Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Reed M., Simon B. — Methods of Modern mathematical physics (vol. 3) Scattering theory
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Methods of Modern mathematical physics (vol. 3) Scattering theoryАвторы: Reed M., Simon B. Аннотация: Scattering theory is the study of an interacting system on a scale of time and/or distance which is large compared to the scale of the interaction itself. As such, it is the most effective means, sometimes the only means, to study microscopic nature. To understand the importance of scattering theory, consider the variety of ways in which it arises. First, there are various phenomena in nature (like the blue of the sky) which are the result of scattering. In order to understand the phenomenon (and to identify it as the result of scattering) one must understand the underlying dynamics and its scattering theory. Second, one often wants to use the scattering of waves or particles whose dynamics on knows to determine the structure and position of small or inaccessible objects. For example, in x-ray crystallography (which led to the discovery of DNA), tomography, and the detection of underwater objects by sonar, the underlying dynamics is well understood. What one would like to construct are correspondences that link, via the dynamics, the position, shape, and internal structure of the object to the scattering data. Ideally, the correspondence should be an explicit formula which allows one to reconstruct, at least approximately, the object from the scattering data. The main test of any proposed particle dynamics is whether one can construct for the dynamics a scattering theory that predicts the observed experimental data. Scattering theory was not always so central the physics. Even thought the Coulomb cross section could have been computed by Newton, had he bothered to ask the right question, its calculation is generally attributed to Rutherford more than two hundred years later. Of course, Rutherford's calculation was in connection with the first experiment in nuclear physics.
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Математическая Физика /Учебники /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 1979Количество страниц: 463Добавлена в каталог: 24.04.2005Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Paley — Wiener theorems 16 17 18 23 109 Parseval’s relation 45—46 Partial wave expansion 128 Partial wave scattering amplitudes 128 Partial wave unitarity 130 Partition 323 Pauli matrices 287 Pearson’s counterexample 71 Pearson’s theorem 24 Periodic potentials 279 Phase shifts 129 Phase space 5 Plancherel theorem 10 Polar decomposition 197 297 Polarization identity 63 Positive commutators 427 Positive operator 195 Principle of least action 279 Principle of uniform boundedness 81 Product formula 295—297 245 Projection 187 Projection valued measure (p.v.m.) 234—235 262—263 Putnam — Kato theorem 427 Quadratic forms 276 Quadratic forms, closed 277 Quadratic forms, form core 277 Quadratic forms, form domain 276l Quadratic forms, Friedrichs’ extension 177 Quadratic forms, infinitesimally bounded 168 Quadratic forms, positive 276 Quadratic forms, relatively bounded 168 Quadratic forms, relatively compact 369 Quantum field scattering, external field 293—316 Quantum field scattering, Haag — Ruelle theory 317—330 Quantum scattering, central potentials 121—168 Quantum scattering, dispersion relations 116—120 Quantum scattering, eigenfunction expansions 96—115 Quantum scattering, long-range potentials 169—183 Quantum scattering, N-body 75—95 Quantum scattering, two-body 54—74 RAGE theorem 341 Rearrangement collisions 77 Reduction formulas 381 Reduction of the S-matrix 121 refinement 89 Regular equation 136 Regular operator 234 Regular pair 244 Regular solution 137 Regular wave packet 42 Relatively bounded 162 Relatively compact 113 Relatively form bounded 168 Relatively form compact 369 Resolvent 188 253 Resolvent set 188 253 Resonance poles 144 Restricted cone property 204 Riemann — Lebesgue lemma 10 Riesz’s lemma 43 Right-hand cut 145 Rollnik class 99 Rosenberg — Spruch bound 148 S-matrix, S-Operator see “Scattering operator” Scattering amplitude 111 127 Scattering amplitude, forward 117 Scattering angle 14 Scattering length 136 Scattering operator, external quantum fields 307 Scattering operator, Lax — Phillips method 212 Scattering operator, quantum fields 322 Scattering operator, quantum mechanics 73 87 Scattering operator, quantum mechanics, cluster properties 93 Scattering theory, acoustical 184—243 Scattering theory, classical particles 5—15 Scattering theory, Enss’s method 331—343 Scattering theory, external quantum fields 293—316 Scattering theory, Hilbert space methods 16—36 Scattering theory, Lax — Phillips method 210—242 Scattering theory, long-range 169—183 Scattering theory, nonlinear wave equations 252—277 Scattering theory, on 382—384 Scattering theory, optical 184—243 Scattering theory, quantum mechanics, 2-body 54—74 Scattering theory, quantum mechanics, central potentials 121—168 Scattering theory, quantum mechanics, dispersion relations 116—120 Scattering theory, quantum mechanics, eigenfunction expansions 96—115 Scattering theory, quantum mechanics, long-range 169—183 Scattering theory, quantum mechanics, N-body 75—95 Scattering theory, spin waves 285—292 Scattering transformation 3 13 Schrodinger equation 303 Schrodinger integral equation 136 137 Schwartz space 133 Schwarz inequality 38 Self-adjoint operator, bounded 187 Self-adjoint operator, unbounded 255 Semibounded operator 137 Semibounded quadratic form 276 Semicomplete wave operator 35 Semigroup, 255 Semigroup, contraction 235 Semigroup, holomorphic 248 252 Semigroup, hypercontractive 258 Semigroup, infinitesimal generator 237 246 248 Semigroup, strongly continuous 235 Singular continuous spectrum, absence of 406—453 Smooth boundary 209 Smooth perturbations 411—437 Smooth solutions of the Klein — Gordon equation 43 Sobolev inequality 31 113 Sobolev lemma 52 Sobolev spaces 50 253 Source 281 Spatial cluster properties 93 Spectral mapping theorem 222 109 181—1834 Spectral measures 228 Spectral measures, associated with a vector 22 5 Spectral projections 234 Spectral theorem, functional calculus form 225 263 Spectral theorem, multiplication operator form 227 260 Spectral theorem, p.v.m.form 235 263—264 Spectrum 188 Spectrum, absolutely continuous 231 Spectrum, approximate point 178 Spectrum, asymptotically in a set 46 Spectrum, continuous 231 Spectrum, continuous singular 231 Spectrum, discrete 236 13 Spectrum, essential 236 Spectrum, point 188 231 Spectrum, residual 188 Spherical Bessel functions 153 Spin down 287 Spin up 287 Starlike 209 Stationary methods 354 Stationary phase 37 Stone’s formula 237 Strong operator topology 182 Strong resolvent sense, convergence in 284—291 Strongly continuous semigroup 235 Strongly continuous unitary group 265 Strongly semibounded local perturbation of 67 subchannels 92 Subcritical 249 Subordinate operators 28 Support of a distribution 139 17 Support of a distribution, singular 88 Symmetric operator 255 Symmetric quadratic form 276 Symplectic transformation 376 T-matrix 107 Tensor product, Hilbert spaces 49 Tensor product, operators 299 Tensor product, operators, spectrum of 177 Threshold for channel a 124 Time delay 14 Time-dependent Schrodinger equation 61 Time-zero fields 300 Trace class 207—210 Transport equation 243 Trotter product formula 295—297 245 Truncated cone 204 Truncated vacuum expection value 323 Twisting trick 241 Uniform boundedness principle see “Principle of uniform boundedness” Uniform operator topology 182 Unitarity cut 145 Unitarity relation for the T-matrix 110 Unitary operator 39 Ursell functions 381 Variable phase equation 133 von Neumann’s theorem 268 143 180 von Neumann’s uniqueness theorem 217 275 Wave operators, complete 35 Wave operators, generalized 17 Wave operators, semicomplete 35 Weak asymptotic completeness 3 Weak topology 93 111 Weak- 30 Weak- 32 Weakly coupled quantum systems 421 Weakly measurable (vector-valued) function 114 Weighted 76 438 Wiener’s theorem 340 Young’s inequality 28 Yukawa potential 120 Yukawa potential, generalized 120
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



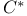 -algebras
-algebras 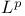 -contractive
-contractive 
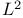 space
space