јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Konheim A.G. Ч Computer Security and Cryptography
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Computer Security and Cryptographyјвтор: Konheim A.G. јннотаци€: Gain the skills and knowledge needed to create effective data security systems
язык: –убрика: Computer science /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: 1st edition√од издани€: 2006 оличество страниц: 544ƒобавлена в каталог: 11.12.2007ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Japanese PURPLE Machine, cribbing PURPLE, finding the C-Stepper 238Ч243 Japanese PURPLE Machine, cribbing PURPLE, finding the V-Stepper 220Ч237 Japanese PURPLE Machine, cryptanalysis by Denning, Mary Jo 218 Japanese PURPLE Machine, cryptanalysis by Ferner, Robert 218 Japanese PURPLE Machine, cryptanalysis by Grotjan, Genevive 218 Japanese PURPLE Machine, cryptanalysis by Rowlett, Frank B. (1908Ч1998) 218 Japanese PURPLE Machine, cryptanalysis by Snyder, Sam 218 Japanese PURPLE Machine, cryptanalysis of 219Ч243 Japanese PURPLE Machine, encipherment of CON-letters 212Ч216 Japanese PURPLE Machine, encipherment of CON-letters, period of 216Ч217 Japanese PURPLE Machine, encipherment of VOW-letters 211Ч212 Japanese PURPLE Machine, key, components of the PURPLE 212Ч218 Japanese PURPLE Machine, partition of letters (VOW-CON) 211 Japanese RED machine 191Ч209 Japanese RED machine, components of 193Ч194 Japanese RED machine, components of, breakwheel of 194Ч196 Japanese RED machine, cribbing RED ciphertext 200Ч298 Japanese RED machine, cribbing RED ciphertext, vowel/consonant pattern in 200Ч201 Japanese RED machine, cribbing RED ciphertext, with all breakwheel pins active 201Ч204 Japanese RED machine, cribbing RED ciphertext, with some inactive breakwheel pins 204Ч209 Japanese RED machine, cribbing RED ciphertext, with some inactive breakwheel pins, estimating number of inactive pins 199Ч200 Japanese RED machine, cribbing RED ciphertext, with some inactive breakwheel pins, stepping equations for 206Ч209 Japanese RED machine, cryptanalysis of 200Ч209 Japanese RED machine, cryptanalysis of, estimating number of pins removed 199 Japanese RED machine, cryptanalysis of, shifted ciphertext 198 Japanese RED machine, encipherment rules of 197Ч198 Japanese RED machine, encipherment rules of, encipherment of CON-letters 197Ч198 Japanese RED machine, encipherment rules of, encipherment of VOW-letters 197Ч198 Japanese RED machine, encipherment rules of, partition of letters: (VOW, CON) 197 Japanese RED machine, generalized vowels/consonants 209 Japanese RED machine, pins of 194Ч195 Japanese RED machine, plugboard of 194 Japanese RED machine, plugboard of, stepping sequence of 194Ч196 Japanese RED machine, plugboard of, stepping shifts of 195 Key 4 Key distribution 335Ч336 Key distribution, in a network 335Ч336 447 Key running 116Ч117 Key space 4 Key stream 244Ч282 Key, Diffie Ч Hellman protocol 448Ч450 Key, Diffie Ч Hellman protocol, El Gamal's extension of 450Ч451 Key, Shamir's autonomous protocol 451Ч453 Knapsack cryptosystem 350Ч371 Knapsack cryptosystem, trapdoor 350Ч371 Knapsack problem (modulo m) 350 Knapsack problem (subset sum problem) 338Ч340 Knapsack problem (subset sum problem), with modular arithmetic 350Ч371 Knapsack vector 344 Knapsack vector, evaluation using 138 Knapsack vector, Kolmogorov Ч Smirnov test 136Ч138 Knapsack vector, significance level in 137 Knapsack vector, super-increasing 345 350Ч354 Kohnfelder, Lauren 341Ч342 467 495 Kohnfelder, Lauren, certificates of 495 Kullback, Dr. Solomon (1903Ч1994) 11 85 Lattice 368Ч370 Lattice, short vectors in 368Ч370 Least common multiple lcmfg 385 Leibler, Richard A. (1914Ч2003) 85 Lenstra's factorization algorithm on elliptic curves 432Ч433 Letter counts and probabilities 32 Letters (of text) 1 2 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR) 245Ч246 254Ч273 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR), characteristic polynomial of a 251Ч253 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR), combining 259 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR), cribbing of LFSR-enciphered ASCII plaintext 260Ч271 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR), irregular clocking of 274Ч278 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR), sequences of 254 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR), sequences of, matrix representation of 260Ч261 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR), sequences of, maximal length LFSR sequences 254Ч258 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR), sequences of, maximal length LFSR sequences, autocorrelation function of 255Ч258 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR), sequences of, maximal length LFSR sequences, linear complexity (equivalence) of 258 Linear feedback shift register (LFSR), sequences of, maximal length LFSR sequences, properties of 258 Lorenz Schluesselzusatz (SZ40/fish) 170Ч190 Lorenz Schluesselzusatz (SZ40/fish), cribbing of ciphertext 176Ч190 Lorenz Schluesselzusatz (SZ40/fish), cryptanalysis problems for 173 Lorenz Schluesselzusatz (SZ40/fish), finding the active pins of 171 Lorenz Schluesselzusatz (SZ40/fish), key of 173 Lorenz Schluesselzusatz (SZ40/fish), key stream generated by 170 Lorenz Schluesselzusatz (SZ40/fish), move indicator of 183Ч190 Lorenz Schluesselzusatz (SZ40/fish), pin wheels of 171Ч173 Lorenz Schluesselzusatz (SZ40/fish), statistical model of pin motion 177Ч183 Lorenz Schluesselzusatz (SZ40/fish), steps in encipherment 174 Lucifer 283Ч287 LUCIFER, implementation in IBM 2984 284Ч287 LUCIFER, key schedule of 285Ч286 LUCIFER, operations in 286Ч287 LUCIFER, P-Box of 286Ч287 LUCIFER, S-box of 285Ч286 M-94 (CSP-488) 6 7 Magnetic stripe technology 482Ч483 Magnetic stripe technology, protecting recording in 482Ч483 Making a secure credit card payment on the Web 502Ч505 Markman hearing 514 Markov log-odds score 38 Markov parameters, Gmarkov 34 Markov parameters, Hmarkov 34 Markov parameters, Smarkov 34 Markov score 34 Markov scoring 34 Markov source 31 32 Markov source, homogeneous 31 Markov source, Law of large numbers for 40 Matyas, Stephen M. 455 Mauborgne, Joseph Oswald (1881Ч1971) 119 Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) 81 Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE), partial maximum likelihood estimation 73Ч78 Menezes Ч Vanstone elliptic curve cryptosystem 443 Merkle Ч Hellman trapdoor knapsack cryptosystem 350Ч371 Merkle Ч Hellman trapdoor knapsack cryptosystem, ASCII-text decipherment of 357Ч358 Merkle Ч Hellman trapdoor knapsack cryptosystem, ASCII-text encipherment of 355Ч356 Merkle Ч Hellman trapdoor knapsack cryptosystem, cryptanalysis of 358Ч372 Merkle, Ralph C. 15 512 Mersenne primes 408Ч409 Mersenne, Marin (1588Ч1648) 409 Message authentication 3 Message authentication code (MAC) 3 466 498Ч500 Message authentication code (MAC), MD5 471Ч473 Message authentication code (MAC), message digest 471 Meyer, Carl H. 455 Miller Ч Rabin primality test 406Ч407 Miller Ч Rabin theorem 405Ч406 Modular arithmetic 346Ч347 Modular arithmetic 347 378 Modular arithmetic 248Ч250 Modular arithmetic 346Ч347 Modular exponentiation 338Ч339 376Ч377 Modular exponentiation, program for 376 Monoalphabetic substitution 1 Monoalphabetic substitution, cryptanalysis of 73 Monoalphabetic substitution, examples of 68Ч73 Monoalphabetic substitution, table for a 64 Multiprecision modular arithmetic 387Ч389 Multiprecision modular arithmetic, basic modular operations 387 Multiprecision modular arithmetic, internal representation of numbers 387 Myer, Albert J. (1828Ч1880) 63Ч64 N-gram 1 National Security Agency (NSA) 9 10 Needham Ч Schroeder protocol 335 456Ч462 Needham Ч Schroeder protocol, using a public key cryptosystem 459Ч462 Needham Ч Schroeder protocol, using a symmetric key crypto system 456Ч459 Needham, Roger M. 335 456 NIST's digital signature algorithm 474Ч475 NIST's secure hash algorithm 473Ч474 NIST's secure hash algorithm, NIST's long run test 139 NIST's secure hash algorithm, NIST's monobit test 138 NIST's secure hash algorithm, NIST's poker test 138 NIST's secure hash algorithm, NIST's runs rest 139 NIST's secure hash algorithm, NIST's statistical tests 138Ч139 Nonlinear feedback shift registers 271Ч273 Nonlinear key stream generation 273Ч274 Nonpatentable subjects 508 Number theory and cryptography 391 Oblivious transfer 478 Odlyzko, Andrew M. 428 One-gram scoring using a Markov language model 75 One-gram scoring using a one-gram language model 74 One-time pad (tape) 119Ч120 128Ч129 One-time pad (tape), detecting reuse of Soviet 130Ч131 One-time pad (tape), Soviet KGB protocol for 128Ч129 One-way function 340 480Ч481 One-way function, trapdoor 340 Parameters of a Markov model, deriving the 34 password cracking 481Ч482 Patents 506Ч509 Patents, 3 C's, 507 Patents, claims of 507Ч508 Patents, claims of, anticipated 508 Patents, claims of, invalid 508 Patents, claims of, means plus function 508 Patents, claims of, obvious 508 Patents, equivalent structures/acts of a 509 Patents, file history 508 Patents, format of 507Ч508 Patents, invalid 508 Patents, prior art 507 Patents, requirements of 507 Patents, requirements of, enablement 507 Patents, requirements of, novelty 507 Patents, requirements of, obviousness / nonobviousness 507 Patents, requirements of, utility 507 Patents, requirements of, written description 508 Patents, role in cryptography 509 Patents, specification of 507 Patents, subjects, Nonpatentable 507Ч508 Patents, submarine 515 Patents, validity of 508 Perfect numbers 408Ч409 Plaintext 2 6 Plaintext language models 30 31 Pohlig Ч Hellman algorithm 415Ч418 Pollard's 394 424Ч426 Pollard's 424Ч426 Pollard's 394 Pollard's p-1 method 391 393Ч394 Polyalphabetic substitution 116 Polyalphabetic substitution, periodic 117 Polyalphabetic substitution, periodic, correlation analysis of 120Ч124 Polyalphabetic substitution, periodic, estimating the period of periodic polyalphabetic substitution using coincidence 126Ч127 Polyalphabetic substitution, periodic, estimating the period of using correlation to find the Vernam Ч Vigenere key of 120Ч124 Polyalphabetic substitution, periodic, estimating the period of using the 127Ч128 Polynomials over 247Ч250 Polynomials over 247Ч248 Polynomials over 249 Polynomials over 249 Polynomials over 247 Polynomials over 248Ч250 Polynomials over 247 Porta, Giambattista della (1538Ч1615) 117 Primality testing 405 Prime number theorem 391 Primes, factorization of integers into 390 Primitive roots modulo p 397 414 Privacy 3 Private information (about a cryptographic system) 5 Private key 337Ч340 354 Product block-cipher 283 Product block-cipher, Feistel-like 283 Project Gutenberg Free eBook Library 34 Pseudo-random bit generator (PRBG) 502 Pseudo-random number generator (PRBG) 257Ч258 Pseudo-random number generator (PRBG), next bit test of 257 502 Pseudorandom sequence 257 Public information (about a cryptographic system) 5 Public key 337Ч340 354 Public key certificates 342 449 495Ч497 Public key cryptography 334Ч341 Public key cryptosystem(s) 334Ч341 Purdy, George B. 480 Pythagorean triples 428 Quadratic residue 396Ч401 Quadratic residue, sieve 403Ч405 Quadratic residue, sieve, factor base in 404 Quadratic residue, sieve, steps in 403 Quantum computers 428 Quantum computers, RSA's 502 Rabin's quadratic residue signature protocol 468Ч470 Rabin, Michael O. 468Ч470 Random factorization (Dixon) 401Ч403 RC4 278Ч280 RC4, key scheduling algorithm of 278Ч279 RC4, pseudorandom number generator (PRGA) of 278Ч280 Relatively prime numbers 377 Riemann hypothesis 407 Riemann hypothesis, generalized 407 Riemann zeta function 407 Rijndael 312Ч326 Rijndael, activity pattern 323Ч325 Rijndael, block sizes of 313 Rijndael, key sizes of 313 Rijndael, operations of 314Ч323 Rijndael, operations of, AddRoundKey 321Ч323 Rijndael, operations of, ByteSub and InvByteSub 316Ч317 Rijndael, operations of, MixColumn and InvMixColumn 320 Rijndael, operations of, ShiftRow and InvShiftRow 317Ч318 Rijndael, propagation of patterns 323Ч326 Ring 10 Rivest, Ronald 340 378 Rotor 150Ч151 Rotor system(s) 152Ч153 Rotor system(s), Hebern's straight-through rotor system 152 161 Rotor system(s), patents of 153Ч154 Rotor, displacement sequence (of a rotor) 158Ч160 Rotor, rotational displacement function of 153 Rotor, wiring by interval method 158Ч160 Rowlett, Frank B. 11 12 218 243 RSA challenge 16 407Ч408 RSA cryptosystem 16 340 378Ч382 RSA cryptosystem, attacks on 382Ч383 RSA cryptosystem, deciphering exponent 378 RSA cryptosystem, enciphering exponent 378 RSA cryptosystem, encipherment/decipherment of ASCII-Plaintext 379Ч382 RSA cryptosystem, encipherment/decipherment transformation 378 RSA cryptosystem, parameter set 378 RSA cryptosystem, William's variation of 383Ч387 RSA cryptosystem, Williams quadratic encipherment 384Ч387 RSA-129 408 Scherbius, Arthur (1878Ч1929) 160Ч161 Schroeder, Michael D. 335 Secrecy 2 Secrecy, digital signatures and authentication, comparison of 468 Secrecy, in GSM 276Ч278 Secrecy, secrecy systems 465 Secure Socket Layer (SSL) 497Ч502 Secure socket layer (SSL), cryptographically secure random number generator for 502 Secure socket layer (SSL), master secret in 500Ч501 Secure socket layer (SSL), message authentication code in 499Ч500 Secure socket layer (SSL), message digest algorithm of 498 499Ч500 Secure socket layer (SSL), messages in 497Ч499 Secure socket layer (SSL), messages in, Client_Hello 497Ч498 Secure socket layer (SSL), messages in, record protocol of 499 Secure socket layer (SSL), messages in, Server_Hello 498 Secure socket layer (SSL), messages in, SessionID of 498 Secure socket layer (SSL), transaction 497Ч499 Secure socket layer (SSL), transaction, data encipherment algorithm in 498 Secure socket layer (SSL), transaction, handshake protocol in 497 Secure socket layer (SSL), transaction, key exchange protocol of 498 500 Secure socket layer (SSL), transaction, key exchange protocol of, anonymous Diffie Ч Hellman 500 Secure socket layer (SSL), transaction, key exchange protocol of, anonymous ephemeral Diffie Ч Hellman 500
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



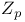
 -algorithm
-algorithm  -value for the cryptanalysis of
-value for the cryptanalysis of