|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Weissbluth M. Ч Atoms and Molecules |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 coupling 441Ч442 (see also Multielectron atom) coupling 441Ч442 (see also Multielectron atom)
Absorption and emmission see also Atomic spectra; Molecular spectra; Radiation and atoms
Absorption and emmission, absorption cross sections 520Ч521
Absorption and emmission, degenerate states 508
Absorption and emmission, Einstein coefficients 510
Absorption and emmission, hydrogen 515Ч517
Absorption and emmission, induced emission 508
Absorption and emmission, line broadening 517Ч520
Absorption and emmission, line shape 518 520
Absorption and emmission, line strength 509
Absorption and emmission, numerical computation 515Ч517
Absorption and emmission, oscillator strengths 512Ч515
Absorption and emmission, PlanckТs law 511Ч512
Absorption and emmission, selection rules 509
Absorption and emmission, spontaneous emission 508
Absorption and emmission, spontaneous lifetime 510
Absorption and emmission, sum rules 513Ч515
Absorption and emmission, transition probabilities 505Ч509
Addition theorem 9
Angular distribution, radiation fields 192Ч193 503Ч504
Angular momentum, and rotations 51Ч53
Angular momentum, Clebsch Ч Gordan coefficients 25 27Ч31
Angular momentum, commutators 44Ч45
Angular momentum, coupling of three angular momenta 36Ч38 47
Angular momentum, coupling of two angular momenta 22Ч27 46Ч47
Angular momentum, definition 13 42
Angular momentum, eigenfunctions and eigenvalues 14Ч17 45 107Ч109
Angular momentum, matrix elements 18 45Ч46
Angular momentum, six  (6 (6 symbols) 38Ч44 symbols) 38Ч44
Angular momentum, spherical components 44
Angular momentum, three  (3 (3 symbols) 12 31Ч35 symbols) 12 31Ч35
Angular momentum, undertime reversal 208
Annihilation operators see Creation and annihilation operators
Anticommutators 256
Antisymmetric wave functions 214Ч215 283 254Ч256 386-387
Atomic spectra 525Ч535 (see also Absorption and emission; Radiation and atoms; X-rays)
Atomic spectra, helium 527Ч529
Atomic spectra, hydrogen 525Ч528
Atomic spectra, Paschen Ч Back 534Ч535
Atomic spectra, Stark 535
Atomic spectra, Zeeman 533Ч534
Atomic units 325
Auger effect 532Ч533 (see also X-rays
Bessel functions 689Ч691
Bohr magneton 347
Bom Ч Oppenheimer approximation 551Ч555 (see also Molecules)
Bose statistics see also Bosons
Bose statistics, diatomic molecules 629Ч631
Bosons 214
Brillouin Ч Wigner expansion 296 (see also Perturbations)
Build-up principle 392
Cartesian tensors see also Tensors
Cartesian tensors, and permutation groups 175Ч178
Cartesian tensors, decomposition 171Ч175 178Ч181
Cartesian tensors, dipole coupling 168Ч170
Cartesian tensors, transformation law 168
Central field approximation 389Ч394
Clebsch Ч Gordan coefficients 25 27Ч31
Clebsch Ч Gordan coefficients, numerical tables 28Ч30
Closed shell see Coulomb interaction; Slater determinant; Hartree Ч Fock formulation
Closure 685 696
Configuration, average energy 464Ч465
Configuration, conjugate 476Ч478
Configuration, interaction 411Ч412
Continuous groups 177Ч181 (see also Rotation groups)
Correlation error 410Ч411
Correlation function 304
Correlation time 304
Coulomb hole 410
Coulomb interaction see also Electrostatic matrix elements
Coulomb interaction, closed shell 251Ч253
Coulomb interaction, direct (Coulomb) integral 247
Coulomb interaction, exchange integral 248
Coulomb interaction, matrix elements 244Ч253
Coulomb interaction, operators 249Ч250
Coulomb interaction, Racah paramaters 249
Coulomb interaction, Slater Ч Condon parameters 247Ч249
Coupled and uncoupled representation 22Ч26 336
Coupling coefficients see Clebsch-Gordan coefficients; Three  (3 (3 ) symbols ) symbols
