibres, organic 200 et seq. Fibroin see Silk natural Finch, electron-diffraction apparatus 237 Focal conic structure of liquid-crystals 253 258 Formic acid, structure in vapour phase 96—97 Fowler (R. H.), partition functions for crystals 22 Fowler structure of water see Bernal and Fowler Free rotation in organic compounds 70—71 94—96 French, diffraction of electrons by polished metals 244 Friedel (G. and E.), liquid-crystals 253 256—258 Gajewski, structure of gaseous molecules 72 Gallium, liquid 125 134 Gases, near critical point 166—168 Gases, radial electron distribution in 58—62 Gases, scattering of electrons by 76 89 Gases, scattering of X-rays by 52—62 Gelatin, structure of 221 Germanium oxide, vitreous 182 Germer, diffraction of electrons by adsorbed gases 241 (see also Davisson and Germer) Glass, conchoidal fracture of 174 Glass, diffraction of X-rays by 175 Glass, Reststrahlen from 186 Glass, results for complex glasses 185 Glass, results for single substance glasses 177 Glucose residues 204 206 Glycerine, effect of temperature on scattering of X-rays 163 Glycine residues 215 Gnomonic projection 7 Goetz, melting of metals 252 Goldschmidt, radius ratio of glass-forming oxides 178 Goldschmidt, values of atomic and ionic radii 264 Goniometer, optical 7 Goniometer, Weissenberg X-ray 202 Grandjeari's terraces 253 Graphite, and amorphous carbons 190 Graphite, change of spacing with crystal size 192 Graphite, crystal structure of 189 Graphite, diffraction of electrons by polished 245 Graphite, inner potential of 245 Graphitic acid 193 Graphitic acid, sorption of potassium between (002) planes 195 Graphitic acid, sorption of water between (002) planes 194 Grinten, van der, effect of heat-motion on scattering of X-rays by 76 Gutta-percha, X-ray examination of 214 H 256 Hair, effect of steam on 219 Hair, stretched and unstretched, structure of 216 Hardy, coefficient of friction and molecular weight 240 Harnwell, scattering of electrons by gases 77 Hartree, method of self-consistent fields 21 53 Haworth, constitution of sugars 204 Heisenberg, allowance for incoherent radiation 74 Hendricks and others, di-iodobenzenes 98 Hengstenberg and Br 96 Hengstenberg, size of ramie crystallites 208 Hengstenberg, size of stretched rubber crystallites 213 Hermann, and Krummacher, effect of electric and magnetic fields on liquid crystals 257 Hermann, C., types of mesophase 254 Hermann, K., liquid crystals 257 Herzog, G., scattering of X-rays by gases 55 Herzog, gelatin 221 Herzog, nitrates of cellulose 209 Herzog, R. O., cellulose 204 Hewlett, diffraction of X-rays by liquids 107—109 Hexafiuorides, structure of molecules 98 100 Hofmann, K. A. and U., structure of amorphous carbons 190 Homeomorphous transition from solid to liquid 252 Hydrate cellulose 207 Hydration of ions 149 150 Hydrocarbons, diffraction of X-rays by liquid 151 Hydrocarbons, structure of single molecules 92 95 Ice, crystal structure of 138—142 Incoherent radiation 53—54 57—61 74 Inner potential 239 Intensity of reflexion of X-rays from crystals 17 Ionisation spectrometer 12 Ions, effect of on structure of water 149—150 Iron, diffraction of electrons by 238 241 Isomers, structure of 70 96 97 Isoprene 212 Ives, aggregation of alkali-metal vapour molecules 132 James and Brindley, tables of atomic scattering factors for X-rays ( 262 James, temperature-factor in X-ray reflexion from crystals 22 James, temperature-factor in X-ray scattering curves for gases 76 James, temperature-factor in X-ray scattering curves for gases, 19 Jauncey, “diffuse” scattering of X-rays by crystals 55 59 Jenkins, polished carbon surfaces 245 Katz, cellulose nitrates 209 Katz, gelatin 221 Katz, liquid fatty acids 158 Katz, rubber 212 Katz, starches 212 Katz, swelling phenomena 210 Keesom and de Smedt, diffraction of X-rays by liquids 128 Keesom and de Smedt, use of Ehrenfest formula 108 Keesom, diffraction of X-rays by liquid alkali metals 130 Keratin see Hair Kikuchi lines 238 Knoll and Ruska, on lenses for electrons 247 Kratky and Kuriyama, natural silk 215 Krishnamurti, diffraction of X-rays by liquids 115 158 160 164 Langmuir, surface layers 3 224 Latex, rubber 212 Laue, diffraction of X-rays by crystals 11 Laue, method of determining crystal structure 12 Laue, method of determining particle size 35 Lawrence, liquid crystals 253 Lead, liquid 134 Lead, metasilicate, vitreous 177 Lennard — Jones, activated adsorption 260 Lennard — Jones, crystal energies 27 Lennard — Jones, crystal spacing and crystal size 48 Lennard — Jones, force constants for gases 105 Lindemann, formula for melting-point 259 Liquid crystals 252 et seq. Liquids, and gases, gradation between 63 166
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



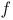 -factor
-factor 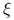 -curves
-curves 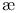 , structure of Valonia ventricosa
, structure of Valonia ventricosa  -curve for sodium
-curve for sodium 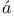 rm
rm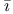 ds and Massey, scattering of electrons by cadmium vapour
ds and Massey, scattering of electrons by cadmium vapour n and Holtsmark, theory of electron-scattering by single atoms
n and Holtsmark, theory of electron-scattering by single atoms 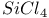 molecules
molecules  ckel, X-ray examination of liquid crystals
ckel, X-ray examination of liquid crystals 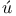 , structure of formic acid
, structure of formic acid