Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Randall J.T. — The Diffraction of X-rays and Electrons By Amorphous Solids, Liquids, and Gases
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: The Diffraction of X-rays and Electrons By Amorphous Solids, Liquids, and GasesАвтор: Randall J.T. Аннотация: For the purposes of structural investigations the various forms of matter may conveniently be divided into four classes,namely, crystalline solids, amorphous solids, liquids, and gases. Following on the work of W. L.Bragg in the years 1912 and 1913 knowledge of the arrangements of atoms and molecules in the crystalline state has increased continually at a very rapid rate.The first investigations on the diffraction of X-rays by amorphous solids and liquids were published by Debye and Scherrer in 1916, but it is only comparatively recently that anything like a proper understanding of the results has been obtained. The theories which have been proposed to explain the experimental results are all ultimately. concerned with the degree of structure in the substances, and the working out of the ideas has depended to a large extent on the results of X-ray crystallography. For example, in order to determine the degree of atomic arrangement that may be assigned to a piece of silica glass or a drop of water, the structures of cristobalite and ice must be accurately known.Between the truly crystalline solid and the amorphous solid there exists a vast region of microcrystalline substances of great chemical and biological importance;of these, carbon blacks, cellulose, stretched rubber, and the proteins may be mentioned.In addition there are the substances which may be microcrystalline in one direction only;this description applies to a large number of surface layers, from those due to chemical action with the underlying substance to the two-dimensional crystal in the form of a gas layer. The method of electron一diffraction is ideally suited to the investigation of structure in such cages as these.Finally, the same method, as well as that of X-ray diffraction,may be used to study the structure of single gaseous molecules.
Язык: Рубрика: Физика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Издание: 1st editionГод издания: 1934Количество страниц: 290Добавлена в каталог: 30.08.2009Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Liquids, Debye's theory 121 124 Liquids, diffraction of X-rays by 106—168 Liquids, Experimental results on 128—168 Liquids, general features of diffraction phenomena 106—107 Liquids, Keesom-de Smedt — Ehrenfest relation 108—109 Liquids, Prins — Zernike theory 116—119 Liquids, Raman's theory 110—113 Liquids, Stewart's theory 115 126 127 Liquids, theories of 104 Lithium metaborate glass 177 Lonsdale, Mrs., nature of benzene ring 159 160 Lowry and Bozorth, effect of size on spacing of 191 Lowry and Bozorth, particle size of carbons 48 M 152—153 Magnetic fields, effect on, on liquid crystals 257 Magnetic fields, focussing in electron-diffraction 237 Mahadevan, diffraction of X-rays by coal 197 Mark, and Wierl, scattering of electrons by carbon tetrachloride 77 Mark, cellulose micelles 208 (see also Meyer and Mark) Mark, distribution of particle size 48 Massey see Bullard and Massey Mathieu, nitrates of cellulose 209 Maxwell, diffraction of electrons by liquids 169 Mecke, model for water molecule 147 Melting 4 22 Melting, of crystals 251 Melting, of glasses 252 Melting, of liquid crystals 252 Melting, of two-dimensional gas layers 244 Melting, point 259 Menke, diffraction of X-rays by liquid carbon tetrachloride 122 Menke, diffraction of X-rays by liquid gallium 125 Mercerised cellulose 207 Mercury, scattering of electrons by liquid 170 Mercury, scattering of electrons by vapour 81—82 Mercury, scattering of X-rays by liquid 118 121 131 134 Mercury, scattering of X-rays by vapour 56 Mesoforms of liquid crystals 253 Methane molecule, electronic structure of 88 Methyl azide 99—100 Methyl bromide and iodide 97 Methylene dichloride 72 Methylene iodide 97 Meyer and Mark, cellulose structure 205 