|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Orlando T.P., Delin K.F. Ч Foundations of Applied Superconductivity |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 -product 454 555p -product 454 555p
Abrikosov, A. 260 527
Amp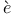 reТs law 27 28 reТs law 27 28
Anisotropy coherence lengths 307Ч311 326p
Anisotropy coherence lengths, conductivity 114Ч123
Anisotropy coherence lengths, first London equation 123 243
Anisotropy coherence lengths, Gibbs free energy 390p
Anisotropy coherence lengths, lower critical field 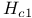 313Ч314 317 390p 313Ч314 317 390p
Anisotropy coherence lengths, mass 123 242 304
Anisotropy coherence lengths, modified second London equation 304
Anisotropy coherence lengths, penetration depths 123 125Ч128 304 577
Anisotropy coherence lengths, principal axis 117
Anisotropy coherence lengths, rotation matrix 120
Anisotropy coherence lengths, rubber sheet model 128 139p 305Ч308 316
Anisotropy coherence lengths, Schr dingerТs equation 242 dingerТs equation 242
Anisotropy coherence lengths, second London equation 124 243 304
Anisotropy coherence lengths, supercurrent density 242
Anisotropy coherence lengths, surface barrier field 391p
Anisotropy coherence lengths, thermodynamic critical field 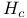 315 317 390p 315 317 390p
Anisotropy coherence lengths, upper critical field 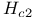 314Ч315 317 390p 314Ч315 317 390p
Bardeen, J. 8 249 527
BCS, coherence length 531 575
BCS, energy gap 8 98 264 309 395Ч398 450 454 575 576
BCS, theory 8 527
Bean, C. 374
Bednorz, J.G. 6
Bessel functions see Modified Bessel functions
BlackТs formula 520
Boltzmann, L. 284
Boundary conditions for superconductors 135p
Boundary conditions, Ginzburg Ч Landau theory 548p
Boundary conditions, MaxwellТs equations 29Ч30
Boundary conditions, MQS systems 42 176
Bulk approximation 63 77 81Ч87 131p 132p 194 209 215p 246 291 293 225 230 231 257p
Charge conservation 27 29
Charge of electron (-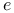 ) 55 ) 55
Charge of superelectrons 8 248
Charge relaxation 35Ч36 208p
Chevrel, R. 6
Chu, P. C. W. 6
Classical model of superconductivity 7 77
Classification of superconductors clean and dirty 531 535
Classification of superconductors, high- 267 267
Classification of superconductors, local and nonlocal 529
Classification of superconductors, type I and type II 7 259 297Ч303 513
Clausius, R. 284
Clean superconductor 531
Clean superconductor, coherence length 531 535
Clean superconductor, penetration depth 535 542
Clean superconductor, sum rule 542 554p
Coenergy 183Ч186 190Ч194
Coenergy, relation to Gibbs free energy 287 292
Coherence length 260 302
Coherence length, anisotropic 310Ч311 312 326p
Coherence length, BCS 531 575
Coherence length, clean limit 531 535
Coherence length, dirty limit 534 535
Coherence length, Ginzburg Ч Landau 499 549p
Coherence length, Pippard 529
Coherence length, temperature dependence 297
Coherence length, vortex radius 264Ч266 549p
Computer elements 90Ч92 479Ч483
Condensation energy 289
Conductivity (normal state) 9
Conductivity (normal state), anisotropy 121 123
Conductivity (normal state), complex conductivity 55
Conductivity (normal state), model of normal state 53Ч58
Conductivity (superconducting state) anisotropy 123 242Ч243
Conductivity (superconducting state), classical model 57Ч60
Conductivity (superconducting state), complex conductivity 59 98 535Ч545
Conductivity (superconducting state), normal channel 96Ч104 554p 555p
Conductivity (superconducting state), quantum model 235Ч242 (also Supercurrent equation)
Conductivity (superconducting state), superconducting channel 96Ч104 554p 555p
Conservation of charge 27 29 30 35 148 238
Constitutive relations 19 31
Conventional superconductors 8 490
Cooper pairs 8 396 531Ч534
Cooper, L.N. 8 249 527
Critical current density 4 10
Critical current density, depairing 266 371 503Ч505
Critical current density, in critical state model 374 380
Critical current density, in Ginzburg Ч Landau theory 503Ч505
Critical current density, in Josephson junctions 402
Critical current density, in type II superconductors 371 372
Critical current, in Josephson junctions 405
Critical current, in SQUIDs 417
Critical magnetic fields 4 290 Thermodynamic Upper Lower
Critical state model of type II superconductors 374
Critical temperature 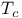 3 6 575Ч577 3 6 575Ч577
Cylinder driven by a current source, normal 51Ч53 132p 133p
Cylinder driven by a current source, perfectly conducting 74p 132p 133p
Cylinder driven by a current source, superconducting 132p 133p
Cylinder in a magnetic field, normal 209p
Cylinder in a magnetic field, superconducting 82Ч83 210p
Cylinder in a magnetic field, vortex 274Ч276 321 322p 386p
DC flux transformer 90Ч92
de Broglie wavelength 222
Decay length 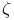 401 401
Delay-power graph 480
Demagnetization factor 215p
