|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Fox R.O. Ч Computational Models for Turbulent Reacting Flows |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Mixture-fraction PDF from FP model 282Ч283
Mixture-fraction PDF, conditional scalar dissipation rate 211 213
Mixture-fraction PDF, LES 109
Mixture-fraction PDF, mixture-fraction covariances 174
Mixture-fraction PDF, mixture-fraction means 174
Mixture-fraction PDF, presumed 110 174Ч177 207 209 211 216
Mixture-fraction PDF, presumed, bi-variate beta 176
Mixture-fraction PDF, presumed, limitations 175
Mixture-fraction PDF, presumed, multi-variate 176
Mixture-fraction PDF, presumed, uni-variate beta 175
Mixture-fraction PDF, relationship to CMC 209
Mixture-fraction PDF, relationship to composition PDF 68
Mixture-fraction PDF, relationship to equilibrium-chemistry limit 179Ч180
Mixture-fraction PDF, relationship to flamelet model 205 206
Mixture-fraction PDF, transport equation in homogeneous flow 212
Mixture-fraction vector 109 141 156Ч179 181 183 193 201 211 212 216 221 222 232Ч234 282Ч284
Mixture-fraction vector in CMC 207
Mixture-fraction vector, allowable region 282
Mixture-fraction vector, definition 161Ч168
Mixture-fraction vector, definition, initial/inlet conditions 167
Mixture-fraction vector, definition, linear mixture 161 162
Mixture-fraction vector, definition, linear-mixture basis 161 166
Mixture-fraction vector, definition, mixture-fraction basis 164
Mixture-fraction vector, definition, transformation matrix 167
Mixture-fraction vector, example flows 168Ч174
Mixture-fraction vector, filtered 239
Mixture-fraction vector, general formulation 157Ч161
Mixture-fraction vector, linear mixture 163
Mixture-fraction vector, PDF 174Ч177
Mixture-fraction vector, principle of linear superposition 157
Mixture-fraction vector, relationship to initial/inlet conditions 157
Mixture-fraction vector, relationship to linear mixture 167
Mixture-fraction vector, relationship to reaction-progress vector 166
Mixture-fraction vector, residual 239
Molecular diffusion 10 13 23 47 56Ч58 65 72 78 109Ч111 113 125 136 149 198 199 239 262 268 269 287 363
Molecular diffusion, coefficients 90 111 146 149 264 267 272 276
Molecular diffusion, differential diffusion 135 267
Molecular diffusion, effect on composition PDF 65 104 240 242 249
Molecular mixing models 24 114 250 262 264Ч266 272 273 275 281 293 351
Molecular mixing models, constraints 262Ч263
Molecular mixing models, constraints, on correlation with velocity field 262
Molecular mixing models, constraints, on joint scalar dissipation rate 262
Molecular mixing models, constraints, on scalar means 262
Molecular mixing models, desirable properties 263Ч265
Molecular mixing models, desirable properties, boundedness 264
Molecular mixing models, desirable properties, dependence on scalar length scales 264
Molecular mixing models, desirable properties, Gaussian limit 264
Molecular mixing models, desirable properties, linearity 264
Molecular mixing models, desirable properties, local mixing 264
Molecular mixing models, desirable properties, Re, Sc, and Da dependence 264
Molecular mixing models, prospects for further improvements 286Ч287
Moment closures 156
Moment closures, chemical source term 90 91 125 150 151 153Ч156
Moment closures, chemical source term, first-order 153Ч155
Moment closures, chemical source term, higher-order 155Ч156
Moment closures, conditional 207Ч216
Moment closures, scalar fields 123Ч127 193
Moment closures, velocity field 114Ч120
Monte-Carlo simulation 26 259 287 298 328 344Ч348 357Ч358
Monte-Carlo simulation, boundary conditions 346Ч348
Monte-Carlo simulation, fractional time stepping 345
Monte-Carlo simulation, relationship to DQMOM 373 383 385
Monte-Carlo simulation, stochastic differential equations 344 345
Monte-Carlo simulation, use in transported PDF codes 240
Multi-environment conditional PDF models 233Ч236
Multi-environment conditional PDF models, one-step reaction 235
Multi-environment conditional PDF models, relationship to CMC 236
Multi-environment presumed PDF models 221Ч239
Multi-environment presumed PDF models, conditioned on mixture fraction 233Ч236
Multi-environment presumed PDF models, extension to LES 237Ч239
Multi-environment presumed PDF models, general formulation 222Ч226
Multi-environment presumed PDF models, inhomogeneous flows 226Ч233
Multi-environment presumed PDF models, micromixing terms 222
Multi-environment presumed PDF models, presumed PDF 222
Multi-environment presumed PDF models, relationship to DQMOM 383Ч384
Multi-environment presumed PDF models, relationship to micromixing models 221
Multi-environment presumed PDF models, spurious dissipation rate 226
Multi-environment presumed PDF models, ternary mixing 232
Navier Ч Stokes equation 16 27 40 41 67 74 82 100 111 244 292
Navier Ч Stokes equation, definition 101
Navier Ч Stokes equation, filtered 104Ч107
Navier Ч Stokes equation, Fourier-transformed 101
Navier Ч Stokes equation, Reynolds-averaged 17 102 114 253
Non-equilibrium models 54 62 71 78 85 118 127 201
Non-equilibrium models, differential diffusion 135Ч139 325Ч326
Non-equilibrium models, reacting scalars 326Ч327
Non-equilibrium models, scalar dissipation rate 127Ч135 322Ч325
Non-premixed reactants 2Ч5 13 14 23 24 58 125 126 141 168 170 172 194 206 212 229 271 284 286 310 326
Non-premixed reactants, binary mixing 161
Non-premixed reactants, relationship to mixture fraction 156
Non-premixed reactants, ternary mixing 161
Notional particles 240 287Ч289 298Ч300 309 310 323 328Ч330 332 335Ч339
Notional particles in Eulerian PDF codes 331Ч332
Notional particles in Lagrangian PDF codes 340Ч344 356Ч357
Notional particles in Lagrangian PDF methods 287
Notional particles, initial distribution 290
Notional particles, particle-field estimation 298Ч300 348Ч352
Notional particles, relationship to computational cost 339 353 360
Notional particles, relationship to empirical PDF 300Ч302 330
Notional particles, relationship to Eulerian PDF 290Ч292
Notional particles, spatial distribution 290 339
Notional particles, stochastic differential equations 288
Notional particles, weights in PDF codes 330 339 342Ч343
Obukhov Ч Corrsin constant 73 75
Obukhov Ч Corrsin constant, relationship to mechanical-to-scalar time-scale ratio 73
One-point PDF 22 26 29Ч32 69 107 205 240 246 271
One-point PDF, composition 18 22 62 64Ч67 242 243 262
One-point PDF, mixture-fraction 174Ч177
One-point PDF, velocity 29Ч32 107
One-point PDF, velocity, composition 44Ч45 62Ч64 67 81 84 140 240 241 245 246
One-step reaction 103 110 154 181Ч184 202 235 272 273 326
One-step reaction, allowable region 266
One-step reaction, fast-chemistry limit 154
One-step reaction, finite-rate 210
One-step reaction, flamelet model 201
One-step reaction, infinite-rate 154 184 271
One-step reaction, limiting cases 183
One-step reaction, mixture fraction 183
One-step reaction, moment closure 155
One-step reaction, non-isothermal 184 201 203 233 235 268
One-step reaction, presumed CMC 209
One-step reaction, reaction-progress variable 183
Parallel reactions 181 189Ч193 210
Parallel reactions, limiting cases 190 191
Parallel reactions, mixing line 191 192
Parallel reactions, mixture fraction 189
Parallel reactions, reaction-progress variables 189
Parallel reactions, sensitivity to micromixing 192 193
Particle transport processes 332Ч335 344Ч348 357Ч358
Particle transport processes, Eulerian PDF codes 332Ч335
Particle transport processes, Eulerian PDF codes, inter-cell 332Ч335
Particle transport processes, Eulerian PDF codes, intra-cell 332
Particle transport processes, Eulerian PDF codes, numerical diffusion 336Ч337
Particle transport processes, Lagrangian PDF codes 344Ч348 357Ч358
Particle transport processes, Lagrangian PDF codes, boundary conditions 346Ч348
Particle transport processes, Lagrangian PDF codes, Monte-Carlo simulation 344Ч346 357Ч358
Particle-field estimation 298Ч308 332 340 341 343Ч346 348Ч352 358Ч359
Particle-field estimation in Lagrangian PDF codes 348Ч352 358Ч359
Particle-field estimation, bi-linear basis functions 350
Particle-field estimation, consistency 358Ч359
Particle-field estimation, empirical PDF 300Ч302
Particle-field estimation, estimation errors 302Ч307
Particle-field estimation, global estimators 350 351
Particle-field estimation, global estimators, GLME 350
Particle-field estimation, local estimators 349
Particle-field estimation, local estimators, LCME 349
Particle-field estimation, local estimators, LLME 351
Particle-field estimation, notional particles 298Ч300
Particle-field estimation, PDF estimation 307Ч308
PDF estimation 307Ч308
| PDF estimation, bi-variate 20
PDF estimation, uni-variate 19
PDF in DQMOM 373
PDF in QMOM 372
PDF simulation codes 328Ч362
PDF simulation codes, Eulerian 331Ч339
PDF simulation codes, hybrid 354Ч361 see composition
PDF simulation codes, Lagrangian 340Ч354
PDF simulation codes, overview 329Ч331
PDF, beta, bi-variate 176
PDF, beta, uni-variate 175
PDF, Eulerian 29 34
Pdf, joint 8
PDF, Lagrangian 288
PDF, LES composition 109
PDF, LES velocity 106Ч108
PDF, LES velocity, composition 109
PDF, marginal 30
PDF, mixture-fraction, dissipation rate 205Ч206
PDF, multi-point 32
PDF, multi-variate 30
PDF, transport equation, composition 249Ч251 374
PDF, transport equation, velocity 255
PDF, transport equation, velocity, composition 244Ч249
PDF, turbulence frequency 322
PDF, two-point 29 32
PDF, two-time 45
PDF, uni-variate 29
PFR model 3 5Ч7 9 10 13 14 194 197
Premixed reactants 2 3 125 161 207 216 269Ч272 286
Presumed PDF methods 141 174 175 205 216Ч221
Presumed PDF methods, multi-environment models 221Ч239
Presumed PDF methods, multi-environment models in DQMOM 383
Presumed PDF methods, multi-environment models in QMOM 372
Presumed PDF methods, multi-environment models, conditional 233Ч236
Presumed PDF methods, multi-environment models, formulation 222Ч226
Presumed PDF methods, multi-environment models, inhomogeneous flows 226Ч233
Presumed PDF methods, multi-environment models, LES 237Ч239
Presumed PDF methods, multiple scalars 218Ч221
Presumed PDF methods, multiple scalars, Gaussian PDF 220
Presumed PDF methods, multiple scalars, limitations 221
Presumed PDF methods, single scalar 216Ч218
Presumed PDF methods, single scalar, conditional PDF 217
Presumed PDF methods, single scalar, limitations 217
QMOM 372Ч373
QMOM, presumed PDF 372
QMOM, product-difference algorithm 373
QMOM, relationship to DQMOM 373
QMOM, relationship to scalar moments 372
Random field 27 44 69 242 245 246 288
Random field, scalar 62 63
Random field, velocity 27Ч29 32 62 107 108
Random process 27 28 64 249 297
Random process, Eulerian 63
Random process, Lagrangian 63
Random variables 29 108 241 249
Random variables, Gaussian 31
Random variables, relationship to sample space 29
RANS models 17 106 110 114Ч127
RANS models, mean velocity 114
RANS models, relationship to LEM 111 112
RANS models, relationship to LES 104
RANS models, relationship to PDF methods 243 249 252Ч254 354 360
RANS models, relationship to PDF methods, mean velocity, derivation of transport equation 252Ч253
RANS models, relationship to PDF methods, Reynolds stresses, derivation of transport equation 254 354
RANS models, Reynolds stresses 117Ч120
RANS models, scalar dissipation rate 126Ч127
RANS models, scalar dissipation rate, equilibrium model 126
RANS models, scalar dissipation rate, non-equilibrium models 127Ч135
RANS models, scalar flux 123Ч125
RANS models, scalar flux, consistency with Reynolds-stress model 124
RANS models, scalar flux, effect of chemical reactions 125
RANS models, scalar flux, gradient-diffusion 122 123
RANS models, scalar flux, modified gradient-diffusion 122
RANS models, scalar mean 120
RANS models, scalar variance 125Ч126
RANS models, turbulence frequency 116
RANS models, turbulent dissipation rate 116
RANS models, turbulent kinetic energy 115
RANS models, turbulent viscosity 116
RANS models, turbulent-diffusivity-based 121Ч122
RANS models, turbulent-diffusivity-based, turbulent diffusivity 122
RANS models, turbulent-viscosity-based 114Ч116
RANS models, turbulent-viscosity-based, 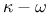 model 116 model 116
RANS models, turbulent-viscosity-based,  model 115 model 115
RANS models, turbulent-viscosity-based, one-equation 115
RANS models, turbulent-viscosity-based, two-equation 115
Reaction mapping 313Ч314
Reaction mapping, direct integration 314
Reaction mapping, Jacobian 312 313
Reaction mapping, linearized 314Ч316
Reaction mapping, linearized, conserved manifold 315
Reaction mapping, linearized, fast manifold 315
Reaction mapping, linearized, sensitivity matrix 315
Reaction mapping, linearized, slow manifold 315
Reaction mapping, linearized, use in ISAT 316
Reaction-progress variables 169 171 173 181Ч183 205 207 209 210 216Ч221 235 236 266 268 272 286
Reaction-progress variables, competitive-consecutive reactions 185
Reaction-progress variables, conditional 209 239
Reaction-progress variables, filtered 239
Reaction-progress variables, flamelet model 203
Reaction-progress variables, initial/inlet conditions 183 204
Reaction-progress variables, one-step reaction 183
Reaction-progress variables, parallel reactions 189
Reaction-progress variables, relationship to reaction-progress vector 166
Reaction-progress variables, simple chemistry 181
Reaction-progress variables, transport equation 203
Reaction-progress vector 156 166 167 171 209 212 221 233 284 286
Reaction-progress vector, conditional 214 233
Reaction-progress vector, equilibrium 178 207
Reaction-progress vector, example flows 168Ч174
Reaction-progress vector, initial/inlet conditions 166 167
Reaction-progress vector, relationship to mixture-fraction vector 166
Reaction-progress vector, transformation matrix 166
Reaction-progress vector, transport equation 177
Reynolds number, Kolmogorov 35
Reynolds number, Taylor-scale 34 35
Reynolds number, turbulence 34Ч36
Reynolds number, turbulent 365
Reynolds stresses 30 37 48Ч51 55 82 83 90 104 106 107 114 123 243 253 259 261 354Ч356 358
Reynolds stresses, anisotropy tensor 118
Reynolds stresses, dissipation rate tensor 50
Reynolds stresses, effect on mean pressure 48
Reynolds stresses, effect on mean velocity 47
Reynolds stresses, normal stresses 48
Reynolds stresses, pressure-diffusion term 50
Reynolds stresses, pressure-rate-of-strain tensor 50
Reynolds stresses, production term 49
Reynolds stresses, relationship to energy spectrum 36
Reynolds stresses, shear stresses 48
Reynolds stresses, transport equation 83
Reynolds stresses, transport equation, consistency with scalar flux 123 259
Reynolds stresses, transport equation, derivation 48Ч51
Reynolds stresses, transport equation, models 117Ч120
Reynolds stresses, transport equation, relationship to PDF methods 254 256Ч258
Reynolds stresses, turbulent-viscosity model 115
Reynolds stresses, velocity-pressure-gradient term 50
RTD theory 3 4 8Ч10 12 25 194
RTD theory, internal-age distribution in CSTR 13
RTD theory, internal-age distribution in PFR 13
RTD theory, relationship to micromixing models 10 12
RTD theory, relationship to PDF methods 8
RTD theory, RTD function 8
RTD theory, RTD function, in CSTR 8
RTD theory, RTD function, in PFR 8
Sample space variables 9 29 308
Sample space variables, composition 9 62
Sample space variables, velocity 27 29 44 63 80
Scalar correlation 96 98 99 136Ч139 218 221 267 277Ч279 282 284 297
Scalar correlation in FP model 277
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



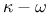 model
model  model
model