Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Olds C.D., Davidoff G. — Geometry of Numbers
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Geometry of NumbersАвторы: Olds C.D., Davidoff G. Аннотация: This book presents a self-contained introduction to the geometry of numbers, beginning with easily understood questions about lattice points on lines, circles, and inside simple polygons in the plane. Little mathematical expertise is required beyond an acquaintance with those objects and with some basic results in geometry.
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 2001Количество страниц: 168Добавлена в каталог: 05.04.2008Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
45 48 56 56 105 121 46 46 83 Absolute value of a complex number 133 Additive structure of plane 133 Admissible lattice 145 Affine transformation 73—74 Approximating irrationals 105—107 Arithmetic-geometric mean inequality 80 Associate primes 135 Axes, major and minor 100 Axes, rotating 113 Bertrand, J. 152 Binary quadratic form 97 104 Blichfeldt, Hans Frederik, life of 153—154 Blichfeldt, Hans Frederik, life of, a packing theorem 149 Blichfeldt, Hans Frederik, life of, on approximating irrationals 124—129 131 Blichfeldt, Hans Frederik, life of, on quadratic minima 105 121 Blichfeldt, Hans Frederik, life of, proof of Minkowski’s Fundamental Theorem 72—73 117 Blichfeldt’s Theorem 113—116 119—121 Blichfeldt’s Theorem, generalization of 116 Bo1yai, Janos 141 Bolzano — Weierstrass theorem 15 Boundary of a polygon 36 Center of symmetry 66 Checkerboard lattice 148—149 Cluster points 15—16 Common divisor 55 complex numbers 54 133—134 Congruence classes 140—141 Congruence notation 56 108 140—141 Congruent numbers 140 Conjugate of z 134 Consecutive sides 35 Contracting an M-set 66 Convex point set 65 Covering, of a lattice point 114 Critical determinant 146 Critical lattice 146 Davenport, Harold 108 de M’eziriac, Claude Bachet 107 Degree of approximation 105 Determinant 73—74 85 Determinant 85 Determinant, critical 146 Difference points 116 Dilating an M-set 67 Diophantine approximations, simultaneous 82 Diophantine equation 28 54 Diophantine inequalities 63 Diophantus 51 54 107 Discriminant d 98 Doubly connected polygon 37 Einstein, Albert 152 Eisenstein, F. 152 ellipse 23 100—101 Equivalent lattices 89 91—92 95 Equivalent primes 135 Euclid’s algorithm 10 136 Euler, Leonhard 97 107 Euler, Leonhard, on representations of n 52 54—56 Expanding an M-set 66 Exterior of a polygon 36 Face-centered cubic (fee) lattice 148 Fermat, Pierre de 52 54 107 Fibonacci sequence 32 Fibonacci, Leonardo 53 Field 140 Four-dimensional sphere 109 Fractional part of x 26 Frederick the Great, Prussian Academy of 107 Fundamental lattice L 3—4 88 Fundamental parallelogram 89—90 Fundamental parallelopiped 74 Fundamental point-lattice Lambda 3—4 18 23 88 90 Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 8 135 Fundamental Theorem of Complex Arithmetic 136 138—139 Gamma function 105 I2l Gauss, Carl Friedrich 152 Gauss, Carl Friedrich, on lattice points in circles 4 45—46 48 57—58 Gauss, Carl Friedrich, on packing 148 Gauss, Carl Friedrich, on quadratic forms 97 105 Gaussian integers 133—134 Gaussian integers, factorization of 134—135 Gaussian integers, unique factorization of 138—139 Gaussian primes 139—134 General affine transformation 73—74 General lattice 88 Geometry of numbers 3 63 75 85 113 Girard, Albert 52 Greatest common divisor 5 7 Greatest integer function 14 25—28 Harriot, Thomas 148 Hermite, Charles 63 105 108 123 152 Hexagon, regular 146 Hilbert, David 151 Hurwitz, Adolf 151 Infimum 146 Integers, divisibility property 7 Integers, expressing, in standard form 52 Integers, gaussian 133—134 Integers, Gaussian, factorization of 134—135 Integers, Gaussian, unique factorization of 138—139 Integers, relatively prime 5 95 Integral part of x 25 Integral solutions 28—31 Intercepts 30 Interior of a polygon 36 Inverse transformation 86—87 Irrational numbers 5 Irrational