Demagnetization factor, as electronic response function 515 520 524
Demagnetization factor, in bulk materials 515
Diamagnetism, perfect see Meissner effect)
dielectric constant 31 515 524
Dielectric, lossy 40
Diffusion constant 530
Dipole fields electric 364
Dipole fields electric, magnetic 49Ч51
Dirty superconductor 531
Dirty superconductor, coherence length 534 535
Dirty superconductor, penetration depth 535 544
Dirty superconductor, sum rule 543Ч544
Dispersion relations plane wave 145
Dispersion relations plane wave, quantum mechanics 224
Dispersion relations plane wave, superconductor 144 145 146 208p
Dispersion relations plane wave, waveguide 158Ч159 163Ч164 169
Displacement current 143
Einstein Ч de Broglie relations 221
Electrodynamics, normal conductor 151
Electrodynamics, superconductor 142Ч151 152Ч172
Electromagnetic power 105Ч113 (see also PoyntingТs theorem)
Electromagnetic power, circuit element 105
Electromagnetic power, distributed systems 108
Electromagnetic power, superconducting 112
Electromagnetic power, time averaged 106
Electromagnetic wavelength 145 528
Electromagnetic wavelength and quasistatic criterion 32Ч33
Electromagnetic wavelength and scattering 243Ч244
Electromechanical systems 187Ч204
Electron volt 222
Electron-lattice interaction 524Ч527 531Ч533
Electroquasistatics (EQS) 35Ч37
Energy and coenergy 183 190
Energy and coenergy of vortex see Vortex
Energy and coenergy, electromagnetic 130 (see also Electromagnetic power)
Energy and coenergy, relation to Helmholtz free energy 325p
Energy and coenergy, stored in electric field 105 108
Energy and coenergy, stored in kinetic energy 112 183
Energy and coenergy, stored in magnetic field 106 108 186Ч187 190 282 283
Energy and coenergy, thermodynamic 282
Energy gap 8 98 264 309 395Ч398 450 454 575 576
Energy-phase relation 239 393
Entropy S 284 327p
Equilibrium 288
FaradayТs law 26Ч27 28
Fermi velocity 243 264 309 530
Field momentum 232
First law of thermodynamics 282
First London equation see London equations
Flux density see Magnetic flux density
| Flux expulsion 4 67
Flux expulsion and Josephson voltage-phase relation 431
Flux expulsion, Lorentzlike force 333 362 363
Flux expulsion, resistance 366Ч367
Flux expulsion, velocity 366 368 372
Flux expulsion, viscosity 368
Flux expulsion, voltage 363 373
Flux flow of vortices 363Ч368 389p
Flux linkage 87
Flux pinning 368Ч383
Flux quantum 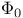 245 245
Flux transporter 88
Fluxoid quantization 245 248Ч251 550p
Force, mechanical 189Ч190 193Ч197 199
Force, mechanical, 21p
Fourier transform 516 571Ч574
Free energy see Gibbs free energy and Helmholtz free energy
Fribbit me wot 580
Gap see Energy gap
Gap voltage 450
Gauge invariance 237 403 404
Gauge transformations 237 403
Gauge-invariant phase difference see Josephson junctions properties)
GaussТs law electric 27 28
GaussТs law electric, magnetic 27 28
GaussТs theorem 28
Generalized potential 226
Gibbs free energy  286Ч287 293 496 286Ч287 293 496
Gibbs free energy  and condensation energy 292 and condensation energy 292
Gibbs free energy  , and coenergy 287 292 , and coenergy 287 292
Gibbs free energy  , anisotropic superconductors 390p , anisotropic superconductors 390p
Gibbs free energy  , at phase transitions 288 , at phase transitions 288
Gibbs free energy  , normal state 293 , normal state 293
Gibbs free energy  , second order transitions 292 , second order transitions 292
Gibbs free energy  , superconducting state 292 289 492 496 498 , superconducting state 292 289 492 496 498
Gibbs free energy  , type I superconductor 289Ч291 , type I superconductor 289Ч291
Gibbs free energy  , vortex 280 293Ч295 313 335 340Ч344 361 390p , vortex 280 293Ч295 313 335 340Ч344 361 390p
Ginzburg Ч Landau parameters 495
Ginzburg Ч Landau parameters, coherence length 499 529p 576 577
Ginzburg Ч Landau parameters, kappa parameter 267
Ginzburg Ч Landau parameters, penetration depth 495 576 577
Ginzburg Ч Landau parameters, temperature dependence 494
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory 8 490Ч514
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory, boundary conditions 502Ч503 548p
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory, equations 501
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory, free energy 492 496 498
Ginzburg Ч Landau theory, in dimensionless units 503
Ginzburg, V.L. 8 563
Gorkov, L.P. 8 490 527
heat capacity 327p
Helium, liquid 2
Helmholtz equation 79 131p 268 330
Helmholtz free energy 325p
High-temperature superconductors 6 15 62 260 262 485 527 548 577
Hilbert transform 537
Hysteretic losses 381Ч383
Image solutions 195 277 387p
Impedance, characteristic 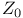 164 164
Impedance, circuit 20 21 25
Impedance, normal state 56 59
Impedance, superconducting 113
Impedance, surface see Surface impedance
Index notation 567Ч570
Inductance, Josephson inductance 443p 470
Inductance, of transmission line 167 170
Internal energy 282
Josephson current-phase relation 402 404 406
Josephson effect in other structures 405 507Ч509
Josephson frequency 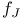 408 408
Josephson junctions, applications 7Ч8 397Ч398
Josephson junctions, computer elements 479Ч483
Josephson junctions, digital circuits 474Ч483
Josephson junctions, magnetometers see SQUIDs
Josephson junctions, properties 7Ч8 396Ч397
Josephson junctions, properties, capacitance 456
Josephson junctions, properties, critical current 405
Josephson junctions, properties, critical current density 402
Josephson junctions, properties, current-voltage characteristics 394Ч398 450 462 464
Josephson junctions, properties, energy 407 428 436
Josephson junctions, properties, gauge-invariant phase difference 404
Josephson junctions, properties, inductance 443p 470
Josephson junctions, properties, penetration depth 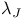 430 432 430 432
Josephson junctions, properties, plasma frequency 438
Josephson junctions, properties, resistance in normal state 452Ч453
Josephson junctions, properties, resistance in subgap region 455
Josephson junctions, properties, Stewart Ч McCumber parameter 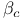 459 459
Josephson junctions, properties, superconducting quantum interference 410Ч420 421 424 471Ч474
Josephson junctions, properties, time constants 459
Josephson junctions, properties, vortices 427 431 433Ч437
Josephson junctions, response to ac sources 409Ч410 442p 444p 466Ч470
Josephson junctions, response to dc sources 408 430Ч431 458Ч466 486p 487p
Josephson junctions, SQUIDs 410Ч420 424 471Ч474
Josephson junctions, transmission lines 437 447p
Josephson junctions, types, basic 398
Josephson junctions, types, extended 420
Josephson junctions, types, generalized 398 449
Josephson junctions, types, long 431
Josephson junctions, types, lumped 405
Josephson junctions, types, short 420Ч431
Josephson junctions, types, two dimensional 445p 446p
Josephson microbridge 405 507Ч509 555p
Josephson phasors 418Ч420
Josephson tunneling 398Ч405
Josephson voltage-phase relation 405 406
Josephson, B.D. 396
Kamerlingh Onnes, H. 2Ч4
Kelvin, Lord 284
Kinematic momentum 223
Kramers Ч Kronig relation 538Ч539
Landau Ч Ginzburg theory see Ginzburg-Landau theory
Landau, L.D. 8 490
LaplaceТs equation 48 73p 175
Latent heat 292 327p
Lattice vibrations 524Ч527
Legendre transformation 183 215p
Length scales, characteristic see Coherence length Electromagnetic Decay Josephson Mean Penetration
LenzТs law 46
Linear system 18
Local electrodynamics 528
London equations and quantum mechanics 239Ч240
London equations, first London equation 59 123 181 239 243 451 537Ч538
London equations, first London, nonlinear 239Ч242
London equations, modified second London equation 272 273Ч278 304
London equations, second London equation 78Ч87 80 124 181 239 243 304
London gauge 257p
London penetration depth  60 542 60 542
London, F. 59 219
London, H. 59
Lorentz force law 54 240
Lower critical field 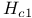 260 295 260 295
Lower critical field 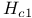 , and magnetization 348 , and magnetization 348
Lower critical field 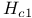 , anisotropic 313Ч314 317 , anisotropic 313Ч314 317
Lower critical field 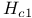 , in Josephson junctions 436 , in Josephson junctions 436
Lower critical field 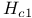 , size effects 386p 387p , size effects 386p 387p
Macroscopic quantum model (MQM) 7 219 234
Macroscopic quantum model (MQM) and Ginzburg Ч Landau theory 501Ч502 513Ч514
Macroscopic quantum model (MQM), charge density 235
Macroscopic quantum model (MQM), current density 236
Macroscopic quantum model (MQM), wavefunction 235
Maglev see Magnetic levitation
Magnetic diffusion 44
Magnetic field 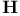 , average , average  357 357
Magnetic field 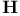 , thermodynamic , thermodynamic 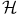 283 346 283 346
Magnetic flux density 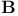 average average  356 357 356 357
Magnetic flux density 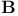 thermodynamic thermodynamic  284 347 389p 284 347 389p
Magnetic levitation 194Ч199 217p
Magnetic monopoles 92Ч94
Magnetization  173Ч176 173Ч176
Magnetization  and electric field 41 and electric field 41
Magnetization  and MaxwellТs equations 37 41Ч42 and MaxwellТs equations 37 41Ч42
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -product
-product  reТs law
reТs law 
 dingerТs equation
dingerТs equation 
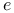 )
) 
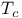
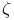
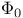

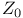
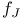
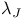
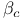

 , average
, average 
 average
average