|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Barlow R. Ч Statistics: A Guide and Reference to the Use of Statistical Methods in the Physical Sciences |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
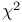 see chi squared see chi squared
 see skew see skew
 see cumulants see cumulants
 see correlation see correlation
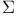 see standard deviatioi see standard deviatioi
ACCEPT 141Ч144
Acceptance region 143Ч145
Action level 10
Alternative hypothesis 142Ч145
Analysis of variance (Anova) 164Ч169
Arithmetic mean 6Ч7
Asymptotic limit for ML estimators 85Ч86
Averaging measurements 51Ч55
Axioms of probability 119
Bar charts 4
Bavesian statistics 121Ч125 127 130Ч132
Bayes* theorem 122
Bessel's correction 77Ч78 80
Between-group variance 165Ч166
Bias of ML estimators 84Ч85
Bias, biased 69Ч73
Binned data 4Ч7
Binned data, fitting 105Ч106
Binned data, goodness of fit 152Ч153
Binning, avoidance of 155
Binomial distribution 24Ч30
Binomial distribution, approximated by Gaussian 41
Binomial distribution, approximated by Poisson 32
Binomial tests 147
Binormal distribution 42Ч44
BLOCKS 4
Breit Ч Wigner distribution 46
Cauchy distribution 11 46
Central confidence interval 127
Central limit theorem 49Ч51
Central limit theorem, proof 196Ч198
Central moments 14
Characteristic function 196
Chebyshev polynomials 184
Chi squared 98
Chi squared and contingency tables 169
Chi squared and run test 154
Chi squared distribution 106Ч108
Chi squared distribution, mean and variance 107
Chi squared distribution, proof 108Ч109
Chi squared for binned data 105Ч106
Chi squared in ANOVA 165
Chi squared of straight line fit 100
Chi squared, approximated by Gaussian 152
Chi squared, critical values 151
Chi squared, matrix expression 111
Chi squared, probability 150
Chi squared, test 150Ч153
Classes 4
CLT see Central Limit Theorem
Collective 120
Combination of errors 55Ч60
Combination of errors, matrix form 60
Combining measurements 53
Composite hypothesis 142
Computing 180Ч186
Concordance 178Ч179
Conditional probability 121Ч122
Confidence belt 128
confidence intervals 125Ч134
Confidence intervals for a constrained quantity 130Ч132
Confidence intervals for a Poisson distribution 133Ч134
Confidence intervals for binomial distribution 132Ч133
Confidence intervals for Gaussian distribution 129Ч130
Confidence intervals, several variables 134
Confidence level 118 125Ч134
Confidence level and hypothesis testing 146
Confidence level, descriptive 125Ч127
Confidence level, estimation 127Ч134
Confidence regions 134
Consistency of ML estimators 84
Consistency, consistent 69Ч70 72
Contingency tables 169Ч170
Continuous data 4
Continuous variables 23 121
Convolution 197
Correlated samples 159Ч161
Correlation and errors 58Ч60
Correlation and the binormal 43 44
Correlation for ranked data 177
Correlation in straight line fit 100Ч102
Correlation matrix 18 59
Correlation of data 15Ч18
Correlation, estimation of coefficient 80
Correlation, Pearson's 177
Correlation, Spearman's 177
Covariance and errors 58Ч60
Covariance in straight line fit 100Ч102
Covariance matrix 18 59
Covariance matrix and chi squared 150
Covariance matrix and systematic errors 65
Covariance of data 15Ч18
Covariance of moments 78
Cramer Ч Rao inequality 75
Critical values, for Student's t 137
Cumulants 198
Curtosis 13
Deciles 13
Degree of belief 123Ч124
Degrees of freedom and chi squared distribution 107Ч108
Degrees of freedom and Student's t 135Ч136
Degrees of freedom in chi squared test 151 -152
Degrees of freedom in contingency tables 170
Degrees of freedom in the F distribution 160Ч164
Descriptive statistics 3
Directional test 142
Discrete data 4
dispersion 8
Distribution free tests 173
Efficiency, efficient 69Ч73
Ensemble 120
Equally-likely cases 121 124
Error 48Ч66
Error matrix 18 59Ч60
Error, estimating 79 107
Error, systematic 61Ч66 80
Error, type I 142
Error, type II 142
Errors on ML estimators 86 87
Estimate, estimation, estimator 68Ч95
Estimation of a half-life 82
Estimation of the correlation coefficient 80
Estimation of the error 79 107
Estimation of the mean 76 83
Estimation of the standard deviation 11 78 83
Estimation of the variance 76
Events 3
expectation value 22Ч24
Expectation value and estimation 70Ч74
Expectation value in the asymptotic limit 85
Extended maximum likelihood 90Ч91
Extrapolation 103
F distribution 160Ч164
Factors (in ANOVA) 167
Failure 24 25
Fisher distribution 160Ч164
Fitting curves 184
Fourier transform 197
Frechet inequality 75
Ftest, and concordance 178