numbers, approximating 80 105 123—131 Jacobi, Carl Gustav Jacob 57 58—59 63 Jordan, Camille 152 Kepler conjecture 148 Kepler.Johannes 148 Kirchhoff.R. 151 Korkine.A. 101 104 105 149 Kronecker, Leopold 151 Kummer, E. 151 Lagrange, Joseph Louis 97 107 Lagrange’s Theorem 107—110 Lattice path 32 Lattice point 3—4 88 Lattice point, covering property 38 114 Lattice point, covering theorem 38 Lattice point, visible 95—96 Lattice square 72 Lattice systems 3 4—10 Lattice, admissible 145 Lattice, checkerboard 148—149 Lattice, critical 146 Lattice, face-centered cubic (fcc) 148 Lattice, general 88 Lattices, equivalent 89 91—92 95 Lcgendre, Adrien Marie 56 97 Least common multiple 8 Lie, Sophus 153 Linear transformation 85 87 Liouville.Joseph 58 Liouville’s identity 58 Lower bound of |f(x, y)\ 98 M-set 65—67 113 Mersenne.Marin 54 Minimum of |f(x, y)| 98 104 Minkowski Theorem, A (for approximating irrationals) 123—129 Minkowski, Hermann 151—153 Minkowski, Hermann, his geometric point of view 3 63—64 75 101 109 113 Minkowski, Hermann, on quadratic minima 105 Minkowski’s First Theorem 76—80 Minkowski’s fundamental theorem 67 Minkowski’s Fundamental Theorem, applications of 75—76 83—84 98 100—101 113 125 Minkowski’s Fundamental Theorem, in y-space 74 Minkowski’s Fundamental Theorem, proofs of 67—73 117—119 Minkowski’s General Theorem 73 109 131 Minkowski’s Second Theorem 79—81 Minkowski’s Third Theorem 82 Mitchell, H.L. III 46 Multiplicative inverses 134 Multiplicative structure of the plane 133 n! 27 N(n) 45 Niven.Ivan 42 Nontrivial factorization 135 Numbers, complex 54 133—134 Numbers, congruent 140 Numbers, irrational 5 Numbers, rational 5 8 Numbers, real 5 Packing of circles 146—147 Packing of circles, of lattices 145—146 Packing of circles, of spheres 145 147—149 Parallel displacement 113 Parallelogram, fundamental 89—90 Parallelogram, primitive 89—90 Parallelopiped.fundamental 74 Path of maximum width 17—20 Path of width d 18 Path, lattice point-free 17—23 Pick.Georg 36 Pick’s Theorem 36 Plane, structure of the 133 Point-lattice, construction of 88—89 Point-lattice, transformation of 91—95 Point-lattices, equivalent 89 Points, difference 116 POLYGONS 35—36 Polygons, doubly connected 37 Positive definite quadratic form 98 102 104 Prime Gaussian integer 135 Primitive parallelogram 89—90 prism 124 Pythagorean Theorem 133 137 Quadratic form, binary 97 104 Quadratic form, positive definite 98 102 104 Quadratic representation 97—98 Quadratic residues 108 Raleigh, Sir Walter 148 Rational numbers 5 8 Rational numbers, approximating irrationals by 105—107 Real numbers 5 Relatively prime Gaussian integers 135 Relatively prime integers 5—6 95 Representation of an integer n 48—53 110; Representation, quadratic 97—98 Representations of prime numbers 54—56 Rhombus 37 Ring 134 Rotating axes 113 Sides of a polygon 35 Simple polygon 35 Simultaneous Diophantine approximations 82 Slope formula 11 Slope, irrational 5 10—17 Slope, rational 5 6—10 Smith, H.J.S. 152 Sphere packing 145 147—149 Sphere, four-dimensional 109 Standard form for integers 52 Steinhaus, Hugo 36 Symmetry about the origin 22 64 Symmetry, center of 66 T(n) 50 Tchebychev, P.L. 123 129 Thue, Alex 54 Transformation, affine 73 Transformation, inverse 86 Transformation, linear 85—87 90—95 Transformation, point-lattice 90—95 translating 113 Translation of an M-set 68 Unique factorization theorem 52 Unit area 20 95 Unit square 72 90 Units of a ring 134 Vectors 74 89 Vertices 35 Visible points 95—96 Voigt, W. 151 Volume of a four-dimensional sphere 109 von Helmholtz, H.L.E 151 Weber, H. 151 Weierstrass, Karl 151 Wilson’s Theorem 140 y-space 74 Zolotareff.E.I. 102 104 105 149 Zuckerman, Herbert 42 [x] 14 25—28
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



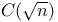
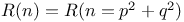
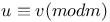
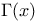

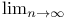
 of a lattice
of a lattice