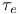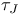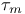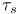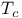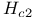|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Orlando T.P., Delin K.F. Ч Foundations of Applied Superconductivity |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Magnetization 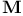 , average , average  357 357
Magnetization 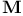 , critical state 377Ч381 , critical state 377Ч381
Magnetization 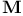 , energy density 108 187 282 283 , energy density 108 187 282 283
Magnetization 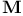 , thermodynamic , thermodynamic 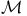 348 351Ч352 389p 348 351Ч352 389p
Magnetoquasistatics (MQS) 37Ч39 41Ч53 151
Magnets applications of 10Ч14
Magnets applications of, materials used in 10
Magnets applications of, type II superconductors 353Ч356 358 382Ч383
Materials, superconducting see Superconducting materials
Matter waves 221 394
MaxwellТs equations 26Ч27 92Ч93
Mean free path  243 528 530 243 528 530
Meissner state 4 66Ч68 172 177 260
Meissner, W. 4
Method I and Method II 179Ч187 216p
Method of images 195 277 387p
Microscopic quantum model 514Ч527 (see also BCS theory)
Models of superconductivity 7Ч9 (see also BCS theory Classical Ginzburg-Landau Macroscopic Microscopic
Modified Bessel functions 268Ч269 563Ч565
Muller, K.A. 6
Multiply connected superconductors 83Ч87 245Ч246
Nonlocal electrodynamics 529
Normal state of electrons and superconductivity see Two-fluid model)
Normal state of electrons, conductivity 53Ч56 452
Normal state of electrons, time constants 205
Normal-superconducting phase boundary 290 295
Ochsenfeld, R. 4
Ohmic conductor 40 146
OhmТs Law 31
Order of phase transition 292
Order parameter 495
Penetration depth  62 143 495 62 143 495
Penetration depth  , anisotropic 123 125Ч128 304 312 , anisotropic 123 125Ч128 304 312
Penetration depth  , clean limit 535 , clean limit 535
Penetration depth  , dirty limit 535 , dirty limit 535
Penetration depth  , Josephson 432 , Josephson 432
Penetration depth  , London penetration depths 62 535 542 , London penetration depths 62 535 542
Penetration depth  , perpendicular 214p , perpendicular 214p
Penetration depth  , temperature dependence 95 , temperature dependence 95
Perfect conductivity as engineering approximation 46Ч47 57Ч58
Perfect conductivity infinite dc conductivity 11 17 537
Perfect conductivity model of 58Ч61
Perfect conductivity versus superconductivity 4 66Ч68
Perfect diamagnetism see Meissner effect)
Permeability  31 31
Permittivity  31 31
Persistent currents 12 86Ч87
phase diagram see Critical magnetic fields
Phase of quantum mechanical wavefunction 228 (see also Josephson phase-current and phase-voltage relations Gauge-invariant and
Phase of quantum mechanical wavefunction in macroscopic quantum model 236
Phase transitions 288 292
Phonons see Electron-lattice interaction)
Pinning of vortices 368Ч383
PlanckТs constant 222
Plasma frequency Josephson 438
Plasma frequency Josephson, normal state 151 210p
Plasma frequency Josephson, superconducting  146Ч150 146Ч150
PoissonТs equation 517
PoyntingТs theorem 107 137p 182
Probability current density 229 233
probability density 227
Quality factor Q 478
Quantization of fluxoid 245
Quantized vortices see Vortex
Quantum interference 410Ч414 (see also SQUIDs)
quantum mechanics 220Ч233
Quasiparticle tunneling 453
Quasistatic criterion 32Ч33 205
Quasistatics 32Ч35 (see also Electroquasistatics and Magnetoquasistatics)
Quenching 374
Reservoir, thermodynamic 285
Resistance in superconductors at finite frequency 98Ч102 113
Resistance in type II superconductors see Flux flow resistance
Resistive transition 3
Resistively shunted junction (RSJ) 458
resistivity see Conductivity
Ring, superconducting 249Ч251 441p 442p
Rubber sheet model 128 139 305Ч307 316
Scalar potential 231
Scalar potential, magnetic 48 174
Scattering of electrons 243 528 529 530
Scattering of superelectrons 54 55 57Ч59 529
Schrieffer, J.R. 8 249 527
SchrodingerТs equation 220Ч227 242 254p 257p 400
Screening length 521
Second law of thermodynamics 285 288
Second London equation see London equations
Sign of the electronТs charge 55
Skin depth 44 62
Slab driven by a current source, critical currents 503Ч505
Slab driven by a current source, normal metal 72p
Slab driven by a current source, superconductor 138p 503Ч505
Slab in a parallel magnetic field, critical magnetic fields 290 323p
Slab in a parallel magnetic field, critical state model 375Ч383
Slab in a parallel magnetic field, normal metal 42Ч47 108Ч111
Slab in a parallel magnetic field, perfectly conducting 46Ч47 61Ч68
Slab in a parallel magnetic field, superconductor 78Ч80
Slab in a parallel magnetic field, vortex in 293Ч295 322p 323p 387p
Specific heat see Heat capacity
Sphere in a magnetic field, normal metal 47Ч51
Sphere in a magnetic field, perfectly conducting 47Ч51 67 176Ч177 178
Sphere in a magnetic field, superconductor 67 81 131p 178
Squids 410Ч420 424 471Ч474
Stewart Ч McCumber parameter, 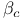 459 459
StokesТs theorem 28
Sum rule 540 554p
Superconducting materials 575Ч577 (see also High-temperature superconductors)
Superconducting materials,  , ,  , ,  6 6
| Superconducting materials, 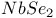 114 114
Superconducting materials, 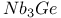 5 372 5 372
Superconducting materials, 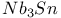 5 10 213 260 371 372 374 5 10 213 260 371 372 374
Superconducting materials,  5 6 114 5 6 114
Superconducting materials,  6 6
Superconducting materials, 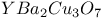 6 114 213 6 114 213
Superconducting materials, Al 456
Superconducting materials, Bi 259
Superconducting materials, CuS 6
Superconducting materials, Hg 3
Superconducting materials, Nb 5 213
Superconducting materials, Nb Ч Ti 5 6 10 200 372 374
Superconducting materials, Pb 259 395 466
Superconducting materials, Pb Ч Bi 6 259
Superconducting materials, W 5
Supercurrent equation 236 238 242 393 402 441p
Superelectrons 8 94
Superelectrons, attractive potential for 523Ч527
Superelectrons, charge 8 248
Superelectrons, current density 96 236
Superelectrons, density 228 491 497
Superelectrons, mass 8
Superelectrons, near vortex core 264Ч267 309Ч311
Superelectrons, tunneling 394Ч398
Superelectrons, velocity 236 264 309 529Ч534
Surface barrier field 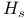 339 339
Surface current 29
Surface energy 509Ч513
Surface impedance 111 113
Surface nucleation field 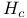 3 507 3 507
Thermodynamic critical field 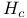 4 289 290 297Ч303 4 289 290 297Ч303
Thermodynamics 281Ч291 (see also Gibbs free Thermodynamics energy Helmholtz Lower Upper and
Thermodynamics and energy density of superconductor 289
Thermodynamics, anisotropic 315 317
Thermodynamics, Ginzburg Ч Landau 494
Thermodynamics, size effects 323p 324p
Thermodynamics, temperature dependence 289
Time constants, capacitive  21 21
Time constants, characteristic 205 206
Time constants, charge relaxation 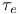 36 208p 36 208p
Time constants, coupling t 21 21
Time constants, electric see Charge relaxation)
Time constants, electromagnetic  33 39 57Ч59 33 39 57Ч59
Time constants, inductive  21 21
Time constants, Josephson 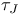 459 476 459 476
Time constants, magnetic see Magnetic diffusion)
Time constants, magnetic diffusion 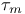 38 38
Time constants, ordering of time constants 22Ч26 57Ч59 477
Time constants, rise  476 477 487p 476 477 487p
Time constants, scattering  54 55 57Ч59 243 54 55 57Ч59 243
Time constants, steering  476 481Ч482 476 481Ч482
Time constants, superconducting 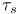 531 531
Time constants, superconducting channel  101Ч102 138p 146 101Ч102 138p 146
Time constants, turn-on  476 478 476 478
Time invariant system 19
Transfer function 19
Transformer, flux 88Ч89
Transition temperature 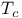 see Critical temperature see Critical temperature
Transmission lines 160Ч172 211p
Transmission lines and Josephson junctions 437
Transmission lines, normal state 162 170 171
Transmission lines, superconducting 160Ч172 170 171 212p
Transmission lines, TEM mode approximation 157 160Ч161 211p
Tunnel junctions see Josephson tunnel junctions
Tunneling 255p 394Ч398
Tunneling, normal state resistance 452Ч453
Tunneling, superconducting see Josephson tunnel junctions
Two-fluid model 94Ч104 149
Two-fluid model, frequency dependence 98 143 145 146
Two-fluid model, temperature dependence 96 100 554p
Type I and type II superconductors 7 259 297Ч303 513
Upper critical field 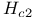 5 260 295 296Ч297 5 260 295 296Ч297
Upper critical field 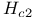 , anisotropy 314Ч315 317 , anisotropy 314Ч315 317
Upper critical field 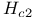 , in Ginzburg Ч Landau theory 505Ч507 , in Ginzburg Ч Landau theory 505Ч507
Upper critical field 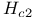 thin film 551p 544p thin film 551p 544p
Vector identities 557
Vector potential 230
Velocity of superelectrons 236 264 309 529Ч534
Velocity of superelectrons, critical velocity near vortex core 264Ч266 309Ч310
Vortex 261
Vortex force on 332 334 338 339 362
Vortex, and fluxoid quantization 262Ч263
Vortex, anisotropic 303Ч318 390p
Vortex, array 261Ч262 273 295Ч297 344-352
Vortex, boundary effects 336Ч340
Vortex, core model 264 267 549p 550p
Vortex, current density of 263Ч264 271 273 308
Vortex, energy 279 280 326p 331 388p
Vortex, energy of single vortex  280 388p 280 388p
Vortex, experimental observation 262
Vortex, Gibbs free energy 293Ч295 335 361 390p
Vortex, interaction between 331Ч324
Vortex, magnetic field of 270 273 306
Vortex, magnetization 348 351Ч352
Vortex, modified London equations for 272
Vortex, motion see Flux flow resistance)
Vortex, motion, number of flux quantum per vortex 261Ч263 388p
Vortex, surface barrier field 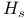 339 339
Vortex, viscosity 368
Vortex, vorticity 272 313
Wave equation, electromagnetic 143 157 163 215p
Wave equation, Josephson junctions 437 446p
Wave equation, quantum mechanical 224 226 227 242
Wave-particle duality 221 254p
Waveguides see Transmission lines
Wavelength see Electromagnetic wavelength)
Weakly coupled superconducting structures 405 507Ч509
Wu, M. Ч K. 6
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



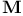 , average
, average 
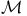





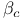
 ,
,  ,
, 
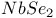
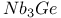
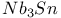


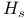
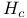 3
3