|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Gardiner A. — Infinite Processes: Background to Analysis |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Acceleration 6 163
Algebra 3 13 19
Algebra, and geometry 14 255ff
Algebraic representation of curves and functions 255ff 263ff 267 275—276
Algebraic representation of curves and functions, advantages of 255 259 260 261—263 266
Algebraic representation of curves and functions, limitations of 260n 263 264 266
Alphabetic numerals 60
Analysis v 6 8 70
Analysis, arithmetisation of 1 18 19 27n
Appolonius (ca. 262—190 BC) 261n
Archimedes (287?—212 BC) 16 186 219 219n 220 220n 221 255 261n
Area 6 16 155 157 163 164ff 173n
Area, definition of 178—179
Arithmetic 13 19 37 59 61ff
Arithmetic, of infinite decimals 123ff 135 136
Babylonians 28n 216—217 217n
Bernoulli, D. (1700—1782) 6
Bernoulli, Jakob (1654—1705) 248
Bernoulli, Johann (1667—1748) 262n
Bhiskara (1114—1185?) 168
Binomial theorem 261 262n
Boole, G. (1815—1864) 18
Borel, E. (1871—1956) 173n
Boyer, C.B. 217n
Briggs, H. (1561—1631) 262
Calculator 10 44 107n 130 150 153—154 252 286
Calculus 3 14 37 159 260 275
Calculus, 1870 version of 4 17 18 27n 121 155 157 276
Calculus, and geometry 9 17 18 38 38n 155 157 162 168 187 233 237
Calculus, and symbolical algebra 17
Calculus, arithmetical interpretation of 1 9 18 19 38 160
Calculus, differential and integral 3
Calculus, inadequate explanations of 5
Calculus, naive, carefree 1 4 6 7 160
Calculus, potential weaknesses of 6
Calculus, separation from geometry and symbolical algebra 9 18
Cantor, G. (1845—1918) 159
Carrol, L. 59
Cauchy, A.L. (1789—1857) 18n 263 269 270 275
Cavalieri's principle 255 255n
Centres of gravity 6 16
Chuquet, N. (1445?—1500?) 261n
Circle, area of 176 188—189 220 226
Circle, perimeter of 189 234 239
Common measure(s) 28 30 31 32 37 38 48 157 158
Common measure(s), and highest common factors 46
Common measure(s), in 1-dimension 40 44ff 51ff 134 164 166—167
Common measure(s), in 2-dimensions 164ff
Common measure(s), in 3-dimensions 206
Complex exponential 296
complex numbers 14 15 161 270 295
Complex numbers, geometrical interpretation of 15 270
Complex plane 161 163 270
cones 215 232 232n
Constructive and non—constructive methods 37ff 53
Continued fractions 25 140ff 188
Continued fractions, endless 144ff
Contradiction 37 38
Convergence 269
Coordinate geometry 3
coordinates 159 255
Counting numbers 15 27 70
Courant, R. 282—284
Creative leaps 19
Cuboids 205—208
Cuboids, inner and outer approximations to 207
Cuboids, reduction to standard cuboid 207—208
CURVES 6 255ff
Curves, continuity of 192—193
Curves, length of 155 157 232ff 239—240
Cycloid 218 219n 229—230 237
Cylinder 220—221 232 232n
Cylinder, surface area of 236 241—243
Davenport, H. 142
de Roberval, G.P. (1602—1675) 218 219n
Decimal fractions 63 70 71 96 99 101n 104 112
Decimal representation 59ff 254
Decimal representation, of decimal fractions 63ff 99 134
Decimal representation, of fractions 71ff
Decimal representation, of whole numbers 61ff
Decimals 25 159
Decimals, arithmetic of 64ff
Decimals, endless 25 67 135
Decimals, finite 100 101
Decimals, recurring 100ff
Dedekind cuts 158n
Dedekind, R. (1831—1916) 38 159
Dehn, M. (1875—1952) 215
Democritus (ca. 460—370 BC) 16
Descartes, R. (1596—1650) 17n 118 159 255
Descartes, R., and philosophy 17n
Diagonal and side 51ff
Diagonal and side, of pentagon 54ff 143 148
Diagonal and side, of square 31ff 51ff 134 153
Dieudonne, J. 182n