Full width at half maximum, FWHM 13
Gaussian and the CLT 49Ч51
Gaussian approximation to binomial 41
Gaussian approximation to chi squared 107 152
Gaussian approximation to the F distribution 161
| Gaussian distribution 34Ч41
Gaussian distribution, and Student's t 134Ч136
Gaussian limit of likelihood function 85
Gaussian, cumulants 198
Gaussian, definite integrals 36Ч37
Gaussian, estimating the mean 73 76 83
Gaussian, estimating the standard deviation 79 83
Gaussian, integrated 37
Gaussian, many dimensional 41 42
Gaussian, one-tailed integral 39
Gaussian, probability content 37
Gaussian, two samples 156Ч161
Gaussian, two-tailed integral 38
Geometric mean 7
Goodness of fit 141 149Ч156
groups 4
Half-life, estimation of 82
Harmonic mean 7
Histograms 4
Histograms, goodness of fit 152Ч153
Hypothesis 141
Hypothesis testing 141Ч171
Hypothesis, alternative 142Ч145
Hypothesis, composite 142
Hypothesis, null 146
Hypothesis, simple 142
Ignorance 125
Inconsistent see consistent
Independent 23
Inefficient see efficient
information 75
Interpretation of experiments 141 145Ч147
Interquartile range 12
Invariance of ML estimators 84 87
Kolmogorov test 155Ч156
Kolmogorov test and the two-sample problem 164
Kolmogorov test for ranked data 174
Kolmogorov, probability axioms 119 188
kurtosis 14
Latin square 169
Law of Large Numbers 21Ч23
Least squares estimation 68 97Ч107
Least squares, derived from maximum likelihood 93
Least squares, fitting a parabola 114Ч115
Least squares, fitting a straight line 99Ч105
Least squares, fitting polynomials 114Ч115
Least squares, several variables (linear) 111Ч115
Least squares, several variables (non-linear) 115Ч116
Least squares, using matrices 111Ч116
Likelihood function 71Ч73 81Ч90 111
Linear least squares 111Ч115
Linearity 112
Loss of precision 180Ч184
Lower limit 127Ч129 132Ч134
Lower quartile 12
Mann Ч Whitney test 174
Many-dimensional Gaussian 41 42
Matched pairs, for ranked data 175Ч177
Matched samples 159Ч161
Matrix inversion 183
Maximum Likelihood Estimation 81Ч90
Maximum likelihood estimation, asymptotic limit 85Ч86 89
Maximum likelihood estimation, confidence intervals 134
Maximum likelihood estimation, efficiency 86
Maximum likelihood estimation, errors 86
Maximum likelihood estimation, several variables 88
Mean 6Ч9
Mean absolute deviation 12
Mean deviation 12
Mean for binomial 26
Mean for chi squared distribution 107
Mean for Gaussian 35
Mean for Poisson 30
Mean of a sum of variables 49 50
Mean, estimation of 76 83
Median 7
Median, sign test for 173
Method of moments 92
Minimum variance bound 73Ч75
ML see maximum likelihood
MODE 7
Moments 14 92
Monte Carlo 185
Multi-dimensional Gaussian 41 42
Multiway analysis of variance 166Ч169
MVB (Minimum Variance Bound) 73Ч75
Neyman Pearson test 144Ч145
Non-directional test 142
Non-linear least squares 115Ч116
Non-numeric data 3
Non-parametric methods 173
Non-uniform bins 4
Normal distribution see Gaussian distribution
Normal equations 111Ч112
Null hvpothesis 146Ч149
Null hvpothesis in ANOVA 165
Null hvpothesis in Mann Ч Whitney test 174
numeric data 3
Numerical methods 180Ч185
One-tailed probability 40
One-tailed test 142
Parabola fit 114Ч115
Parent distribution 11
Parent population 69
Pearson's correlation 177
Pearson's skew 14
Peirce, C.S. 120
Percentage errors 58
Percentiles 13
Poisson approximated by Gaussian 40
Poisson approximation of binomial 32
Poisson distribution 28Ч33
Poisson tests 148
Polynomials 92 114
Polynomials, Chebyshev 184
Pooled estimate of standard deviation 158 165
Popper, K. 121 188
Power 143Ч144
Precision, loss of 180Ч184
probability 118Ч125
Probability as limit of a frequency 119Ч120 124 128
probability density 23 24
probability distribution 21
Probability, Bayesian 121Ч125
Probability, conditional 121Ч122
Probability, empirical 119Ч120
Probability, mathematical 119
Probability, objective 120Ч121 124
Probability, subjective 121Ч125
Programming 185
Propagation of errors see combination of errors
Propensity 120Ч121 124
Quadratic equations, and significance errors 183
Quadrature 57
Qualitative data 3Ч4
Quantitative data 3Ч4
Random errors 61 64
Random number distribution, arbitrary function 184
Random number distribution, exponential 184
Random number distribution, Gaussian 51
Random number distribution, weighted rejection 184
Random numbers 184
RANGE 12
Rank 7 172Ч179
Rank sum test 174
Regression 104Ч105
Rejecting a hypothesis 141Ч144
Rejecting measurements 54Ч55
Rejection region 143Ч145
Repeated measurements 51Ч52 76
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте