|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Kao E. Ч Introduction to Stochastic Processes |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 queue 91 queue 91
 queue 67Ч68 queue 67Ч68
 queue 65Ч67 queue 65Ч67
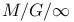 queue, departure process 68Ч69 82Ч83 queue, departure process 68Ч69 82Ч83
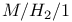 queue, waiting time, distribution of 25Ч26 queue, waiting time, distribution of 25Ч26
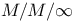 queue, time dependent probability 90 queue, time dependent probability 90
Absorbing state 174 241
Accessibility 172
Alternating renewal process see "Renewal process"
Aperioidic state and chain 171
Arbitrage 402
Arrival theorem see "Closed queueing network"
Asymptotic-rate theorem 27 42 100
Balance equation see also "Detailed balance equation"
Balance equation for continuous-time Markov chain 253Ч254
Balance equation for discrete-time Markov chain 177Ч179
Bellman's functional equation 409
Beta of a security 407
Birth and death process 242Ч243 254Ч255 260Ч263
Birth rates 242
Black Ч Scholes differential equation 402Ч403
Blackwell's renewal theorem 128
Branching process 40Ч41
Brownian motion 374Ч375
Brownian motion, arithmetic 397 399
Brownian motion, geometric 398Ч401
Brownian motion, integrated 417
Brownian motion, reflected at origin 419
Brownian motion, standard 394
Brownian motion, with two barriers 384Ч385
Call option, European 403Ч404
Canonical form of Markov chain 173 185Ч186
Capital asset pricing 407Ч409
Cash management problem 190Ч192 214 282Ч284
Censored discrete-time Markov chain 200Ч201
Central limit theorem 128 401
Central server model 306
Cesaro limit see "Time average"
Chapman Ч Kolmogorov equation of continuous-time Markov chain 240
Chapman Ч Kolmogorov equation of diffusion process 385Ч386
Chapman Ч Kolmogorov equation of discrete-time Markov chain 165Ч166
Characteristic function 28
Closed queueing network 293Ч294 308
Closed queueing network with blocking 296 314Ч315
Closed queueing network, arrival theorem for 295
Closed queueing network, Buzen's algorithm 294Ч295 320
Closed queueing network, normalizing constant 294
Closed queueing network, product form solution 294
Closed queueing network, waiting time at server 295
Coefficient of variation 73 305
Communication 168
Compering exponential 19Ч21 242 350
Compound random variable 10
Compound random variable, generating function 10
Compound random variable, mean and variance 10Ч11
Contingent claim 402
Continuous distribution, random variable, 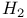 with balanced means 25 305 with balanced means 25 305
Continuous distribution, random variable, bivariate normal 408
Continuous distribution, random variable, Erlang 21
Continuous distribution, random variable, exponential 19
Continuous distribution, random variable, gamma 21 123 126
Continuous distribution, random variable, generalized Erlang 267
Continuous distribution, random variable, hyperexponential 268
Continuous distribution, random variable, mixture of generalized Erlang 269
Continuous distribution, random variable, mixture of two Erlang 305
Continuous distribution, random variable, multivariate normal 395
Continuous distribution, random variable, normal 281 386 400 403
Continuous distribution, random variable, Weibull 205Ч206
Continuous-time Markov chain 239
Continuous-time Markov chain as Markov renewal process 331
Continuous-time Markov chain of QBD type 309Ч310
Continuous-time Markov chain two-dimensional 306
Continuous-time Markov chain, absorbing chains 256Ч258
Continuous-time Markov jump process 276
Convolution 18 335
Counting process 5
Coupon collection problem 199Ч200
Covariance 395 417
Current life, or age, or backward recurrence time 107
Current life, or age, or backward recurrence time, distribution of 114Ч115
Data base management 89 219 381Ч382
Death rates 242
Defective random variable 130 170
Delayed renewal process see "Renewal process"
Denumerable Markov chain 162
Derivative security 402
Detailed balance equation of reversible Markov chain 209
Diffusion equations for Brownian motion, backward equation 376Ч377
Diffusion equations for Brownian motion, forward equation 377Ч378 418
Diffusion process 385
Diffusion process with reflecting barrier 386
Diffusion process, generalized 391Ч393
Diffusion process, limiting density 392
Directly Riemann integrable 102 120
Discounted reward 203 277Ч280
Discrete distribution, random variable, binomial 8
Discrete distribution, random variable, generalized negative binomial 198Ч199
Discrete distribution, random variable, geometric 9 11 130 171
Discrete distribution, random variable, negative binomial 9
Discrete distribution, random variable, Poisson 8
Discrete renewal process 144Ч146
Discrete renewal process, delayed 171
Discrete renewal process, excess life 145Ч146
Discrete renewal process, limiting excess life 211Ч212
Discrete-time Markov chain 162
Discrete-time Markov chain of GI/M/1 type 223
Discrete-time Markov chain of QBD type 221
Discrete-time Markov chain, absorbing chain 173Ч174 188Ч190
Discrete-time Markov chain, classification of state 167Ч169
Discrete-time Markov chain, decomposition of state space 172Ч173 229Ч230
Discrete-time Markov chain, embedded in a continuous-time Markov chain 242 274
Discrete-time Markov chain, embedded in a Markov renewal process 337 343
Discrete-time Markov chain, equivalence class 168
Discrete-time Markov chain, n-step transition probability 165
Discrete-time process 2
Drift of a Brownian motion 376
Elementary renewal theorem 101 128
Equilibrium renewal process see "Stationary renewal process"
Ergodic discrete-time Markov chain 175Ч176
Erlang loss formula 288
Excess life, or residual life, or forward recurrence time 107
Excess life, or residual life, or forward recurrence time under semi-regenerative process paradigm 349
Excess life, or residual life, or forward recurrence time, distribution of 109
Excess life, or residual life, or forward recurrence time, limiting distribution of 110
Excess life, or residual life, or forward recurrence time, limiting mean excess life 110
Excess life, or residual life, or forward recurrence time, time average of expected excess life 127
Filtered nonhomogeneous Poisson process 91
Filtered Poisson process 76Ч80
Filtered Poisson process, mean and variance for 79
Filtered Poisson process, probability generation function for 79
Filtered Poisson process, response function of 77
Final value property of generating function 6 35 41
Final value property of Laplace transform 18 35 41
First passage time of Brownian motion 379Ч380 395 419
First passage time of discrete-time Markov chain 168Ч169 175 190
Flexible manufacturing system 296Ч297 306Ч308 365Ч366
Fork Join queue 308
Forward contract 401Ч403
Function of bounded variation 31
Fundamental matrix of continuous-time Markov chain 257
Fundamental matrix of discrete-time Markov chain 189
Gain rate 203 277
Gamma function 21
Gauss kernel 418
Gaussian process 395
Generating function 6 294
Generating function, finding moments 8
Generating function, numerical inversion 16Ч17 44Ч45
Geometric transform see "Generating function"
GI/G/1 queue, diffusion approximation 386Ч389
| GI/G/c queue, diffusion approximation 393Ч394
GI/M/1 queue under Markov renewal paradigm 329
GI/M/1 queue, limiting probabilities 181Ч183
GI/M/1 queue, queue length distribution 359Ч362
GI/M/c queue queue 86Ч87
Gordon Ч Newell network see "Closed queueing network"
Hamilton Ч Jacobi Ч Bellman equation 411Ч412 414Ч416
Holding time distribution 323
Holding time distribution, mean 337
Independent increments 4 49 51 400
Index bond, Fisher's model of 405Ч407
Index set 2
Infinitesimal generator 242
Instantaneous state 241
Insurance problem 21Ч24
Integrate intensity function 56
Intensity function 56
Inventory models 88
Inventory models, (S-1,S) policy 90
Inventory models, continuous review (s,S) policy 120
Inventory models, continuous review, unit demand 147Ч148
Inventory models, discrete-time with batch demands 346Ч347
Inventory models, periodic review (s,S) policy 113 149 164 167 204
Inventory models, two-echelon repairable item 312Ч313
Irreducible Markov chain 168
Ito's lemma, process 398Ч399 404Ч405
Jackson network see "Open Jackson network"
Jensen's inequality 407
Kelly's lemma 289
Key renewal theorem 102
Kolmogorov criteria see "Reversible Markov chain"
Kolmogorov differential equations, backward 245Ч246
Kolmogorov differential equations, forward 246 265
Kolmogorov differential equations, Laplace transform 246Ч247 265
Lack of anticipation assumption (LAA) 85
Laplace transform 17
Laplace transform of renewal function 99Ч100
Laplace transform, finding moments 18
Laplace transform, numerical inversion 25 26 45Ч46
Laplace Ч Stieltjes transform 32Ч34 331
Laws of total probability 12 19 103 331 351
Left limit 28
Leibnitz's rule 35Ч36
Length biased sampling 108 157
Limiting state probability of continuous-time Markov chain 252Ч254
Limiting state probability of discrete-time Markov chain 175Ч178 233
Limiting state probability of Markov renewal process 338
Limiting state probability, solution by state reduction 201Ч203
Little's formula 140Ч141 293
Little-oh function 20 22Ч23 34Ч35 65Ч66
M/G/1 queue under Markov renewal paradigm 325Ч327
M/G/1 queue with group arrivals 366
M/G/1 queue, control with an N policy 138Ч140 366
M/G/1 queue, Laplace Ч Stieltjes transform of sojourn time 223
M/G/1 queue, limiting probabilities 180Ч181
M/G/1 queue, Pollaczek Ч Khintchine formula 218
M/G/1 queue, queue length distribution 136Ч138 350Ч351 357Ч359
M/G/1 queue, special service after an idle period 366
M/G/c queue 86
M/M/1 queue 263
M/M/3 queue, departure process of 327Ч328
M/M/s queue 244 255Ч256 263Ч264 285Ч286
M/M/s/s queue 287Ч288
M/PH/1 queue 224 310
Marked Poisson process see "Poisson process"
Markov chain subordinated to a Poisson process 273 278
Markov jump process with reward 277Ч282
Markov process 385
Markov renewal equation 336
Markov renewal equation, limiting solution 339
Markov renewal function 331Ч336
Markov renewal process 323
Markov renewal process, embedded in semi-Markov process 339Ч340
Markov renewal process, embedded in semi-regenerative process 348Ч351
Markov renewal type of equation 352
Markov reward processes, continuous-time 277Ч281
Markov reward processes, discrete-time 203
Markovian property 162
Matrix exponential 247Ч248 251
Maximum likelihood estimator 62
Mean holding time 337
Mean value function 57
Memory less property 21 241
Merton's Portfolio selection problem 398 415Ч417
Method of embedding 164
Moment generating function 27
Moment generating function of normal distribution 28
Multiprogramming system 390Ч391
Nonhomogeneous Poisson process 56Ч58
Nonhomogeneous Poisson process, arrival time condition on arrival count 58Ч59
Nonhomogeneous Poisson process, filtered see "Filtered nonhomogeneous Poisson process"
Nonhomogeneous Poisson process, transform arrival time to that of Poisson 60Ч61
Nonstationary Poisson process see "Nonhomogeneous Poisson process"
Null recurrent state 169 175
Occupancy-time statistics of continuous-time Markov chain 257Ч258
Occupancy-time statistics of discrete-time Markov chain 171 189
Open Jackson network 290Ч293
Open Jackson network, product form solution 291
Ornstein Ч Uhlenbeck process 417
Palm theorem 56
Palm theorem, with nonhomogeneous Poisson arrivals 91
Partial fraction expansion 14
Periodic discrete-time Markov chain 176
Periodic discrete-time Markov chain, canonical form of 185Ч188 232Ч233
Periodicity of discrete-time Markov chain 171
Perpetual warrant 382Ч383
PH/M/1 queue 224
PH/M/c queue 311Ч312
Phase-type distribution, approximation by 270Ч271
Phase-type distribution, continuous-time 264Ч266 361Ч362 387
Phase-type distribution, convolution 266Ч267
Phase-type distribution, discrete-time 197Ч198
Phase-type distribution, limiting excess-life distribution 311
Phase-type distribution, moments 266
Phase-type distribution, order of 265
Phase-type renewal process 271Ч273
Pointwise limit 35
Poisson arrival see time averages (PASTA) 83Ч87
Poisson arrival see time averages (PASTA), applied to GI/M/c queue 86Ч87
Poisson arrival see time averages (PASTA), applied to M/G/1 queue 137 359
Poisson process 48
Poisson process as a birth and death process 244
Poisson process, arrival time condition on arrival count 52Ч53
Poisson process, compound 72Ч76
Poisson process, decomposition 54
Poisson process, generating arrival count by simulation 52
Poisson process, generating arrival times by simulation 52
Poisson process, interarrival time of 51
Poisson process, logarithmic Poisson 74Ч75
Poisson process, marked 80
Poisson process, stuttering Poisson 75Ч76
Poisson process, two-dimensional 80Ч83
Positive recurrence 169 175
Probability generating function 7
Probability generating function, finding moments 8
Product form solution, nonexistence of 296
Product warranty problems 112 148
Pure birth process 304
Quality control 183Ч185
Quasi birth and death (QBD) process 222
Queueing network with blocking 315
R matrix of QBD process 272
Random sum see "Compound random variable"
Random walk 221
Random walk with a reflecting barrier 179
Random walk, approximate a Brownian motion 374Ч375
Random walk, Markov chain formulation 220Ч221
Random walk, simple 41 104Ч105 150Ч151
rcll 29
Recurrence time of a renewal process see "Total life"
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 queue
queue  queue
queue  queue
queue 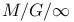 queue, departure process
queue, departure process 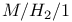 queue, waiting time, distribution of
queue, waiting time, distribution of 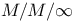 queue, time dependent probability
queue, time dependent probability 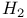 with balanced means
with balanced means