|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Bijvoet J.M., Kolkmeyer N.H., Macgillavry C.H. — X-Ray Analysis of Crystals |

Обсудите книгу на
Нашли опечатку?
Выделите ее мышкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter
|
Название: X-Ray Analysis of Crystals
Авторы: Bijvoet J.M., Kolkmeyer N.H., Macgillavry C.H.
Язык: 
Рубрика: Физика/
Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц
ed2k:
Издание: 1st edition
Год издания: 1951
Количество страниц: 304
Добавлена в каталог: 09.08.2009
Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
 -splitting 40 57 -splitting 40 57
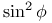 formulae 24 242—243 formulae 24 242—243
Absence conditions, general 67 80
Absence conditions, special 68 80
Absence conditions, systematic 67 80 81 253
Absorption coefficient 75
Absorption factor 74 75
Absorption of electronic rays 281
Absorption of electronic x-rays 40 75
Adipic acid 207 216
Albite 169
Alcohols 128
Aliphatic chains, rotation of see also “paraffins” 158
Alkali fluoborates, rotation in 159
Alkali halides 118 123
Alkali ions 118
Alkali metals, structure of 129
Alkali perchlorates, rotation in 159
Alkylammonium halides 157
Alloys: Ag-Al 152
Alloys: Ag-Au 150
Alloys: Au-Cu 151
Alloys: Cu-Si 152
Alloys: Cu-Zn 48 49 153
Alloys: Na-K 150
Alternation of properties in dicarboxylic acids 201 206
Aluminium in silicates 174 175
Aluminium phosphate 147
Aluminium texture 139 146
Alums, one dimensional Fourier analysis 109
Amino acids,  209 217 209 217
Ammonium halides 159
Ammonium nitrate 159
Ammoniumates 166
Amorphous proteins 209
Amorphous substances 46 209
Amphiboles 172
Amplitude, Fourier 102ff
Analysis, x ray spectroscopic 46
Angstrom unit A 1
Anisotropy 6
annealing 54 55
Anode 26 38 41
Anorthite 169
Anthophyllite 183 186
anthracene 98 192 197
Antimony 130
Antimony explosive 47
Apparatus, Braggs 26
Apparatus, for electronic rays 280
Apparatus, for powder method 27
Apparatus, for x rays 26 42
Apparatus, von Laue's 5
Apparatus, Weissenberg's 34
Aragonite 147
Aragonite double refraction of 141
Aragonite isomorphous series of 147
Aragonite type 147
Aromatic compounds 197
Arsenic 130 131
Arsenic trioxide 127 128
Artificial rubber 209
Artificial wool 222
Asbestos 169
Atomic distances see “interatomic D.”
Atomic distances radius 131—137 198
Atomic distances scattering power 69
Atoms, diffraction by row of 17
Averaged cell content 149 276
Avogadro number 1 44 45
Axes intercepts on 23 236
Axes of complex symmetry 12
Axes of rotatory inversion 12 226
Axes screw 11 12 68 86 99 214 232
Axes symmetry 7 11 12 18 APp. II
Axial length 23
Back reflection 57
Background blackening 41 270 274
Beil by layer 288
benzene 100 192 197
Benzyl penicillin 117 118
Beryllium aluminate, isomorphism of 132
Beryllium fluoride 163
Beryllium ion 163 184
Beryllium oxide, refractive index of 184
Bismuth 130
Body centred lattice 13 62 67
Bond types 123ff 292
Bond types, combinations of 130 176 292
Bond types, heteropolar 123—125 292
Bond types, homopolar 126 292
Bond types, intermediate 130 292
Bond types, metallic 128 150—154 292
Bond types, van der Waals 126—128 292
Borides 137
Bragg, interpretation by W. L. 16 17 22 23
Bragg, method 21
brass 48—50
Bravais lattices 13 14 81 232
Bravais lattices, absence conditions for 67
Cadmium bromide, random structure of 275
Cadmium chloride type 164
Cadmium halides 162 165
Cadmium hydroxide 165
Caesium chloride 62 71 137
Caesium chloride, structure factor 62
Caesium chloride, type 64 124
Calcite, cleavage 138
Calcite, double refraction of 141
Calcite, isomorphous series of 147
Calcite, standard value of cleavage spacing in 45
Calcite, structure 77 123
Calcite, type 147
Calcium chloride 166
Calcium fluoride 95 163
Calcium tungstate 147 154
Calomel 142
Camera 27
Camera cone shaped 208
Camphor 159
Carbides 137
carbon black 47
Carbon-carbon distances 130 196—198
Carbon-nitrogen 198
Catalyser 287
cell 3—6
Cell constants see “cell dimensions”
Cell dimensions 4 6 CHap. 23—24 29 33 45 51 101 201 241
Cell dimensions, absolute 42 45
Cell dimensions, from large scattering angles 51
Cellobiose 213
Cellulose structure 137 195 211—216
Centre in Laue photograph 37 81
Centre of symmetry 12
Centred lattices 11—14 62—64
Centred lattices, absence conditions for 67
Cerium tungstate 147 154
Chain structure see “fibre cleavage”
Chains, long 201 208
Chair type 99 100
Characteristic radiation 39
Chemotropy 167
Chlorite 180 181
Cholesterol see “sterol”
Cholesteryl bromide 267
Cholesteryl iodide 117 195
Chromates 143
Chrysene 197
Chrysoberyl 147
Class, crystal APp. I
| Class, Laue 37 226
Cleavage 96 137 138 181 185
Cleavage fibre see “fibre C.”
Cleavage in cyanuric acid 199
Cleavage in silicates 164 182
Cleavage laminar see “sheet C.”
Cleavage of layer structures 126
Close packing 128ff
Close packing, of oxygen 149 182
Cobalt 128
Cobalt sulphide 150
Cold working 146
Collagen 218
Colloids, soil 46
Complex representation of structure factor 238—239
Composition boundary in alloys 49
Composition of oscillations 67
Compound (-mixture-mixed crystal) 47
Conduction see “electric C.”
Construction, Ewald's 256 271
Continuous intensity factors 69
Coordination number 95 124 126 134 162—168 184—186
Coordination number eight see “also surroundings” 95 124 162—168
Coordination number for aluminium in silicates 176
Coordination number four 95 162 168 184 186
Coordination number six 123 162 168 184
Coordination structures 123 126 131 134 137 162
Copper alloys with gold 151—152
Copper alloys with zinc 49
Copper structure 128
Copper wire, texture of 53
Coronene 197
Correction for film thickness 241
Correction for rod diameter 241
Coulomb forces 164
Cristobalite 19 47 96 174
Cristobalite type 174
Crystal chemistry, basic law of 162
Crystal classes 9—10 14 81 APp.
Crystal compound ( ) 151 ) 151
Crystal deformation 56
Crystal disturbances 270ff
Crystal lattice faults 145
Crystal lattices see also “Bravais lattices space bond 3 16
Crystal structure of:  124 124
Crystal structure of:  124 124
Crystal structure of: adipic acid 207
Crystal structure of: alkali halides 123
Crystal structure of: alkali metals 129
Crystal structure of: aluminium oxide (corundum) 182
Crystal structure of: ammonium halides 124
Crystal structure of: amphiboles 172
Crystal structure of: anthracene 98 192
Crystal structure of: antimony 130
Crystal structure of: arsenic trioxide 127 128
Crystal structure of: barium carbonate 147
Crystal structure of: benzene 100 192
Crystal structure of: beryllium fluoride 163
Crystal structure of: beryllium oxide 184
Crystal structure of: borides 137
Crystal structure of: cadmium calcite see “calcium carbonate”
Crystal structure of: cadmium halides 162—165 275
Crystal structure of: cadmium hydroxide 165
Crystal structure of: caesium halides 62 123
Crystal structure of: calcium carbonate 123
Crystal structure of: calcium fluoride 163
Crystal structure of: calcium halides 162 163 166
Crystal structure of: camphor 159
Crystal structure of: carbides 137
Crystal structure of: cellulose 211—216
Crystal structure of: cerium tungstate 154
Crystal structure of: chlorite 180 181
Crystal structure of: cholesteryl bromide 267
Crystal structure of: cholesteryl iodide 195
Crystal structure of: copper 65
Crystal structure of: copper Au and Zn alloys 49 151—152
Crystal structure of: corundum see “beryllium fluoride”
Crystal structure of: cristobalite 174
Crystal structure of: cyanuric acid 199
Crystal structure of: cyanuric triazide 193
Crystal structure of: diamond 125
Crystal structure of: dibenzyl 200
Crystal structure of: dicarboxylic acids 206
Crystal structure of: dihalides 162—163
Crystal structure of: diopside 172 183
Crystal structure of: edingtonite 175
Crystal structure of: enstatite 171
Crystal structure of: fatty acids 203
Crystal structure of: feldspars 175 176
Crystal structure of: fluorite 163
Crystal structure of: geranylamine hydrochloride 117 196 211
Crystal structure of: glucosamine hydrochloric and hydrobromic acids 114
Crystal structure of: glycine 196
Crystal structure of: gold copper alloy 151
Crystal structure of: gutta percha 215
Crystal structure of: haemoglobin 220
Crystal structure of: halogens 128 131
Crystal structure of: hexamethylbenzene 97
Crystal structure of: hexamethylenetetramine 191
Crystal structure of: hydrides 137
Crystal structure of: intermetallic compounds 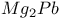 168 168
Crystal structure of: iodine 11 127
Crystal structure of: iron carbonate 147
Crystal structure of: iron disulphide 167
Crystal structure of: kaolin 181
Crystal structure of: keratin 218
Crystal structure of: lead carbonate 147
Crystal structure of: lead halides 165—167
Crystal structure of: lithium chloride 148
Crystal structure of: lithium cyanide 111—112
Crystal structure of: lithium ferrite 154
Crystal structure of: lithium titanate 154
Crystal structure of: magnesium carbonate 147
Crystal structure of: magnesium halides 163
Crystal structure of: magnesium margarite 180
Crystal structure of: magnesium mercuric chloride 32 84ff
Crystal structure of: magnesium mercury halides 33 84ff 166—167
Crystal structure of: magnesium micas 173 178 181
Crystal structure of: magnesium molybdenum sulphide 167
Crystal structure of: magnesium montmorillonite 181
Crystal structure of: magnesium muscovite 173 178 180
Crystal structure of: magnesium oxide 124
Crystal structure of: manganese  129 129
Crystal structure of: metals 64 128
Crystal structure of: naphthalene 98 197
Crystal structure of: nitrides 137
Crystal structure of: nylon 217
Crystal structure of: olivine 171 183—184
Crystal structure of: orthoclase 174
Crystal structure of: paraffins 158 203
Crystal structure of: penicillin 117 194
Crystal structure of: pentaerythritol 200
Crystal structure of: perovskite 124
Crystal structure of: phenacite 185
Crystal structure of: phosphorus pentoxide 143 144
Crystal structure of: phthalocyanins 113 192 198
Crystal structure of: pimelic acid 207
Crystal structure of: polyethylene 205
Crystal structure of: polyisoprene 215
Crystal structure of: polypeptides 218
Crystal structure of: polyvinyl alcohol 210
Crystal structure of: polyvinyl chloride 210
Crystal structure of: potassium benzyl penicillin 117
Crystal structure of: potassium chloroplatinate 123
Crystal structure of: potassium nickel fluoride 123
Crystal structure of: pyrite see “iron disulphide”
Crystal structure of: pyroxenes 172
Crystal structure of: quartz 11 175
Crystal structure of: quinol compounds 195
Crystal structure of: rubber, stretched 216
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 -splitting
-splitting 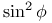 formulae
formulae 
 )
)