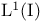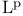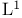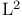|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Weir A.J. — Lebesgue Integration and Measure |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
 37—43 47—50 78—81 37—43 47—50 78—81
 126 126
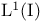 40 79 40 79
 33—36 41 46 78 33—36 41 46 78
 126 126
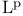 162—222 162—222
 165—166 165—166
Absolutely convergent series 5
Affine mapping 139—144
Almost everywhere 32 77
Almost everywhere, convergence 168
angle 174
Archimedes, Axiom of, 3n 14 164
Area 71 82 87
Baire classes 122
Ball, closed 82
Ball, open 82 224
Banach space 221
Bessel's equation 198
Bessel's inequality 198
Bolzano — Weierstrass theorem 239
Bonnet's Mean Value Theorem 134 210
Borel seta 145
Boundary 227
Bounded convergence theorem 110 112
Bounded set 233
Bounded variation 65 209
Brouwer's theorem 158
Cantor 16 17
Cantor, ternary set 20 69 145
Cauchy General Principle of Convergence 116 163 169
Cauchy sequence 164
Cesaro 211 218
Characteristic function 23 72
Clarkson's inequalities 181
Closed ball 82
Closed disk 82
Closed set 135 227
Closure 193 227
Closure of an interval 71
Compact set 135 234—236
Completeness of 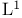 42 42
Completeness of 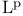 170 170
Completeness of a metric space 164
Completeness of a set in 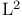 196 196
Completeness of R 2—13 162—164
complex numbers 13
Connected set 229—233
Continuous function 46—50 79—81 228—238
Continuously differentiable function 156
Convergence of a sequence 2—10
Convergence of a series 5
Convergence, almost everywhere 168—171
Convergence, in mean (strong) 168—171 207
Convergence, pointwise 168—171 202—214
Convex set 176
Countable set 15
Cross-section 85 87
cube 71
Darboux's theorem 52
Decimal expansion 5—7 10 17
Decreasing function 48
Decreasing sequence 2
Dedekind's Theorem 14
Dense 15 196
Density function 146—161 185—186
Derivative 55—69
Derivative measure 152—154
Derivative, directional 155
Derivative, linear 156—159
Derivative, partial 155
Determinant 144
Differentiation under the integral sign 118
DIMENSION 192
Dirichlet kernels 206—213 216—217
Disk, closed 82
Disk, open 82 89
Distance 1 70 155 223
Dominated Convergence Theorem 106 109 113
du Bois-Reymond 214
Dual spaces 166 184 187
Eigenvalue, maximum 240
Elementary figure 75
Erlanger Programm 134
Euclidean space 70—92 124 219
Exchange Lemma 193
Exterior 227
Fatou's lemma 110 116
Fejer 211
Fejer kernels 212—214
Fejer theorem 213 214
Finite dimensional subspace 191
Fourier series 188 194—199 202—219
Fubini's theorem 83 90 123 142
Function 22
Function absolutely continuous 67
Function of bounded variation 65 209
Function, continuous 46—50 79—81 228—238
Function, continuously differentiable 156
Function, generalised step 128
Function, increasing, decreasing, monotone 48
Function, measurable 120—124 128—133
Function, simple 128 130
Function, step 25—30 72—76
Fundamental theorem of the calculus 56 67 112
Gamma function 111
Geometry 134
Geometry, of 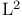 172—181 172—181
Gibbs' constant 218
Gibbs' phenomenon 207 218
Gram — Schmidt Theorem 191
Hausdorff space 238
Heine — Borel theorem 34 233
Heisenberg matrix theory 200
Hermite functions 201
Hilbert space 221—222
Hoelder's inequality 167
Homeomorphism 144 238
Hyperplane 71
Increasing function 48
Increasing sequence 2
Infimum 9
Inner product 172
Integers 1
Integrable function 37 79
| Integrable set 125
Integral, definite 44—50
Integral, indefinite 54—62
Integral, Lebesgue 37—43 79—91
Integration by parts 58 103
Integration by substitution 59 104
Interior 227
Intermediate Value Theorem 231
interval 1 2 70 71
Interval length 2
Interval measure 71
Inverse mapping theorem 159
Isometry 137—144
Jacobian formula 158
Jacobian matrix 155
Jordan's Theorem 209
Klein, Felix 134
Laguerre polynomials 200
Lebesgue ix et sqq. 202
Lebesgue integral on  70—92 70—92
Lebesgue integral on R 22—69
Lebesgue measure 124 et sqq.
Legendre polynomials 200 202
Length 2 24 28 87
Levi, Beppo 93 107
Limit point 226
Linear dependence, independence 192 194
Linear functionals 182
Linear mapping 138
Linear operator 72
Linear space 22 72 165 199 220
Linear subspace 176 220
Lipschitz condition 69
Localization principle 206
Lower bound 3 9
Matrix 139
Matrix, unit, invertible, elementary, diagonal 140
Mean value theorem 237
Mean Value Theorem for Integrals 41
Mean, arithmetic, geometric 62
Measurable function 120—124
Measurable set 124
Measure 75 87 124—146
Measure, derivative 152
Measure, of a bounded interval 71
Metric 223
Metric space 163 220 223
Metric, complete 164
Metric, discrete 224
Minkowski's inequality 167 172
Monotone Convergence Theorem 93 96 103 106
Monotone function 48
Monotone sequence 2
Neighbourhood 239
Nested intervals 14
Non-measurable set 131
Norm 70 154 165 199 220
Null set 18 77
Open ball 82 224
Open set 135 225 237
Open, relatively 230
Ordered field 12
Ordinate set 88 133
Origin 1
Orthogonal 174
Orthogonal complement 180
Orthogonal projection 180
Orthonormal set 191—201
Parallelogram 175
Parseval's equation 199—200
Pointwise convergence 168—171 202—214
Polar transformation 146 159
Polar transformation, cylindrical 159
Polar transformation, spherical 160
Positive 1
Projection 179
Pythagoras' theorem 6 7 174
Radon — Nikodym theorem 152 185
Rational numbers 1
Real line 1
Relatively open set 230
Riemann integral 47 51—54 83
Riemann integral, improper 106
Riemann — Lebesgue lemma 115 204
Riesz — Fischer theorem 199
Riesz's Toolroom for 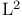 183 183
Rolle's theorem 236
Scalar product 137 199 221
Scalar product (inner product) 172
Schroedinger 200
Schwarz' inequality 137 173
Segment 174
SEQUENCE 2
Sequence, convergence almost everywhere 168—171
Sequence, convergence in mean 168—171 207
Sequence, increasing, decreasing, monotone 2
Sequence, pointwise convergence 168—171 202—114
Sequence, upper, lower 107
Series 4
Series, absolute convergence 5
Series, convergence 5
Series, convergence in 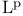 169 169
Sets, union, intersection, difference, symmetric difference of 23
Simple function 128—130
Step function 25—30 72—76
Step function, generalised 128
Strong convergence 168—171 207
Summable (O,1) 211
Supremum 9 12
Symmetric difference 23
Tonelli's theorem 123
Topological mapping 144 238
topology 223—240
Topology, general 226 237
Triangle inequality 138 165 173 223
Trigonometric polynomial 190
Uniform continuity, convergence 218
Upper bound 3 9 12
Variation, bounded 65 68
Variation, positive, negative 68
Variation, total 68
Vector space 220
Volume 71 73 83 87
Weierstrass' approximation theorem 218
Well-ordering of positive integers 8
Zorn's lemma 221
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте