јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Konheim A.G. Ч Computer Security and Cryptography
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Computer Security and Cryptographyјвтор: Konheim A.G. јннотаци€: Gain the skills and knowledge needed to create effective data security systems
язык: –убрика: Computer science /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: 1st edition√од издани€: 2006 оличество страниц: 544ƒобавлена в каталог: 11.12.2007ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
157Ч158 67 Absolute secrecy 17 Access control 2 Adelman, Len 340Ч341 378 ADFGVX encipherment 47 48 Alphabet 1 ANSI Standard X9.1Ч1980 489Ч491 ANSI Standard X9.1Ч1980, track 3 format of 490 ATM transaction(s) 489Ч490 ATM transaction(s), Atalla Technovations, implementation by 488Ч489 ATM transaction(s), ATM authentication protocol of 489 ATM transaction(s), Chubb Integrated Systems, ATM authentication protocol of 484Ч487 ATM transaction(s), Chubb Integrated Systems, implementation by 487 510Ч511 ATM transaction(s), IBM Liberty banking system, Bond Ч Zelinski, PIN attack by 488Ч489 ATM transaction(s), IBM Liberty banking system, common cryptographic architecture, program, IBM 487 ATM transaction(s), IBM Liberty banking system, decimalization table 487 ATM transaction(s), IBM Liberty banking system, implementation in 487 ATM transaction(s), PANЧPIN table 485 ATM transaction(s), personal identification number (PIN) 484Ч487 ATM transaction(s), personal identification number, PAN(User_ID), PIN(User_ID), PINOffset(User_ ID), U-PIN(User_ID) 487 ATM transaction(s), primary account number (PAN) 484 Authentication 2Ч3 464Ч466 Authentication in GSM 276 automated teller machine (ATM) 484 Automated teller machine (ATM), customer authentication at a 484Ч487 Automated teller machine (ATM), on/off-line operation of 486 Baby-step, giant-step algorithm (Shank's) 420 BART system: The Case of the Larcenous Laundry 484 BART system: Wattenberg, Dr. Bill 483 Baudot code 118 Baum, Leonard 78 81 85 Bent functions 327 Berlekamp's algorithm 399Ч400 Bezout's theorem 431 Birthday paradox 395 Block ciphers 283 Block ciphers, (a) class of 329Ч332 Block ciphers, IDEA 332 Block ciphers, nonlinearity of 326Ч327 Block ciphers, nonlinearity of, Nyberg's criteria for 327 Block ciphers, nonlinearity of, Pierpryzk's criteria for 326Ч327 Block ciphers, product 283Ч322 Block ciphers, secure 326Ч327 Block ciphers, which generate the symmetric group 327Ч329 Bombe (fr.) 8 166 168 Book cipher 11 116 Caesar's cipher (substitution) 65 Caesar's cipher (substitution), (affine) Caesar cipher (substitution) 65 Caesar's cipher (substitution), Caesar shift 65 Captain Midnight's decoding badge 64Ч65 Carmichael numbers 377 405 Carmichael numbers, properties of 405 Certicom 16 445 Certicom, challenge 445 certificates 341Ч342 495Ч499 502Ч505 Certificates, public key 495Ч497 Certificates, public key, certificate authority (CA), issuance by 496 503Ч505 Certificates, public key, certificate hierarchies 503Ч505 Certificates, public key, Certification Authorities (CA) (Level 3) 503Ч505 Certificates, public key, interaction of 503Ч505 Certificates, public key, Internet Policy Registration Authority (IPRA) (Level 1) 503Ч505 Certificates, public key, Policy Certification Authorities (PCA) (Level 2) 503Ч505 Certificates, public key, X.509 495Ч497 Certificates, public key, X.509, example of 497 Certificates, public key, X.509, structure of 496Ч497 Chinese remainder theorem 400Ч401 Chosen plaintext attack 6 Ciphertext 2 Ciphertext, alphabet(s) 153 218 223 Ciphertext, cryptanalysis with (ciphertext) only 6 Cocks, Clifford C. 342 Coincidence 124Ч126 Coincidence, estimating the period of periodic polyalphabetic substitution using 126Ч127 Columnar transposition encipherment 18 Columnar transposition encipherment, based on a grille 49 50 Columnar transposition encipherment, examples of 25 Columnar transposition encipherment, invertibility of 19 Columnar transposition encipherment, size of key space 20 Columnar transposition encipherment, testing possible widths 25 Communications Intelligence (COMINT) 9 Communications Security (COMSEC) 9 complexity 338 Composite number 405Ч407 Composite number, integer factorization, problem of 405 468 Computer Electronics Security Group (CESG) 342Ч343 Conjugacy 155 Conjugacy, characteristic property of 155 Continued fraction algorithm 365Ч366 Continued fraction algorithm, convergents of 365 Corresponding plain- and ciphertext attack 6 Counting k-grams (of text) 33 Counting k-grams (of text), jumping window 33 Counting k-grams (of text), sliding window 33 Crib 21 Crib, subcribs 21 Crib, subcribs, complete set of 24 Cribbing 21 Cribbing, examples of 25Ч30 Cribbing, using isomorphs for 66 Cryptanalysis 4 6 Cryptanalysis, Kerckhoffs' principles of 4 CRYPTO 'N 15 358 Cryptographic salt 480Ч481 Cryptographic system(s) 4 12 Cryptosystem 4 Cryptosystem, knapsack-like 371 Cryptosystem, weaknesses in a 136 Data Encryption Standard (DES) 288Ч311 Data Encryption Standard (DES), chaining in 295Ч297 Data Encryption Standard (DES), components of initial permutation (IP) 292 Data Encryption Standard (DES), components of key schedule (PC-1, PC-3, KS) 292Ч293 Data Encryption Standard (DES), components of P-box 292 Data Encryption Standard (DES), components of S-box(es) 289Ч292 Data Encryption Standard (DES), cryptanalysis of 300Ч309 Data Encryption Standard (DES), DES-cracker 308Ч310 Data Encryption Standard (DES), DES-cracker, architecture of 309 Data Encryption Standard (DES), DES-cracker, key search algorithm of 309Ч310 Data Encryption Standard (DES), DES-cracker, operation of 310 Data Encryption Standard (DES), differential cryptanalysis of 302Ч309 Data Encryption Standard (DES), export of 309Ч311 Data Encryption Standard (DES), initial seed in 299 Data Encryption Standard (DES), Matsui's linear cryptanalysis of 302 Data Encryption Standard (DES), output-feedback mode (OFB) of 299Ч300 Data Encryption Standard (DES), randomness of 297Ч299 Data Encryption Standard (DES), sample encipherment of 296 Data Encryption Standard (DES), semi-weak keys of 294 Data Encryption Standard (DES), weak keys of 293Ч294 de Vigenere, Blaise (1523Ч1596) 117 Decipherment 2 decryption 2 Diagnosis 139Ч149 Diffie Ч Hellman key-exchange 448Ч450 Diffie Ч Hellman key-exchange, El Gamal's extension of 450Ч451 Diffie, Whittfield 334 337 339Ч340 Digital signature system(s) 467Ч470 Digital signature system(s), El Gamal's signature protocol 475 Digital signature system(s), MD5 471Ч473 Digital signature system(s), NIST's digital signature algorithm 474Ч475 Digital signature system(s), public key cryptography and 467Ч468 Digital signature system(s), Rabin's quadratic residue 468Ч470 Digital signature system(s), TRAnsactions in a SECure manner (TRASEC) 494Ч495 Digital signature system(s), TRAnsactions in a SECure manner (TRASEC), authentication scheme in 494 Digital signature(s) (SIG) 3 337 465Ч470 Digital signature(s) (SIG), desiderata of 466 Digital signature(s) (SIG), message digest 470Ч471 Digital signature(s) (SIG), using elliptic curve cryptosystems 444Ч445 Diophantine approximation 364 Diophantine approximation, simultaneous 366Ч370 Diophantine approximation, simultaneous, unusually good (UGSDA) 367Ч370 Diophantine equations 364 Diophantus of Alexandria (c. 200/214 Ч c. 284/298) 364 Dirichlet L-series 407 Discrete logarithm problem (DLP) 16 414Ч426 Discrete logarithm problem (DLP), Adelman's subexponential algorithm for 419 Discrete logarithm problem (DLP), current state of research on 428 Discrete logarithm problem (DLP), in a group 414 420Ч426 Discrete logarithm problem (DLP), modulo p 414Ч419 Discrete logarithm problem (DLP), Pohlig Ч Hellman's solution of 415Ч418 Discrete logarithm problem (DLP), solution by index-calculus method 422Ч424 Display of plain- and ciphertext, convention on 20 Division algorithm for integers 346 Division algorithm for polynomials 247Ч248 Doctrine of equitable estoppel 514 Electronic commerce (e-commerce) 334 336Ч337 Electronic purse (electronic wallet) 493 Elliptic curve cryptosystem(s) 443Ч445 Elliptic curve cryptosystem(s), digital signature system for 444Ч445 Elliptic curve cryptosystem(s), integrated encryption standard (ECIEC) 444 Elliptic curve cryptosystem(s), NSA's case for 445 Elliptic curve(s) 429 Elliptic curve(s), Bezout's Theorem for 431 Elliptic curve(s), chord-tangent group law of 431 Elliptic curve(s), Diffie Ч Hellman key exchange 442 Elliptic curve(s), discriminant of 429 Elliptic curve(s), Lenstra's factorization algorithm on 432 Elliptic curve(s), supersingular 441 Elliptic group over the 434Ч436 Elliptic group over the field $Z_{m 2}$ 436Ч437 Elliptic group over the reals 431Ч432 Elliptic group, computations in the elliptic group $Z_{m 2}(a b)$ 438Ч441 Ellis, James H. 342 Encipherment 2 Encryption 2 Engima machine 7 160Ч170 Engima machine, components of 160 Engima machine, cryptanalysis of Enigma by Rejewski, Marian (1903Ч1990) 166 Engima machine, cryptanalysis of Enigma by Rozycki, Jerzy (1909Ч1942) 166 Engima machine, cryptanalysis of Enigma by Welchman, Gordon (1906Ч1985) 166Ч167 Engima machine, cryptanalysis of Enigma by Zygalski, Henryzk (1906Ч1978) 166 Engima machine, cryptanalysis of Enigma ciphertext 166Ч170 Engima machine, cryptanalysis of Enigma ciphertext, by cribbing 167Ч170 Engima machine, cryptanalysis of Enigma ciphertext, using double-ended Enigmas 168Ч170 Engima machine, encipherment equation of the 165Ч166 Engima machine, key distribution protocol for the 163Ч164 Engima machine, message indicator, indicator setting, and discriminant of Enigma ciphertext 164Ч165 Engima machine, plugboard of the 162Ч163 Engima machine, reflecting rotor (stator) 161Ч163 Eratosthenes (276BC Ч 194BC) 390Ч391 Eratosthenes, measurement of earth's circumference 390Ч391 Eratosthenes, sieve of 390Ч393 Euclidean algorithm 348Ч350 Euclidean algorithm for polynomials 398Ч399 Euler totient function f(n) 350 Euler's theorem 378 Expectation method (EM) 81 Extension field 421 426Ч428 Facility keyed-access cards (IBM Series/1) 491 Facility keyed-access cards (IBM Series/1), cryptographic algorithm for 329Ч330 491 Factorization of integers 339 391 393Ч394 Factorization of integers, Pollard's r-algorithm for 394Ч396 Feedback shift register (FSR) 245 Feige, Uriel 477 Feistel, Horst (1915Ч1990) 283 Fermat witness 405 Fermat's little theorem 377 397 Fermat's primality test 405 Fiat Ч Shamir identification scheme 477Ч478 Fiat Ч Shamir signature scheme 476Ч477 Fiat, Amos 476Ч478 Field 10 347 414 Floyd's cycle detecting algorithm 395Ч396 424 Floyd, Robert W. (1936Ч2001) 395Ч396 424 Friedman, William F. (1891Ч1969) 10 11 63 126Ч127 Future Advanced Data Encryption Standard 312 Future Advanced Data Encryption Standard, requirements of 312 Gardner, Martin 16 408 Gardner, Meredith (1912Ч2002) 130 Gary Miller's theorem 407 Gaussian elimination 91Ч111 Gaussian elimination for factorization 402Ч403 408 Gaussian elimination, elementary row and column matrix-transformations 103Ч106 Gaussian elimination, over the integers modulo m 109 Gaussian elimination, used to solve an overdetermined system 108 Global system for mobile communication (GSM) 274Ч278 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM), A5 algorithms in 276Ч278 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM), A5 algorithms in, cryptanalysis of 278 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM), authentication in 275 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM), secrecy in 276Ч278 Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) 342 Greatest common divisor gcd 347Ч348 377Ч378 Greatest common divisor gcd, Euclidean algorithm 348Ч350 378 Half-rotor 191Ч193 Half-rotor, slip ring(s) of 192 Hash function(s) 470Ч474 Hash function(s), collision-resistant 470 Hash function(s), MD5 471Ч473 Hash function(s), one-way hash 470 Hash function(s), secure hash algorithm, NIST's 473Ч474 Hashing 480 Hebern, Edward H. (1869Ч1952) 153Ч155 Hellman, Martin 334 337 339Ч340 Hidden Markov model (HMM) 78Ч90 Hidden Markov model (HMM), Expectation method for the parameters of a 81 Hidden Markov model (HMM), forward-backward recursions (of HMMs) 80 Hidden Markov model (HMM), parameter re-estimation (in the HMM) 80Ч89 Hidden Markov model (HMM), parameter re-estimation (in the HMM), critical point conditions for 81Ч89 Hidden Markov model (HMM), parameter re-estimation (in the HMM), Q-function in the 85 Hidden Markov model (HMM), scaling (in the HMM) 89Ч90 Hill encipherment 90Ч100 Hill encipherment, cribbing Hill ciphertext 100Ч102 Hill encipherment, finding the Hill matrix; plain- and ciphertext known 91Ч100 Hill, Lester (1891Ч1961) 90 IBM 2984 (Cashing Issuing Terminal) 284Ч287 IBM 2984 (Cashing Issuing Terminal), encipherment steps in 284 IBM 2984 (Cashing Issuing Terminal), nibbles in 285Ч286 IBM 2984 (Cashing Issuing Terminal), round transformation T 284Ч285 IBM Research's DES-Group, Adler, Roy L. 284 IBM Research's DES-Group, Coppersmith, Don 284 IBM Research's DES-Group, Grossman, Edna 284 IBM Research's DES-Group, Hoffman, Alan J. 284 IBM Research's DES-Group, Tuckerman, Bryant (1915Ч2002) 284 IDEA block cipher 328 332 IEEE 802.11b 280Ч281 Independent and identically distributed trials (chance experiments) 31 Index-calculus algorithm 422Ч424 Index-calculus method 420Ч421 Index-calculus method for $Z_{m 2}$ 422Ч424 Index-calculus method, factor base in 422 Inequality of the arithmetic and geometric means 41 Infringement 509 Integer factorization, problem of 390 468 International Standards Organization (ISO) 492 497 International Standards Organization (ISO), open systems interconnection model of 497 International Standards Organization (ISO), open systems interconnection model of, computer network architectures (SNA, DNA) 497 International Telegraph Union (ITU) 496 International Telegraph Union (ITU), Comite Consultatif Internationale de Telegraphique et Telephonique (CCITT) 496 Invertible 100 Isomorphs 66 Isomorphs, pruning from a table of 68Ч73 Jacobi symbol 384 Jacobi symbol, properties of 384 Japanese PURPLE Machine 210Ч243 Japanese PURPLE Machine, components of 211Ч212 Japanese PURPLE Machine, components of, C-steppers 212Ч216 Japanese PURPLE Machine, components of, consonant banks of 212Ч214 Japanese PURPLE Machine, components of, stepping switches (steppers) 211 Japanese PURPLE Machine, components of, V-stepper 211Ч212 Japanese PURPLE Machine, components of, wiper (blade) 211 Japanese PURPLE Machine, cribbing PURPLE, determining the Vowel/Consonant subdivision 220
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



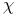 -value
-value 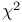 -test of hypothesis
-test of hypothesis 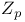
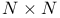 matrices, number of
matrices, number of