|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Weissbluth M. Ч Atoms and Molecules |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Magnetic field interaction, with spin-orbit coupling 350Ч354
Magnetic field interaction, Zeeman levels 349Ч350
Magnetic hyperfine interaction 358Ч374
Magnetic hyperfine interaction, and magnetic field 371Ч374
Magnetic hyperfine interaction, coupling tensor 367
Magnetic hyperfine interaction, Fermi contact term 367
Magnetic hyperfine interaction, Hamiltonian 358Ч367
Magnetic hyperfine interaction, one-electron system 367Ч374
Magnetic moment, gyromagnetic ratio 367
Magnetic moment, operators 347Ч349
magnetization 277Ч278
Matrix element, reduced 159 162Ч163
Matrix element, theorem 88Ч90 103Ч104
Molecular orbitals see also Molecules
Molecular orbitals, angular momentum properties 577Ч578
Molecular orbitals, antibonding 600
Molecular orbitals, bond order matrix 599
Molecular orbitals, bonding 600
Molecular orbitals, CNDO (complete neglect of differential overlap) 563
Molecular orbitals, computational methods 561Ч565
Molecular orbitals, EHM (extended Hvickel method) 564
Molecular orbitals, H ckel method 597Ч603 ckel method 597Ч603
Molecular orbitals, Hartree Ч Fock 556Ч560
Molecular orbitals, inversion symmetry 578
Molecular orbitals, L wdin orbitals 564Ч565 wdin orbitals 564Ч565
Molecular orbitals, LCAO (linear combination of atomic orbitals) 556
Molecular orbitals, NDO (neglect of differential overlap) 562
Molecular orbitals, nonbonding 594 600
Molecular orbitals, pi ( )-electron approximation 596Ч603 )-electron approximation 596Ч603
Molecular orbitals, PPP (Pariser Ч Parr Ч Pope) method 604Ч605
Molecular orbitals, Roothaan method 556Ч560
Molecular orbitals, sigma ( ) and pi ( ) and pi ( ) bonds 574Ч576 ) bonds 574Ч576
Molecular spectra 606Ч649
Molecular spectra, diatomic molecules 615Ч631
Molecules 551Ч649 (see also Bom Ч Oppenheimer approximation; Diatomic molecules; Hydrogen molecule; Hydrogen molecule ion; Molecular orbitals; Molecular spectra)
Molecules, benzene 600Ч603
Molecules, bonds 575Ч576 587Ч589 594 600
Molecules, butadiene 597Ч600
Molecules, carbon dioxide 590Ч591
Molecules, electronic states 566Ч605
Molecules, ethylene 604Ч605
Molecules, formaldehyde 595Ч596
Molecules, hybrid orbitals 591Ч596
Molecules, oxygen 585Ч587
Molecules, polyatomic 631Ч641
Molecules, polyenes 602
Molecules, population analysis 588Ч589
Molecules, vibrations 606Ч609 611 617 635Ч641
Molecules, water 594Ч595
Morse potential 608Ч609 (see also Diatomic molecules)
Multielectron atom 385Ч481 (see also Hartree Ч Fock formulation; Multiplet)
Multielectron atom, 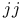 coupling 441Ч442 coupling 441Ч442
Multielectron atom, closed shell 392
Multielectron atom, configuration 392
Multielectron atom, electric field interaction 479Ч480
Multielectron atom, equivalent electrons 392
Multielectron atom, Hamiltonian 385Ч389
Multielectron atom, levels 393
Multielectron atom, LS (Russell Ч Saunders) coupling 388
Multielectron atom, magnetic field interaction 478Ч479
Multielectron atom, parity 391
Multielectron atom, terms 393
Multiplet 413Ч442 (see also Multielectron atom)
Multiplet Fluorescence 530 647Ч648
Multiplet, coefficients of fractional parentage (cfp) 430Ч435
Multiplet, equivalent electrons 421 425
Multiplet, group properties 435Ч441
Multiplet, HundТs rules 426 586
Multiplet, inverted 478
Multiplet, Land interval rule 467 472 interval rule 467 472
Multiplet, multiplicity 415
Multiplet, normal 467
Multiplet, parity 425
Multiplet, regular 477
Multiplet, seniority number 426
Multiplet, terms from equivalent electrons 418Ч420
Multiplet, two-electron 413Ч420
Multiplet, wave functions 427Ч435
Normal coordinates 633
Number operator 260
Occupation number space see Fock space
One-electron, matrix elements 454Ч457
One-electron, spin orbital 335
One-electron, wave functions 334Ч337
Optical susceptibility 547Ч550
Optical susceptibility, nonlinear effects 548Ч550
Orbital angular momentum 1Ч3 8-9
Orbital angular momentum, commutation rules 2
Orbital angular momentum, eigenvalues and eigenfunctions 8Ч9
Oscillator strengths 512Ч515
Oscillator strengths, sum rules 513Ч514
Pauli principle 257Ч258 288
Permutation groups 143Ч150 435Ч441
Permutation groups, basis functions 148Ч150
Permutation groups, CayleyТs theorem 145
Permutation groups, irreducible representations 147
Permutation groups, Young diagrams 145Ч147
Permutation groups, Young operator 148Ч150
Perturbations, Brillouin Ч Wigner expansion 296
Perturbations, FermiТs golden rule 299Ч301
Perturbations, harmonic potential 298Ч299
Perturbations, random 301Ч305
Perturbations, Rayleigh Ч Schrodinger expansion 296
Perturbations, time-dependent 297Ч299 (see also Evolution operator)
Perturbations, time-independent 294Ч297
Phosphorescence 648
photoelectric effect 521Ч525
PlanckТs radiation law 511Ч512
Plane wave expansion 193Ч196
Plane wave expansion, multipoles 199Ч202
Point groups, character tables 115Ч120
Point groups, classification 114
Point groups, coupling coefficients 132Ч142
Point groups, double (extented) groups 121Ч127 140
Point groups, nomenclature 112Ч113 124 127 142
Point groups, symmetry operations 111Ч112 124 127 142
Polyatomic molecules, electronic transitions 641
Polyatomic molecules, Raman scattering 644Ч646
Polyatomic molecules, relaxation 646Ч649
Polyatomic molecules, vibrational transitions 642Ч643
Polyatomic molecules, vibronic interaction 643 644
Quadrupole interaction see Electric quadrupole interaction
Quantum mechanics and group theory 203Ч207
Quenching see Ligand fields
Racah parameters 249
Racah W coefficients 39 (see also Six  (6 (6 ) symbols) ) symbols)
Radiation and atoms see also Absorption and emission; Electromagnetic interactions
| Radiation and atoms, angular distribution 503Ч504
Radiation and atoms, electric dipole 494 497Ч500
Radiation and atoms, electric quadrupole 496Ч497 500
Radiation and atoms, Hamiltonian 492Ч493
Radiation and atoms, magnetic dipole 495Ч496 500
Radiation and atoms, matrix elements 493Ч494
Radiation and atoms, nonlinear effects 309Ч310 547Ч550
Radiation and atoms, selection rules 500Ч502
Radiation field see also Radiation and atoms
Radiation field, box normalization 483Ч484
Radiation field, creation and annihilation operators 488Ч490
Radiation field, Hamiltonian 483Ч488
Radiation field, photon description 489Ч490
Radiation field, polarization 484Ч485
Radiation field, quantization 488Ч492
Radiation field, rotational properties 491
Radiation field, transversality 484
Radiation field, zero point energy 490
Raman scattering 644Ч646 (see also Polyatomic molecules)
Rayleigh scattering 544
Rayleigh Ч Schr dinger expansion 296 dinger expansion 296
Reaction matrix 232
Reduced matrix element see Wigner Ч Eckart theorem
Relaxation, molecular 646Ч649
Response function 305Ч307 309Ч312
Roothaan method 556Ч560 (see also Molecular orbitals)
Rotation groups 91Ч110
Rotation groups, relation between 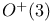 and SU(2) 98Ч100 and SU(2) 98Ч100
Rotation groups, three-dimensional 93 95 100Ч103
Rotation groups, two-dimensional 91Ч93
Rotational transitions, diatomic 618Ч620
Rotations see also Rotational transitions; Rotation groups
Rotations, and angular momenta 51 53
Rotations, diatomic molecules 609Ч615
Rotations, Euler angles 54Ч55
Rotations, HundТs cases 614Ч615
Rotations, transformation of angular momentum eigenfunctions 55Ч59
Scaling 572 (see also Virial theorem)
Scattering, Kramers Ч Heisenberg formula 536Ч542
Scattering, matrix elements 230Ч232
Scattering, operator 228
Scattering, Raman 542Ч544 644Ч646
Scattering, Rayleigh 542Ч544
Scattering, Thomson 542
Schr dinger representation 216Ч220 dinger representation 216Ч220
Selection rules see also Wigner Ч Eckart theorem
Selection rules, absorption and emission 509
Selection rules, by group theory 89Ч90 103Ч104
Selection rules, diatomic molecules 627Ч631
Selection rules, Raman 645Ч646
Selection rules, rotational 617Ч619
Selection rules, three-dimensional rotation group 103 104
Selection rules, vibrational 617
Seniority number 426
Six  (6 (6 ) symbols 38Ч44 ) symbols 38Ч44
Six  (6 (6 ) symbols, numerical values 43Ч44 ) symbols, numerical values 43Ч44
Six  (6 (6 ) symbols, special formulas 40Ч42 ) symbols, special formulas 40Ч42
Slater determinant 215 240Ч253 391 395
Slater determinant, closed shell 251Ч253
Slater determinant, matrix elements 240Ч243
Slater orbitals 409
Slater Ч Condon parameters 247Ч249 (see also Coulomb interaction)
Spectra see Atomic spectra; Molecular spectra
Spherical harmonics 3Ч12
Spherical harmonics, Condon Ч Shortley convention 5
Spherical harmonics, Gaunt formula 12
Spherical harmonics, real combinations 6
Spin, density 271Ч273 287
Spin, eigenvalues and eigenfunctions 20Ч22 46
Spin, Hamiltonian 675Ч677 (see also Ligand fields)
Spin, matrix elements 20Ч22 45
Spin, orbital 335
Spin, Pauli matrices 22
Spin, under rotation 107
Spin, undertime reversal 208Ч210
Spin-orbit interaction 337Ч341 465Ч476
Spin-orbit interaction, and magnetic fields 350Ч354
Stark effect 479Ч480
susceptibility 306Ч312
Susceptibility, energy dissipation 306Ч307
Susceptibility, Kramers Ч Kronig relations 307Ч309
Susceptibility, nonlinear 309Ч310
Susceptibility, quantum mechanical 311Ч312
Symmetry see also Groups
Symmetry, diatomic molecules 622Ч631
Symmetry, hydrogen molecule ion 573Ч579
Symmetry, of the Hamiltonian 203Ч215
Symmetry, reduction due to a perturbation 204Ч207
Tensors see also Irreducible tensor operators
Tensors, basis for permutation groups 435Ч441
Tensors, cartesian 167Ч175
Tensors, product 153 155Ч159
Terms see also Diatomic molecules; Multiplet
Terms, equivalent electrons 418Ч420
Terms, seniority number 426
Three  (3 (3 ) symbols 12 31Ч35 ) symbols 12 31Ч35
Three  (3 (3 ) symbols, numerical tables 34Ч35 ) symbols, numerical tables 34Ч35
Three  (3 (3 ) symbols, special formulas 33 ) symbols, special formulas 33
Three  (3 (3 ) symbols, triangle condition 12 ) symbols, triangle condition 12
Time reversal 207Ч213 (see also KramersТ theorem)
transitions see Atomic spectra; Molecular spectra; Polyatomic molecules
Unit tensor operator 456 (see also Irreducible tensor operators)
Unit vectors 153Ч155 186 189 686Ч687
United atom treatment 579Ч580 (see also Hydrogen molecule ion)
Vacuum state 254
Valence bond method 583 (see also Hydrogen molecule)
Variational method 290Ч294
Vector fields 182Ч202
Vector spherical harmonics 187Ч193
Vibrations, diatomic molecules 606Ч609 611 617
Vibrations, group theory 635Ч641
Vibrations, Morse potential 608Ч609
Vibrations, normal coordinates 633
Vibrations, polyatomic molecules 631Ч641
Vibrations, vibronic interactions 643 644
Virial theorem 570Ч572
Wigner Ч Eckart theorem 159Ч167 377Ч379
Wigner Ч Eckart theorem, Land formula 348 364Ч367 379 formula 348 364Ч367 379
Wigner Ч Eckart theorem, reduced matrix element 159 162Ч163 166
Wigner Ч Eckart theorem, selection rules 160Ч161
X-rays, absorption spectra 532
X-rays, Auger effect 532Ч533
X-rays, fluorescence 530
X-rays, selection rules 530
X-rays, terms 530Ч532
Young diagrams see Permutation groups
Zeeman effect see Magnetic field interaction
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 ckel method
ckel method  wdin orbitals
wdin orbitals  )-electron approximation
)-electron approximation  ) and pi (
) and pi (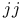 coupling
coupling  interval rule
interval rule  (6
(6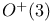 and SU(2)
and SU(2)