|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Luder S., Zuffanti W.F. — The Electronic Theory of Acids and Bases |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Hydrogen fluoride 16
Hydrogen fluoride, catalyst in sulfonations and nitrations 132
Hydrogen fluoride, catalytic effect of 108 110 115 121 122 125
Hydrogen ion 3
Hydrogen ion, as an oxidizing agent 10 11
Hydrogen sulfide as an acid 4
Hydrogen-molecule ion 21
hydrolysis 8 63
Hydrolysis, of benzyl chloride 130
Hydronium ion 7 8 9 10
Hydroquinone, amphoteric behavior of 75
Hydrosulfide ion 9
Hydroxy ketones, preparation of 124
Hydroxyl ion 3 7 9
Hydroxyl ion, catalytic effect of 112
Hydroxyl ion, reducing action 53
Hydroxylamine, reaction with carbonyl compounds 127
Indicators 15 16 95 96
Inert solvents 4 57
Iodination with silver perchlorate catalyst 129
Iodine 55
Iodine heptafluoride 20 32 34
Iodine monochloride 32
Iodine pentachloride 32
Iodine trichloride 32
Iodine, basic behavior of 129
Ionic complexes, in Friedel — Crafts reactions 115
Ionic complexes, in halogenations 128
Ionization potentials 36
Jander 11
Knoevenagel reaction 143
Lavoisier 3
Leveling effect 57 104 105
Liebig 3
Magnesium aluminum alkoxides, catalytic action of 150
Magnesium, reaction with water 10 29 46
Malachite green 96
Mechanism, of acylations 123
Mechanism, of aldolization 138 151
Mechanism, of alkylation 110 116 119
Mechanism, of base-catalyzed Cannizzaro reaction 146
Mechanism, of benzoin reaction 147
Mechanism, of carbonyl condensations 138 139 140 141 143
Mechanism, of Claisen reaction 140
Mechanism, of crotonization 151
Mechanism, of cyclic ketone formation 132
Mechanism, of glycol ester formation 155
Mechanism, of halogenation 129 130
Mechanism, of Knoevenagel reaction 143
Mechanism, of nitration 131
Mechanism, of Perkin reaction 141
Mechanism, of sulfonation 131
Mercuric chloride, as an acid 4
Mercuric salts, acidic behavior of 130
Mercuric salts, catalytic effect of 130
Meta-directing groups 62 81
Metals, reactions of acids with 10 11 46 53 69
Metathesis 77 78
Methyl alcohol 4
Methyl iodide 14
Methylene blue, absorption curve 109
Molecular compounds 88
Molybdenum chlorides 20
Negative fragments 84
Neutralization, and Br nsted theory 87 99 nsted theory 87 99
Neutralization, and displacement 87 103
Neutralization, electronic theory 15 16 17 43
Neutralization, Lewis theory 15 16 17 43
Neutralization, positive-negative theory 14
Neutralization, primary acids and bases 15 16 17 43 87
Neutralization, secondary acids and bases 60 87
Neutralization, solvent effect in 102 103
Neutralization, solvent-systems theory 10 11 12
Neutralization, water theory 3
Nitration mechanism 131
Nitric acid, titration of 92
Nitro radicals 81 82 85
Nitrobenzene, substitution in 82 85
Nitrogen dioxide 76
Non-metals, reactions of bases with 53 69
Nucleophilic radicals 80
Octet theory 19 20
Odd-electron molecules 75 76 77
Olefins, alkylation with 111
Oleum, catalyst in anthraquinone formation 133
One-electron bonds 21
One-element theories 5
Orbitals, atomic 18 21 22 23 25
Ortho- and para-directing groups 62 81
Osmium chlorides 35
Osmium fluorides 20 35
Oxidation-reduction 69 70 77 78
Oxidation-reduction, in positive-negative theory 14
Oxidizing agents, ammonium ion 10
Oxidizing agents, ammonium ion, cation of solvent 10 11 53 54 69
Oxidizing agents, ammonium ion, hydrogen ion 10 11 69
Oxidizing agents, ammonium ion, silver ion 73
Oximcs, formation of 127
Oxonium hydroxide 4
Oxonium salts 3
Oxyacids 38
Oxygen as a constituent of acids 5
Parachor 21
Perchloric acid 34 38
Periodic chart 24
Perkin reaction 141
Permanganic acid 34
Phenanthrene, halogenation of 129
Phenol, substitution in 83 85
Phenolphthalein 4
Phosgene 10 11 12 45 49 50
Phosphates, catalytic action of 142
Phosphorus pentabromide 30
Phosphorus pentachloride 30
Phosphorus pentafluoride 19 27 29 30
Phosphorus trifluoride 30
Piperidine 9
Positive fragments 84 108 109 110 111 128
Positive-negative theory 13 14
Potassium amide 10 12
Potassium chloride 12
Potassium cyanide 14
Potassium ethoxide 12
Potassium sulfite as a base 12
| Primary acids and bases 60
Protective coatings 57
Proton-donor theory 6 (see also Br nsted — Lowry theory) nsted — Lowry theory)
Pyridine 16 43 44 45 49 51 63
Pyridine, basic behavior of 138
Pyridine, catalytic action of 142
Pyridine, titration of 91 92 94
Quantum numbers 23
Qumoline, catalytic action of 142
Radicals, acidic 81 82
Radicals, basic 81 83
Radicals, electron-release characteristics 81 83 84
Radicals, electron-withdrawal characteristics 81 82
Radicals, meta-directing 62 81
Radicals, nucleophilic 80
Radicals, ortho- and para-directing 62 81
Rare earths 24 28
Reducing agents, amide ion 73
Reducing agents, anion of solvent 53 54 55 69
Reducing agents, hydroxyl ion 53 69
Reducing agents, iodide ion 74
Reducing agents, sulfide ion 73
Related metals 21 24 25 26
Representative elements 20 24
Resonance 37 38
Rule of eight 19 20
rule of two 27 28 32
Salts 88
Secondary acids and bases 60
Selenium oxychloride 12 51 53 54
Semicarbazones, formation of 127
Sharing of electrons 23
Sidgwick 16
Silicon dioxide 5
Silicon tetrachloride 12
Silicon tetrafluoride 29 59
Silver hydroxide 101
Silver perchlorate, acidic behavior of 129
Silver perchlorate, titration of 91
smith 12
Sodium 14
Sodium amide 10
Sodium amoxide 4
Sodium ethoxide 4
Sodium hydroxide 15 16
Sodium oxide 6 14
Solvent, inert 4 57 102
Solvent, ionizable 102
Solvent, reaction of acids and bases with 46—58 165
Solvent-systems theory 9 10 11 12 13 45
Solvo acid 11
Stannic chloride 12 16 17 28 39 54 59
Stannic chloride, absorption curve 109
Stannic chloride, titration of 91 92
Strength of acids and bases 47 49 57 58 105 106
Substitution mechanism, acidic radicals in 84 85
Substitution mechanism, basic radicals in 84 85
Sulfates, catalytic action of 142
Sulfide ion 9
Sulfo radicals 81
Sulfonation, mechanism of 131
Sulfonation, of benzene 63 109
Sulfur dioxide, electronic formula 37
Sulfur dioxide, solvent 54
Sulfur fluorides 19 20 27 31
Sulfur hexafluoride 19 20 27
Sulfur monoxide 36 37 54 55
Sulfur trioxide, as an acid 12 14 16 43 46 47 63 109
Sulfur trioxide, catalytic activity of 110
Sulfur trioxide, electronic formula of 37
Sulfuric acid, conductance in ether 51
Sulfuric acid, electronic formula of 33 37 38
Sulfuric acid, solvent 4
Sulfuric acid, titration of 92
Tetramethylammonium sulfite 11
Thionyl chloride 11 54
Titanium chloride 12
Titration 15 16 92
Titration, of 1,four-dioxane 92
Titration, of acetic acid 92
Titration, of alcohols 92 93
Titration, of aluminum chloride 93
Titration, of ammonia 92
Titration, of anhydrides 93
Titration, of boron trichloride 91 92 93
Titration, of esters 94
Titration, of ethers 96
Titration, of H-acids 92
Titration, of hydrochloric acid 92
Titration, of nitric acid 92
Titration, of pyridine 91 92 94
Titration, of silver perchlorate 91
Titration, of stannic chloride 91 92
Titration, of sulfuric acid 92
Titration, of triethylamine 91 94
Titrations, in carbon tetrachloride solutions 93
Titrations, in chlorobenzene solutions 92
Titrations, in water solutions 92
Toluene as a solvent 4
Tri-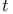 -butylboron 106 -butylboron 106
Triethylamine 16 53
Triethylamine, titration of 91 94
Trimethylamine 14 16 106
Trimethylboron 106
Triphenylmcthyl carbanion 140
Tungsten chlorides 20
Usanovich 13 14
Valence, coordinate covalence 38 39 40 41 42
Valence, covalence 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
Valence, electrovalence 28
Valence, origin of 27
Walden 46
Water solutions, titrations in 92 93
Water theory, inadequacy of 3 5
Water, as a base 4 8 43 44 70 72 75
Water, as a reducing agent 75
Water, as a solvent 12
Water, as an acid 7 45 72 75
Water, as an oxidizing agent 75
Wickert 12
Zinc acetate 56
Zinc amide 10 56
Zinc chloride, catalytic effect of 110 130
Zinc hydroxide 10 56
Zinc ion, hydrolysis 63
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 nsted theory
nsted theory -butylboron
-butylboron