Creation and annihilation operators 254Ч259 (see also Harmonic oscillator)
Crystal field see Ligand field
Darwin term see Hydrogen atom
Density matrices 268Ч289
Density matrices, equation of motion 278Ч280
Density matrices, Fock Ч Dirac 283Ч285
Density matrices, interaction representation 280
Density matrices, mixed states 260Ч270
Density matrices, molecular orbitals 558
Density matrices, multielectron system 280Ч283
Density matrices, one-particle 282
Density matrices, pair function 288
Density matrices, pure states 269Ч270
Density matrices, random perturbation 301Ч305
Density matrices, reduced 273Ч276
Density matrices, spin 271Ч273 287
Density matrices, spinless 285Ч289
Density matrices, thermal equilibrium 276Ч277
Density matrices, two-particle 282
Diagrams see Electromagnetic interactions; Perturbations
Diamagnetism 354Ч355 (see also Magnetic field interaction)
Diatomic molecules, electronic states 584Ч589
Diatomic molecules, Franck Ч Condon principle 621 622
Diatomic molecules, heteronuclear 587Ч589 623Ч624
Diatomic molecules, homonuclear 579Ч587 624Ч631
Diatomic molecules, HundТs cases 614Ч615
Diatomic molecules, Morse potential 608Ч609
Diatomic molecules, nuclear spin effect 629Ч631
Diatomic molecules, ortho and para modifications 631
Diatomic molecules, rotational properties 609Ч619
Diatomic molecules, selection rules 627Ч631
Diatomic molecules, symmetry properties 622Ч631
Diatomic molecules, terms 585Ч587
Diatomic molecules, transitions 615Ч631
Diatomic molecules, vibrations 606Ч609 611 617
Dipole-dipole interaction 168Ч170
Dirac delta ( ) function 694Ч696 ) function 694Ч696
Dirac equation 313 3 21
Dirac notation 681
Dispersion relations see Kramers Ч Kronig relations
Doppler broadening see Line broadening
Dyson chronological operator 224Ч225
Eigenvalues and eigenfunctions 684Ч685
Einstein coefficients 510
Electric field interaction see also Stark effect
Electric field interaction, hydrogen atom 356Ч357
Electric quadrupole interaction 374Ч384
Electromagnetic field, Helmholtz equations 196Ч198
Electromagnetic field, Maxwell equations 19 6
Electromagnetic field, multipole expansion 196Ч202
Electromagnetic field, parity 199Ч200
Electromagnetic interactions see also Absorption and emission; Radiation and atoms; Scattering
Electromagnetic interactions, diagrams 544Ч547
Electromagnetic interactions, higher order 536Ч550
Electromagnetic interactions, nonlinear effects 547Ч550
Electromagnetic interactions, optical susceptibility 547Ч550
Electromagnetic interactions, two-photon processes 545Ч547
Electronic repulsion energy see Electrostatic matrix elements
Electrostatic matrix elements 443Ч454 457Ч465
emission see Absorption and emission
Equivalent electrons see Multiplet
Euler angles 54
Evolution operator, equation of motion 223
Evolution operator, infinite limits 227Ч232
Evolution operator, integral form 223Ч225
Evolution operator, interaction representation 222Ч232
Evolution operator, Schr dinger representation 216Ч218 dinger representation 216Ч218
Exchange integral see Coulomb interaction
Extended H ckel method (EHM) see Molecular orbitals ckel method (EHM) see Molecular orbitals
Fermi see also Fermion; Hartree Ч Fock formulation
Fermi, correlation 288
| Fermi, golden rule 299Ч301
Fermi, statistics 629Ч631
Fermion 214Ч215
Fermion operators 257Ч258
Field operator 265Ч267
Fine structure see Hydrogen atom;
Fock space 255
Fractional parentage see Multiplet wave functions
Franck Ч Condon principle 621Ч622
Gaunt formula 11Ч12 (see also Spherical harmonics)
Gaussian line shape 520 (see also Line broadening)
Group representations see also Groups
Group representations, basis functions 75Ч78
Group representations, character 68
Group representations, classification 123Ч124
Group representations, coupling coefficients 132Ч142
Group representations, equivalent 67
Group representations, irreducible 70Ч74
Group representations, product 83 88 126
Group representations, reducible 68Ч74 127
Group representations, regular 74Ч75
Group representations, symmetric and antisymmetric 85Ч87
Group representations, unit 66
groups 60Ч90 (see also Group representation; Permutation groups; Point groups; Rotation groups)
Groups, Abelian 65
Groups, class 65
Groups, conjugate elements 65
Groups, double (extended) 121Ч127 140
Groups, finite 111Ч150
Groups, matrix element theorem 88Ч90 103Ч104
Groups, projection operators 78Ч83
Groups, relation to quantum mechanics 203Ч207
Groups, rotation 91Ч93
Groups, selection rules 89Ч90 103Ч104
Groups, SU(2) 95Ч100
Groups, subgroups 65
gyromagnetic ratio see Magnetic moment
harmonic oscillator 233Ч239
Harmonic oscillator, creation and annihilation operators 234Ч238
Harmonic oscillator, Heisenberg representation 239
Harmonic oscillator, matrix formulation 234Ч238
Harmonic oscillator, Schr dinger formulation 233Ч234 dinger formulation 233Ч234
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, Brillouin theorem 403Ч404
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, closed shell 404Ч407
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, computational methods 407Ч410 561Ч565
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, density matrix formulation 398Ч399 400
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, equations 394Ч401
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, exchange hole 400
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, exchange probability density 400
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, Fermi hole 400
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, Fock operator 398
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, KoopmansТ theorem 402Ч403
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, nonlocal potential 400
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, open shell 408Ч409
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, orthogonality of the orbitals 401Ч402
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, restricted and unrestricted 409
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, Roothaan method 409Ч410 556Ч560
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, Slater approximation 410
Hartree Ч Fock formulation, solutions 401Ч407
Heisenberg equation 221
Heisenberg representation 220Ч221
Hellmann Ч Feynman theorem 554Ч555 570
Hermite polynomials 693
Hilbert transforms 309
HundТs rules 426 586
Hvickel method see Molecular orbitals
Hybrid orbitals 591Ч596
Hydrogen atom 322Ч345
Hydrogen atom, Darwin term 343Ч344
Hydrogen atom, electric field 356Ч357
Hydrogen atom, energy levels 331 345
Hydrogen atom, Lamb shift 344
Hydrogen atom, magnetic field 350Ч354
Hydrogen atom, magnetic hyperfine interaction 368Ч373
Hydrogen atom, quantum numbers 327
Hydrogen atom, radial charge density 331Ч332
Hydrogen atom, radial expectation values 333
Hydrogen atom, radial wave function 323Ч327 330
Hydrogen atom, relativistic mass correction 341Ч343
Hydrogen atom, Schr dinger equation 322Ч334 dinger equation 322Ч334
Hydrogen atom, spectra 525Ч528
Hydrogen atom, spin-orbit coupling 339Ч341
Hydrogen atom, Stark effect 356Ч357
Hydrogen atom, wave functions 327Ч329
Hydrogen molecule ion (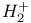 ) 566Ч573 579Ч580 ) 566Ч573 579Ч580
Hydrogen molecule ion (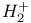 ), correlation diagram 580 ), correlation diagram 580
Hydrogen molecule ion (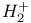 ), electronic charge distribution 569 ), electronic charge distribution 569
Hydrogen molecule ion (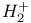 ), energy levels 568 ), energy levels 568
Hydrogen molecule ion (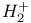 ), molecular orbitals 567Ч569 ), molecular orbitals 567Ч569
Hydrogen molecule ion (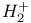 ), overlap population 570 ), overlap population 570
Hydrogen molecule ion (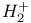 ), scaling 572Ч573 ), scaling 572Ч573
Hydrogen molecule ion (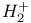 ), symmetry properties 573Ч579 ), symmetry properties 573Ч579
Hydrogen molecule ion (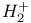 ), united atom treatment 579Ч580 ), united atom treatment 579Ч580
Hydrogen molecule ion (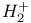 ), virial theorem 571Ч572 ), virial theorem 571Ч572
Hydrogen molecule, electronic states 579Ч584
Hydrogen molecule, energies 583
Hydrogen molecule, Hamiltonian 579
Hydrogen molecule, molecular orbitals 580Ч584
Hydrogen molecule, para and ortho modifications 631
Hydrogen molecule, valence bond method 583
Hydrogen molecule, wave functions 581Ч584
Hyperfine interactions see Electric quadrupole interaction; Magnetic hyperfine interaction
Indistinguishability of particles 213Ч215
Interaction representation 221Ч227
Internal conversion 648
Intersystem crossing 648
Irreducible tensor operators 151Ч175 (see also Tensors)
Irreducible tensor operators, definition 151Ч152
Irreducible tensor operators, direct product 166Ч167
Irreducible tensor operators, matrix elements 166
Irreducible tensor operators, unit tensor operator 456
Irreducible tensor operators, Wigner Ч Eckhart theorem 159Ч167
Jahn Ч Teller theorem 676
KoopmansТ theorem 403
Kramers Ч Heisenberg formula 536Ч542
Kramers Ч Kronig relations 307Ч309
KramersТ operator 207
KramersТ theorem 210Ч212
L wdin orbitals 564Ч565 (see also Molecular orbitals) wdin orbitals 564Ч565 (see also Molecular orbitals)
Laguerre polynomials 692
Lamb shift 344
Land  factor 349 (see also Magnetic field interaction) factor 349 (see also Magnetic field interaction)
Land interval rule 467 472 interval rule 467 472
Lande formula 348 364Ч367 379
LCAO (linear combination of atomic orbitals) see Molecular orbitals
Ligand field 650Ч680
Ligand field,  value 673Ч674 value 673Ч674
Ligand field, Hamiltonian 650
Ligand field, KramersТ theorem 671Ч672
Ligand field, magnetic field 672Ч677
Ligand field, molecular orbitals 677Ч680
Ligand field, multielectron configurations 666Ч672
Ligand field, potentials 651Ч655
Ligand field, quenching of orbital angular momentum 664
Ligand field, spin Hamiltonian 675 677
Ligand field, spin-orbit coupling 651 657Ч666
Ligand field, splitting in 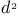 configuration 666Ч667 configuration 666Ч667
Ligand field, splitting of d orbital 655Ч656
Ligand field, terms 668Ч671
Ligand field, wave functions in  configuration 667 configuration 667
Line broadening 517Ч520
Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation 230
Lorentzian line shape 518 (see also Line broadening
LS (Russell Ч Saunders) coupling 388 (see also Multielectron atom)
Magnetic field interaction 346Ч355 478Ч479
Magnetic field interaction, diamagnetism 354Ч355
Magnetic field interaction, Hamiltonian 346
Magnetic field interaction, Land  factor 349 factor 349
Magnetic field interaction, paramagnetism 355
Magnetic field interaction, Paschen Ч Back region 352Ч353
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 coupling
coupling  (6
(6 ) function
) function  dinger representation
dinger representation  ckel method (EHM)
ckel method (EHM)  )
) 
 factor
factor  configuration
configuration 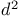 configuration
configuration