Meyer and Mark, fibroin structure 215 Meyer, A. W., diffraction of X-rays by liquid mixtures 164 165 Meyer, H. H., diffraction of X-rays by solutions 150 Meyer, H. H., diffraction of X-rays by water 138 Meyer, K. H., and von Susich, diffraction of X-rays by gelatin 221 Microcrystalline solids, diffraction of X-rays by 28 173 200 Miles and Craik, cellulose nitrates 209 Miller indices 6 Morphotropic transition from solid to liquid 252 Morrow, liquid fatty acids 158 (see also Stewart and Morrow) Mott, theory of elastic scattering of electrons by gases 81—84 Murison, diffraction of electrons by organic surface layers 240 Muscle, X-ray examination of 221 Naray — Szabo, nitrocellulose structure 209 Nematic mesoform 253 Nematogenic crystals 255 Nickel, diffraction of electrons by 233 236 Nickel, gas layers on 241 Nitrogen, adsorption on hydrogen on nickel 244 Nitrogen, gas, scattering of electrons by 86 88 Nitrogen, gas, scattering of X-rays by 72 Nitrogen, liquid, scattering of X-rays by 128 Nitrous oxide, structure of 92 Noll, diffraction of X-rays by ethyl ether 167 Normand, scattering of slow electrons 88 Normann's compound 210 Oils, diffraction of electrons by 170 241 Orientation, in cold-drawn wires 14 Orientation, in organic fibres 200 Orientation, of molecules in surface layers 225 240 Ornstein and Kast, effect of high-frequency fields on liquid crystals 257 Ornstein, swarm theory of liquid crystals 258 Palmitic acid, arrangement of layers of 226 Para-azoxyanisole 254 Para-crystalline, use of term 253 Paraffins, liquid 151 155 Paraffins, M 152 153 Paraffins, Warren’s work on 154 155 Particle size, dependence of crystal spacing on 48—50 Particle size, determination from X-ray measurements 28 47 Particle size, distribution of 47 Pauling, values of atomic and ionic radii 264 Pearson and Arnquist, scattering of electrons by argon 79 Pelzer, determination of particle size 38 42 Pentane, structure of 92 95 Phosphorus, similarity of red and violet forms 198 Phosphorus, trichloride, structure of molecule 92 Pierce, diffraction of X-rays by dichlorobenzene 76 Platinum, sputtered films of 241 Polanyi, X-ray diagrams of fibres 203 204 Polish on various surfaces 244 Polyesters, fibre structure of 222 Polyoxymethylenes, fibre structure of 222 Polypeptide chains 215 Potassium, alloy with sodium 164 Potassium, crystal structure of 130 Potassium, diffraction of X-rays by liquid 130 Potassium, interplanar sorption by carbon 195 Powdered-crystal method 13 Protein structure 214 et seq. Raman and Ramanathan, theory of X-ray diffraction by liquids 110 Ramie fibre, size of crystallites 208 Ramie fibre, X-ray diagram of 202 Ramsauer effect 88 89 Randall and Rooksby, diffraction of X-rays by glasses 175—178 184—187 Randall and Rooksby, diffraction of X-rays by liquid metals 129—131 Randall and Rooksby, diffraction of X-rays by phosphorus 197—198 Randall and Rooksby, particle size of amorphous carbons 48 191 Randall and Rooksby, polish on metals 245 Rare gases, comparison with Born — Mott theory 85 Rare gases, elastic scattering of electrons by 80 Rare gases, results for krypton compared with Holtsmark theory 87 Richter, structure of chlorine molecule 76 Rinne, liquid crystals 253 Rotation-photographs of single crystals 12 Rotation-photographs of single crystals, similarity to fibre diagrams 201 Rubber, crystallite size in stretched 213 Rubber, X-ray examination of 212 Rupp, diffraction of electrons by by iron 238 Rupp, diffraction of electrons by by nickel 236 Rupp, diffraction of electrons by by thin films 232 Rupp, diffraction of electrons by mineral oils 170 Sauerwald and Teske, structure of liquid gallium 134 Scattering of slow electrons by gases 76—89 Scherrer, and St 56 Scherrer, on particle size determination 31 Schr 85 228 Selenium, crystalline and vitreous 183 Seljakov, formula for crystal size 31 Seljakov, X-ray examination of glasses 175 Sherman, tables of sin 267 Silica, crystals, cubic 23 Silica, vitreous 176—182 Silicates, complex vitreous 187 Silicates, crystalline 25 Silicon tetrachloride, structure of molecule 76 Silk, artificial 207 211 Silk, natural 215 Single crystal surfaces, diffraction of electrons by 238 Smectic mesoform 253 Smectogenic crystals 255 Sodium chloride, 20 Sodium chloride, crystal structure of 23 Sodium chloride, effect of aggregation on spacing of 50 Sodium chloride, intensity measurements on 20 Sodium, borate, vitreous 177 Sodium, liquid 130 Sodium, metasilicate, vitreous 177 Sodium, oleate, liquid crystalline 256 Sogani, diffraction of X-rays by liquids 112 151 158 Solutions and liquid mixtures, diffraction of X-rays by 150 164 Spangler, diffraction of X-rays by ethyl ether 167 Speakman, physical properties of wool 216 Starches 212 Staudinger, constitution of sugars 204 Stereographic projection 7 Stewart and Morrow, liquid alcohols 156 Stewart, theory of diffraction of X-rays by benzene 160 Stewart, theory of diffraction of X-rays by liquid paraffins 151 Stewart, theory of diffraction of X-rays by liquids 115 126—127 Stewart, theory of diffraction of X-rays by other hydrocarbons 155 Stewart, theory of diffraction of X-rays by water 138 Stock and Wierl, structure of 95 Structure factor 16 Sugars 204 206 Sulphur, dioxide, S—O distance in 92 Sulphur, liquid, scattering of X-rays by 135 136 Sulphur, plastic 184 Surface lines in electron diffraction 239 Surface structure, examination by electrons 238 240 Surface structure, examination by X-rays 224 Surface structure, in layers of fatty acids 225 Temperature, concept of “structural” 151 Temperature, effect of, on diffraction of X-rays by crystals 22 Temperature, effect of, on diffraction of X-rays by liquids 162—164 Temperature, effect of, on diffraction of X-rays by vapours 76 Tendon, X-ray examination of see Collagen Tertiary butylbromide 97 Tetrachlorethylene 97 Tetrahedral molecules 65—69 76 92—93 100 Thallium oleate and stearate 257 Thallous palmitate 254 Thomson, diffraction of electrons by single crystal surfaces 236 238 Thomson, diffraction of electrons by thin films 230 241 Thomson, G. P., wave-nature of electron 3 76 228 Trichlorethylene, structure of 97 Trillat, diffraction of electrons by mercury 170 Trillat, films of organic compounds 241 Trillat, structure of nitrates of. cellulose 209 Trillat, surface layers 224—225 Triphenylmethane, powder and liquid, scattering of X-rays by 117 Trogus and Hess, cellulose structure 204 209 Tungsten, cold-drawn wire 14 Tungsten, crystal structure of 15 Tungsten, diffraction of electrons by polished 245 Tungsten, diffraction of electrons by single crystal of 238 Vapours, models of typical molecules 100 Vapours, scattering of electrons by 89 101 Vapours, scattering of X-rays by 62 76 Vaseline, diffraction of electrons by 240 Vinyl bromide, structure of 97 von Susich, nitrates of cellulose 209 von Susich, rubber 213 Vorl 253 Warren, diffraction of X-rays by glasses 178 Warren, diffraction of X-rays by liquids 153 158 Water, degree of hydration of ions 149 Water, diffraction of X-rays by 136—151 Water, effect of ions on structure of 149 Water, mobility of 151 Water, structure of single molecule 72 146—147 Weissenberg X-ray goniometer 202 Wentzel, intensity of incoherent radiation 54 Wierl, scattering of electrons by gases and vapours 77 90 91—96 Wollan, scattering of X-rays by gases 54 55 57 58 60 61 Wood, W. A., particle size in steel 47 Wood, X-ray examination of 211 Wyckoff, Crystal Structure 203 Wyckoff, diffraction of X-rays by glasses 175 Wyckoff, diffraction of X-rays by solutions 164 Zachariason, structure of glass 178 Zernike, liquids 3 116 Zinc, scattering of electrons by vapour 88 Zocher, liquid crystals 258 Zworykin, electron-optics 247
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 ller, structure of solid hydrocarbons near melting-point
ller, structure of solid hydrocarbons near melting-point 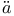 ger, diffraction of X-rays by mercury vapour
ger, diffraction of X-rays by mercury vapour  dinger equation
dinger equation 
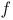 -factor for
-factor for 
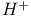 and
and  ions in
ions in