Differential calculus 3
Differential calculus, Leibniz notation 16 59
Differential geometry 3
Differentials 16 18
Diophantos (ca. 250 AD) 261n
Dirichlet, P.G.L. (1805—1859) 40 263 272—275 275n
Dissection method, in 2-dimensions 168 179ff
Dissection method, in 3-dimensions 207—208 209ff
Dynamics 3 16 163
D’Alembert, J. (1717—1783) 6
e, 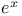 122 294 296—300 122 294 296—300
Egyptians, volume of pyramid 217
Elementary functions 263 264 280 283 284
Ellipse, area of 176 226
Ellipse, perimeter of 284
Endless, continued fractions 25 144ff
Endless, counting process 61 134 247
Endless, decimals 25 67 72 135
Endless, polynomials 20 21 22 264
Endless, products 20 21 22
Endless, sequences 33 233—236
Endless, sequences of finite sums 83ff 97—99
Endless, sums 74—76 81ff 96 97
Endpoint 87 98 119
Eratosthenes (ca. 284—192 BC) 219n
Error term 85ff
Euclid (fl. ca. 300 BC) 18 19 40 158 220
Euclid, game of 40ff 47 48 113 134
Euclidean algorithm 40 42 44 48
Eudoxus (408?—355? BC) 37 38
Euler, L. (1707—1783) 6 19 20 21 22 248 249 260 279 295
Existential approach 38
Exponential functions 285ff
Exponential functions, and trigonometric functions 14
Exponential functions, continuity of 298—299
Exponential functions, official definition 286 287 294
Exponents 13
Fermat, P. (1601—1665) 255 263n
Fibonacci sequence 48
Finite processes 81
Finite processes, in geometry 25
Finite sums 74
Fourier series 11 263 272—274 275n
Fourier, J.J. (1768—1830) 7 8 267 268 271—272
Fractions 27 100ff
Function-concept 245 254ff 280—284
Function-concept, modern 270—272 274
Functions 9 37 251 254ff
Functions, accepted meaning of 263ff
Functions, algebraic representation of 255ff 263ff 267 275—276
Functions, continuous 193 268—269
Functions, continuous, nowhere differentiable 277—278
Functions, geometric representation of 255ff 275—276
Functions, inverse 283
Functions, particular algorithms for 288—289 288n
| Functions, single-valuedness 291 295
Fundamental property of real numbers 118ff 123 124 126 128—129 146 147 151—152 155 168 173 177 178 248 252
Galileo (1564—1642) 16 256
Game of Euclid 40ff 47 48 113 134
Gauss, C.F. (1777—1855) 22 275n
Geometric series 82ff 121n
Geometrical representation of curves and functions 255ff 275—276
Geometrical representation of curves and functions, advantages of 259 266
Geometrical representation of curves and functions, limitations of 255 259
Geometry 3 9 16 17 18 37 38 157ff 162 270 270n
Geometry, and algebra 14 255ff
Geometry, dependence on calculus 9 155 168 187 233 237
Geometry, separation from calculus 9 18 155 157 179 234
graphs 3 163n 255n
Grattan-Guinness, I. 6 8n 187
Greatest common measure 40 41 44ff 49 53 137 140 141
Greeks 16 18 27 37 38 40 157 158 158n 159 186 186n 187 255 256
Hardy, G.H. 120 287n
Hawkins, T. 187 276
Heat equation 7 267
Heiberg, J.L. 219n
Henle, J. 18n
Heptagon, side and diagonal of 57
Hexagon, side and diagonal of 57
Heximals 78
Highest common factors 40ff 103 106ff 134
Highest common factors, and common measures 46
Hilbert, D. (1862—1943) 159 214—215
Honsberger, R. 77 231 300
Increments 256
Index law 261 285
Indirect arguments 38 53
Indivisible atoms 16
Infinite decimals 9 70ff 81ff 96 118
Infinite decimals, arithmetic of 123ff 135 136
Infinite processes 4 5 9 17 25 53 56 60 70 81 157
Infinite sums 4 8 12 19 73
Infinite sums, of sines and cosines 6 7 8
Infinitely large 16
Infinitesimal(s) 4 5 16 17 18 256 266
Infinitesimally small 16 17
Inner and outer approximations, in 2-dimensions 167 169ff 180
Inner and outer approximations, in 3-dimensions 204—205 207ff
Integration, and arclength 232—233
Integration, and area 187
Intuition, intuitive ideas 4 5 162—163 257
Intuition, intuitive ideas, and experience 17 163
Inverse functions 283
Irrational numbers 9 27
Irrational numbers, approximation by continued fractions 141
Irrational ratio 164 165
Johnson, J. 257n
Jordan, C. (1838—1922) 173n
Kasner, E. 247n
Kepler, J. (1571—1630) 16
Khinchin, A.Ya. 143
Klein, F. 22n
Kleinberg, E. 18n
Kline, M. 275n
Knuth, D. 18n
Lacroix, S.F. (1765—1843) 265n 271 272
Lagrange, J. (1736—1813) 263 265 266 270
Lakatos, I. 179 209n 275n
Lebesgue, H. (1875—1941) 173n
Lebesgue, H., integral 209 217 276
Lebesgue, H., measure 217
Leibniz, G.W. (1646—1716) 5 16 17 17n 59 82 256 260n 262n 276
Leibniz, G.W., and philosophy 17n
Leibniz, G.W., infinitesimal calculus 16 17 260n
Length, of a curve 155 232ff 239
Length, of a line segment 157 164
Limits 4 10 269
Limits, one-sided 273—274
Logarithmic integral 283n
Logarithms 14 159 262
Logarithms, infinite-valuedness of 279—280
Logarithms, natural 249 297
Logic 37
Magnitudes 158
Mathematical induction 46
Mathematics, as stock of truth 13 14
Mathematics, constructive 38 39
Mathematics, evolution of 13 14 19 287 290—291
Mathematics, existential 38
Mathematics, in 1-dimension 167
Mathematics, in 2-dimensions 167
Mathematics, measurement 25
Mathematics, naively constructive 38 71
Mersenne, M. (1588—1648) 118
Method of slices 209 217ff
Moments of inertia 6
Monster-barring 179
Morgenstern, C. 59
Moscow papyrus 217
Motion 6
Musical harmonies 28
Musical harmonies, and rational numbers 28
Napier, J. (1550—1617) 159 262
negative numbers 14 15 121
Neugebauer, O. 217
Newman, J. 247n
Newton, I. (1642—1727) 5 17 17n 256 260n 262n 264 275
Newton, I., fluxional calculus 17 260n
Newton, I., Principia 5
Nietzsche, F. vi 20
Non-Euclidean geometries 18
Notation 59 134
Number and geometry 159
Number and geometry, separation of 158 160
Number line 15 121 159n 161 162 163 254
Number-concepts 160
Numbers 37 157ff
Numbers, and geometry 157ff
Numbers, decimal representation of 59ff 254
Octagon, side and diagonal of 57
Olds, C.D. 142
Oresme, N. (ca. 1323—1382) 261n
parabola 186—187
Paradox 33
Parallelepipeds 211
Parallelogram, reduction to standard rectangle 184
Partial fractions 282
Pascal's triangle 261
Pentagon, side and diagonal of 54ff 143 148—149 158
Penultimate move 47 48
Physical systems 38n
Physics 3 256
Pi,  8 10 12 22 141—142 248 277 295 8 10 12 22 141—142 248 277 295
Pi,  , area and perimeter of circle 188—189 220 220n 226 230 , area and perimeter of circle 188—189 220 220n 226 230
Pi,  , irrationality of 165n 189—191 , irrationality of 165n 189—191
Pi,  , volume of sphere 220 230 , volume of sphere 220 230
Place-value 70
Poincare, H. 162
Polygons, inner and outer approximations to 176 208
Polygons, reduction to standard rectangle 185 210 212
Polyhedra 209—210
Polyhedra, dissection into tetrahedra 214 227—228
Polyhedra, reduction to standard cuboid 210 212ff
Polynomial functions 281
Power series 264—266
PRECISION v 4 6 155
Precision, lack of 1 4 6
PRIMES 34 38 39 108ff 114 117
Pyramids 213 215—217 226
Pyramids, reduction to standard cuboid 214
Pyramids, truncated, volume of 216 228
Pythagoras' theorem 28 29 30 34 158 164 168
Pythagorean triples 35
Pythagoreans 27 28 29 30 157
Quadrature 186n
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте