|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Falconer K. Ч Fractal Geometry: Mathematical Foundations and Applications |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
( -)well approximable number(s) 155Ч157 205 207 -)well approximable number(s) 155Ч157 205 207
(delta-)/( -)cover 27 28 30 36 -)cover 27 28 30 36
(delta-)/( -)neighbourhood 4 45 112 124 -)neighbourhood 4 45 112 124
(delta-)/( -)parallel body 4 -)parallel body 4
(s-)capacity 72
(s-)energy 70
(s-)potential 70
(sigma-)/ -finite measure 95 -finite measure 95
Affine transformation 8 139
Affinity 7 8
Almost all 16 85
Almost everywhere 16
Almost surely 19
Analytic function 138 180 215
Antennas 309Ч311
arc, dimension print 56
Area 14
Area, scaling of 29
Arnold's cat map 213
Astronomical evidence, for small divisors 208
Attractive orbit 228
Attractive point 216 222
Attractor 123Ч128 139 140 187
Attractor in continuous dynamical system 201Ч205
Attractor in discrete dynamical system 187 189 192 194
Autocorrelation 169Ч173 268
Autocorrelation function 170
Average 21
Avogadro's number 258
Baker's transformation 193Ч194 210 211
Ball 4
Banach's contraction mapping theorem 124 125
Basic interval 35 62 127 152
Basin of attraction 187 201 222 238Ч241
Besicovitch construction 178 179
Besicovitch set 179
Bi-Lipschitz equivalence 236
Bi-lipschitz function 8 103
Bi-Lipschitz transformation 32 33 41
Bifurcation diagram 192
Bijection 7 236
Binary interval 16 36
Borel set(s) 6
Borel set(s) and duality 178
Borel set(s) and intersections 111
Borel set(s) and products 100 101 105 106
Borel set(s) and projections 90 93
Borel set(s) and subrings 183Ч184
Borel set(s) and subsets of finite measure 68 69 70
Borel set(s), measure on 11Ч12
Boundary 5 6
Bounded set 5 114
Bounded variation 86
Box counting 283 298
Box(-counting) dimension 41Ч47
Box(-counting) dimension and growth 299Ч300
Box(-counting) dimension and Hausdorff dimension 46 60
Box(-counting) dimension, Brownian motion 263 265
Box(-counting) dimension, fractional Brownian motion 268
Box(-counting) dimension, fractional Brownian surface 273
Box(-counting) dimension, Levy stable process 272
Box(-counting) dimension, limitations 48
Box(-counting) dimension, modified 49Ч50
Box(-counting) dimension, problems 48Ч49
Box(-counting) dimension, properties 47Ч48
Box(-counting) dimension, ways of finding 44 47
Branch 223
Branching process theory 250
Brownian graph 266
Brownian motion 37 258Ч267 298 299 311Ч315
Brownian motion, Fourier series representation 260
Brownian motion, fractional 173 267Ч271 275
Brownian motion, index- fractional 267Ч271 311 fractional 267Ч271 311
Brownian motion, multifractional 271
Brownian motion, n-dimensional 260
Brownian sample function 259 261 262
Brownian sample function, graph 265Ч266
Brownian sample function, index- fractional 273 fractional 273
Brownian sample function, multiple points 265
Brownian surface, fractional 273Ч275
Brownian trail(s) 258 261 262 264Ч265
Cantor dust xx xxi 94 126
Cantor dust, calculation of Hausdorff dimension 34
Cantor dust, construction of xxi 34
Cantor set as attractor 189 192 194
Cantor set, construction of 61Ч62
Cantor set, dimension of xxiii 34Ч35 47
Cantor set, middle  64 64
Cantor set, middle third xvii xviii 34Ч35 47 60 61 63Ч64 87 99 100 112 123Ч124 127 129 188 189
Cantor set, non-linear 136Ч137 154
Cantor set, random 245Ч250 256
Cantor set, uniform 63Ч64 103 141
Capacity dimension 41
Cartesian product 4 87 99 100
Cat map 213
Cauchy sequence 125
Central limit theorem 24 259
Chaos 189
Chaotic attractor 189 192
Chaotic repeller 189
Characteristic function 271
Choleski decomposition 270
Circle perimeter, dimension print 56
Class 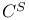 113Ч118 157 113Ч118 157
Class 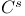 , member 113 , member 113
Closed ball 4 66
Closed interval 4
Closed loop, as attractor 201
Closed set 5 114 201
Closure of set 6
Cloud boundaries 244 298
Coarse multifractal spectrum 278Ч279
Coarse multifractal spectrum, lower 280
Coarse multifractal spectrum, upper 280
Coastline(s) 54 244 298
Codomain 7
Collage theorem 145
Compact set 6 48
Complement of a set 4
Complete metric 125
Complex dynamics 216
Composition of functions 7
Computer drawings 127Ч128 145Ч148 196 227 232 233 234 239 240 244 260 269 270Ч271 275
Conditional expectation 22
Conditional probability 19
Conformal mapping 138Ч139 180 241
Congruence(s) 7 112
Congruence(s), direct 8
Conjugacy 223
Connected component 6
Connected set 6
Content, Minkowski 45
Content, s-dimensional 45
Continued fraction expansion 153
Continued fraction(s) 153Ч154
Continued fraction(s), examples 153
Continuity equation 203
Continuous dynamical systems 201Ч205
Continuous function 10
Continuously differentiable function 10
contours 275
Contracting similarity 123
Contraction 123
Contraction mapping theorem 124 125
Convergence 8
Convergence of sequence 5
Convergence, pointwise 10
Convergence, uniform 10 17
Convex function 181Ч182 287
Convex surface 182
| Convolution theorem 73 172
Coordinate cube 4
Copper sulphate, electrolysis of 300Ч301 302Ч304
Correlation 169Ч173 268 311
Countable set 4 32 41
Countable stability of dimension print 55
Countable stability of Hausdorff dimension 32 41
Counting measure 13
Covariance matrix 270
Cover of a set 27 28 30 35Ч36
Covering lemma 66Ч67
critical exponent 54
Critical point 227 228
Cross section 202
cube 4 42
Cubic polynomial, Newton's method for 239Ч241
Curve 53 81
Curve, fractal 133Ч134
Curve, Jordan 53 81
Curve, rectifiable 81Ч84 85Ч86 181Ч182
Curve-free set 81 83Ч84
Curve-like set 81 82Ч84
Darcy's law 305
Data compression 145Ч148
Decomposition of 1-sets 80Ч81
Dendrite 232
Dense set 6
density 76Ч80 84 88 152
Density function 306
Density lower 77 84
Density upper 77
Derivative 10
Diameter of subset 5 27
Difference of sets 4
Differentiability 10 137Ч138 160 182
Differentiability, continuous 10
Diffusion equation 303
Diffusion limited aggregation (DLA) model 301Ч306
Digital sundial 96Ч97
DIMENSION xxiЧxxv xxiv
Dimension function 37
Dimension of ( -)well approximate number 155 -)well approximate number 155
Dimension of a measure 288
Dimension of attractors and repellers 186Ч201
Dimension of Cantor set xxiii
Dimension of graphs of functions 160Ч169
Dimension of intersections 109Ч118
Dimension of products 99Ч107
Dimension of projections 90Ч97
Dimension of random sets 246Ч251 259Ч275
Dimension of self-affine sets 106Ч107 139Ч144 166Ч169
Dimension of self-similar sets xxiv 128Ч135
Dimension of von Koch curve xxiii
Dimension print 54Ч57
Dimension print, disadvantages 55Ч56
Dimension print, examples 56
Dimension, alternative definitions 39Ч58
Dimension, approximations to 299 305
Dimension, box(-counting) 41Ч50 60 263 265 268 272 273 299Ч300
Dimension, calculation of 34Ч35 59Ч75 128Ч135
Dimension, capacity 41
Dimension, characterization of quasi-circles by 235Ч237
Dimension, divider 39 53Ч54
Dimension, entropy 41
Dimension, experimental estimation of 39Ч40 299Ч300
Dimension, finer definitions 36Ч37
Dimension, Fourier 74
Dimension, Hausdorff xxiv 27 31Ч33 35Ч36 40 54 70 92
Dimension, Hausdorff dimension of a measure 209 288
Dimension, Hausdorff Ч Besicovitch 31
Dimension, information 41
Dimension, local 283
Dimension, lower box(-counting) 41 43
Dimension, metric 41
Dimension, Minkowski( Ч Bouligand) 46
Dimension, modified box-counting 49Ч50
Dimension, one-sided 54
Dimension, packing 50Ч53
Dimension, similarity xxiv
Dimension, topological xxv
Dimension, upper box(-counting) 41 43
Dimensionally homogeneous set 50
Diophantine approximation 153 154Ч157 205
Direct congruence 8
Dirichlet's theorem 154
Discrete dynamical system 186Ч201
Disjoint binary intervals 36
Disjoint collection of sets 4
Distance set 183
Distribution of digits 151Ч153
Distribution, Gaussian 23
Distribution, multidimensional normal 262
Distribution, normal 23 260
Distribution, uniform 23
Divider dimension 39 53Ч54
Domain 7
Double sector 85
Duality method 176Ч179
Dynamical systems 186Ч212
Dynamical systems, continuous 201Ч205
Dynamical systems, discrete 186Ч201
Dynamics, complex 216
Eddies 308
Egoroff's theorem 17 79
Electrical discharge in gas 305
Electrodynamics 310
Electrolysis 300Ч301 302Ч304
Electrostatic potential 70 305 306Ч307
entropy 209Ч211
Entropy dimension 41
Ergodic theory 128 209
Euclidean distance or metric 3
Euclidean space 3
Event 18
Event space 18
Event, independence of 20
Exchange rate variation 311 313
Expectation 21
Expectation equation 247 250
Expectation, conditional 22
Experiment (probabilistic) 18
Experimental approach to fractals 39Ч40 299Ч300
Exterior of loop 223
Extinction probability 250
Fatou set 216 235
Feigenbaum constant 193
Figure of eight 223 228
Filled-in Julia set 215
finance 186 311Ч315
Fine (Hausdorff) multifractal spectrum 284
Fine multifractal analysis 277 283Ч286
First return map 202
Fixed point 125 186 216
Fluid dynamics 277 307Ч309
Forked lightning 298 300
Fourier dimension 74
Fourier series 206
Fourier transform 73 92
Fourier transform, methods using 73Ч74 112 171Ч173 260 271
Fractal curve 133Ч134 216
Fractal growth 300Ч306
Fractal interpolation 169 170
Fractal percolation 251Ч255
Fractal, definition xxii xxv
Fractally homogeneous turbulence 309
Fractional Brownian motion 173 261Ч211
Fractional Brownian surface(s) 273Ч275
Fractions, continued 153Ч154
Frostman's lemma 70
Full square 254
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -)well approximable number(s)
-)well approximable number(s)  -)cover
-)cover  -finite measure
-finite measure 
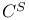
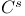 , member
, member