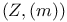|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Rosenberg J. — Algebraic K-Theory and Its Applications |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
 1.1.5 1.1.5
 , behavior under Cartesian product 1.2.8 , behavior under Cartesian product 1.2.8
 , continuity of 1.2.5 , continuity of 1.2.5
 , Morita invariance of 1.2.4 , Morita invariance of 1.2.4
 , of division ring 1—1.6 , of division ring 1—1.6
 , of local ring 1.3.11 , of local ring 1.3.11
 , of PID 13.1 , of PID 13.1
 , ring structure on 1.1—9 , ring structure on 1.1—9
 2.1.5 2.1.5
 , behavior under Cartesian product 2.1.6 , behavior under Cartesian product 2.1.6
 , continuity of 2.1.9 , continuity of 2.1.9
 , Morita invariance of 2.1.8 , Morita invariance of 2.1.8
 , of a field 2.2.1 , of a field 2.2.1
 , of Dedekind domain 2.3.5 , of Dedekind domain 2.3.5
 , of division ring 2.2.6 , of division ring 2.2.6
 , of Euclidean domain 2.3.2 , of Euclidean domain 2.3.2
 , of local ring 2.2.6 , of local ring 2.2.6
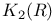 4.2.2 4.2.10 4.2.2 4.2.10
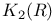 , behavior under Cartesian product 4.3.18 , behavior under Cartesian product 4.3.18
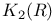 , Morita invariance of 4.2.23 , Morita invariance of 4.2.23
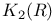 , of , of 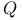 4.4.9 4.4.9
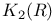 , of , of 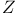 4.3.20 4.3.20
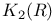 , of , of 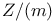 4.3.19 4.3.19
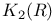 , of (commutative) field 4.3.15 , of (commutative) field 4.3.15
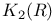 , of finite field 4.3.13 4.3.14 , of finite field 4.3.13 4.3.14
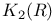 , of rings of functions 4.4.19 , of rings of functions 4.4.19
 5.2.6 5.2.6
 , of , of 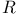 and and 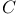 5.3.9 5.3.9
 , of , of 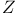 5.3.10—14 5.3.10—14
 , of algebraically closed field 5.3.8 , of algebraically closed field 5.3.8
 , of division algebra 5.3.40 , of division algebra 5.3.40
 , of finite field 5.3.2 , of finite field 5.3.2
 , of purely transcendental extension field 5.3.36 5.3.37 , of purely transcendental extension field 5.3.36 5.3.37
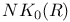 3.2.14 3.2.14
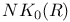 and and 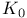 of Laurent polynomial rings 3.3.2 of Laurent polynomial rings 3.3.2
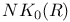 , non-triviality of 3.2.24 , non-triviality of 3.2.24
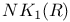 3.2.14 3.2.14
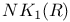 and and 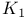 of Laurent polynomial rings 3.2.22 of Laurent polynomial rings 3.2.22
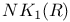 and Nil R 3.2.22 and Nil R 3.2.22
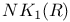 , non-finite generation of 3.2.29 , non-finite generation of 3.2.29
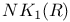 , non-triviality of 3.2.23 , non-triviality of 3.2.23
Abelian category remarks preceding 3.1.1
Acyclic complex 1.7.1
Acyclic space 5.3.31
Adams operation 5.3.2
Additive category remarks preceding 3.1.1
Alexander trick remarks following 2.4.5
Almost-commuting algebra 4.4.20
Alternating group 4.1.27 5.2.19
Assembly map in cyclic homology 6.2.11
Assembly map in Hochschild homology 6.2.11
Assembly map in K-theory 6.3.18 6.3.21
Augmented algebra 6.1.27(3) 6.1.40
Baer sum 4.1.16
Banach algebra remarks following 1.6.5 3.3.8
Bass — Heller — Swan Theorem 3.2.20 3.2.22
Bass — Heller — Swan Theorem, analogue in cyclic homology 6.1.49
Bass — Heller — Swan Theorem, analogue in Hochschild homology 6.1.48
Beilinson conjectures remarks following 5.3.14
Bernoulli numbers remarks following 5.3.14
Bloch's formula remarks following 5.3.30
Block sum 1.2.3 2.1.5 5.2.12
Borel's Theorem on K-groups of rings of integers 5.3.13
Bott Periodicity Theorem 1.6.13 3.3.8(2)
Boundaries 1.7.1
Bounded h-cobordism remarks following 3.3.5
Brauer group 4.4.13
Brauer group and Galois cohomology 4.4.14
Brauer lift 5.3.4
Brauer's Theorem on Characters 5.3.4
Brown — Douglas — Fillmore invariant 4.4.24
C*-algebra 3.3.8(4) 6.3.8
C*-algebra of a group 6.3.9
Campbell — Baker — Hausdorff formula 2.2.10 4.4.30(4)
Category with exact sequences 3.1.1
Cayley graph 6.3.15
Cellular approximation theorem remarks following 2.4.9 5.1.12
Cellular homology remarks following 5.1.13
Central extension 4.1.1
Central extension of Lie groups 4.1.5
Central simple algebra 4.4.13
Chain complex 1.7.1
Chain homotopy 1.7.2
Chapman's Theorem remarks following 2.4.9
Chern character for 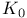 6.2.7 6.2.7
Chern character for Chow ring remarks following 5.3.30
Chern character for higher K-groups 6.2.14
Chern character for lower K-groups 6.2.24
Chern character relative 6.2.22
Chern character with coefficients 6.3.26
Chern character, classical beginning of 6.2
Chinese remainder theorem 1.3.14 1.4.22 2.3.5 4.3.19
Chow ring remarks following 5.3.30
Class group 1.4.3
Class group of cubic number field 6.3.7
Class group of cyclotomic number field 3.3.5(b)
Class group of quadratic number field 1.4.24 6.3.6
Class group, finiteness theorem for 1.4.19
Classifying space, for topological K-theory 5.3.2 5.3.9
Classifying space, of a group 5.1.16
Classifying space, of a small category 5.3.15
Classifying space, universal property of 5.1.32
Clutching 2.5.4
Coherent sheaf 3.1.2(7) remarks
Cohomology, cyclic 6.1.34
Cohomology, de Rham beginning of 6.2
Cohomology, exceptional (or generalized) beginning of 1.6 6.3.19
Cohomology, group 4.1.7
Cohomology, Hochschild 6.1.33
Cohomology, sheaf remarks following 3.1.16
Compact operators 2.2.10 6.3.4
Compact supports, Jf-theory with 1.6.14
Congruence Subgroup Problem 2.5.21
Connes periodicity operator 6.1.18 6.1.34
Contractible 1.7.2
Corestriction 4.1.21
Covering map 5.1.5 5.1.25
Crossed product 4.4.14
CW-complex remarks preceding 2.4.6 5.1.7
Cycles 1.7.1
Cyclic homology 6.1.12
Cyclic homology, behavior under Cartesian product 6.1.44
Cyclic homology, calculation for ![$k[v, v^{-1}]$](/math_tex/58056f63554b7eeba3b36b61ebdc6cce82.gif) 6.1.43 6.1.49 6.1.43 6.1.49
Cyclic homology, calculation for ![$\mathbb Z[\sqrt{D}]$](/math_tex/9b7b742bd0293f590bf52e15d0c0b8e982.gif) 6.2.10(b) 6.2.10(b)
Cyclic homology, calculation for dual numbers 6.1.27(b)
Cyclic homology, calculation for ground ring 6.1.16
Cyclic homology, calculation for group ring 6.2.11
Cyclic homology, calculation for k[t] 6.1.20(b) 6.1.42
Cyclic homology, Morita invariance of 6.1.37
Dedekind domain 1.4.2
Dedekind domain, 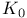 of 1.4.12 of 1.4.12
Dedekind domain, 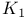 of 2.3.5 of 2.3.5
Dedekind domain, characterization of 1.4.17
Dedekind domain, class group of 1.4.3
Dedekind domain, examples of 1.4.18 1.4.20 1.4.23 1.4.24
Dennis trace map 6.2.14
Determinant, class (of operators) 2.2.10(4)
Determinant, Dieudonne 2.2.5
Determinant, of an operator 2.2.10
Devissage Theorem 3.1.8 5.3.24
Dirichlet Theorem on primes in arithmetic progressions 2.5.17 4.4.1
Dirichlet unit theorem 2.3.8
Divisor (in algebraic geometry) remarks following 3.1.16 3.1.25
Dolbeault's theorem remarks following 3.1.18
Double complex 1.7.17 6.1.10 6.1.31
Dual numbers 6.1.7(b)
Elementary collapse 2.4.7 2.4.8
Elementary matrix 2.1.1
Elementary row and column operations 2.1.5 2.2.5
End (of a space) 1.7.14
| Euclidean Domain 2.3.1
Euler characteristic 1.7.9 remarks
Euler-Poincare Principle 1.7.10 3.1.10
Exact sequence of Connes 6.1.19 6.1.34
Exact sequence of K-groups 1.5.5 2.5.4 3.3.4 4.3.1
Exact sequence, localization 5.3.27 5.3.28
Excision, failure for 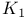 2.5.20 2.5.20
Excision, Theorem for 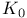 1.5.9 1.5.9
Factorization into prime ideals 1.4.7
Fibration 5.1.19
Fibration, fiber of 5.1.23
Fibration, Hopf 5.1.26
Fibration, local nature of 5.1.22
Fibration, long exact homotopy sequence of 5.1.24
Finitely dominated space beginning of 1.7 remarks
Flat ring extension remarks following 3.2.6 5.3.23
Fractional ideal 1.4.1
Free group 5.1.17 remarks
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic remarks preceding 1.4.7 4.4.9
Fundamental Theorem of homological algebra 1.7.6
Fundamental Theorem of K-theory (see also Bass — Heller — Swan Theorem) 3.3.3 5.3.30
G-groups 3.1.6 3.1.16 5.3.23 5.3.26
G-module 4.1.6
Galois field extension 1.4.18 2.3.8 4.4.6 4.4.14—4.4.18
Genus (of a curve) remarks following 3.1.16
Grothendieck group 1.1.3
Grothendieck's Theorem on 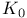 of polynomial extensions 3.2.12 3.2.13 of polynomial extensions 3.2.12 3.2.13
Grothendieck's Theorem on 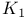 of polynomial extensions 3.2.16 3.2.17 of polynomial extensions 3.2.16 3.2.17
Grothendieck's Theorem on the map from 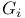 to to 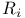 3.1.16 3.1.16
Group completion 1.1.3
h-cobordism 2.4.4
H-group 5.1.11
H-space 5.1.11
Halo 5.1.1
Helton — Howe determinant invariant 4.4.23 4.4.24
Helton — Howe trace invariant 6.3.29
Hilbert basis theorem 3.2.1
Hilbert symbol 4.3.3
Hilbert syzygy theorem 3.2.3
Hilbert's Nullstellensatz 5.3.34(1)
Hilbert's Theorem 90 4.4.16
Hochschild complex 6.1.1
Hochschild complex, reduced 6.1.38
Hochschild homology 6.1.1
Hochschild homology, behavior under Cartesian product 6.1.44
Hochschild homology, calculation for ![$k[v, v^{-1}]$](/math_tex/58056f63554b7eeba3b36b61ebdc6cce82.gif) 6.1.43 6.1.48 6.1.43 6.1.48
Hochschild homology, calculation for dual numbers 6.1.7(a)
Hochschild homology, calculation for group ring 6.1.45
Hochschild homology, calculation for k[t] 6.1.7(a)
Hochschild homology, Morita invariance of 6.1.36
Homology, and direct and inverse limits 4.1.29
Homology, calculation for a finite cyclic group 4.1.25
Homology, calculation for a free abelian group 4.1.31
Homology, cyclic 6.1.12
Homology, generalized remarks following 6.3.19
Homology, Hochschild 6.1.1
Homology, non-commutative de Rham 6.1.39
Homology, of a chain complex 1.7.1
Homology, of a group 4.1.7
Homotopy Extension Theorem 5.1.8
Homotopy group 5.1.6
Homotopy invariance 1.6.11 remarks
Hurewicz Theorem 5.1.14
Hurewicz Theorem with coefficients 5.3.7
Icosahedral group 4.1.27 5.2.16
Idempotent beginning of 1.2
Inflation-restriction sequence 4.1.20
Jacobson radical 1.3.6
Join of spaces 5.1.15
Jordan-Holder Theorem 3.1.2(5)
Kadison Conjecture 6.3.17
Karoubi Density Theorem 1.6.16
Laurent polynomial ring beginning of 3.2
Laurent power series ring 3.3.8(3)
Laurent power series ring in commutative algebra 3.2.2 3.2.4
Laurent power series ring, cyclic homology of 6.1.43 6.1.49
Laurent power series ring, Hochschild homology of 6.1.43 6.1.48
Laurent power series ring, K-theory of 3.2.12 3.3.3 5.3.30
Left regular ring 3.1.2(4)
Left regular ring, Grothendieck's Theorem on K-theory of 3.1.16
Lichtenbaum conjecture remarks following 5.3.14
Local field 4.4.6
Local ring 1.3.3
Local ring, 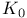 of 1.3.11 of 1.3.11
Local ring, 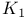 of 2.2.6 of 2.2.6
Local ring, characterization of 1.3.4
Localization theorem 5.3.27 5.3.30
Loday product 5.3.1 6.3.22
Logarithmic derivative 6.1.43 6.2.16 6.2.18 6.3.4
Loop space 5.1.14
Mapping cone 1.7.5
Mapping cylinder remarks following 2.4.9 5.1.13
Matsumoto's Theorem 4.3.15
Mennicke symbol 2.3.6
Mennicke's Theorem on relative  2.5.17 4.4.1 2.5.17 4.4.1
Mercurjev — Suslin Theorem remarks following 4.4.18
Mittag — Leffler condition 1.7.14 6.1.22
Mixed complex 6.1.28
Morita invariance 1.2.4 2.1.8 4.2.23 6.1.36 6.1.37
Multitrace 6.1.34
n-connected 5.1.6
n-regular ring 3.2.26
Nakayama's lemma 1.3.9 1.3.13
Negative K-groups 3.3.1
Negative K-groups of 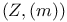 3.3.10 3.3.10
Negative K-groups of a Banach algebra 3.3.8
Negative K-groups of group rings 3.3.10
Non-commutative de Rham homology 6.1.39
Non-commutative de Rham homology and cyclic homology 6.1.40
Non-commutative differential forms 6.1.38
Norm for a field extension 1.4.19 1.4.24(3) 2.3.8 4.4.4—4.4.9 4.4.16—4.4.18 6.3.6—6.3.7
Norm in a Euclidean domain 2.3.1
Norm of an ideal 1.4.19
Norm of an operator 2.2.10
Norm residue symbol 4.4.18 4.4.28 4.4.29
Norm, Schatten 2.2.10
Orthogonal group 1.6.13 5.1.17
Orthogonal projection 6.3.8
Paracompact 5.1.4 5.1.22
Partition of unity 1.6.3 5.1.4
Path space 5.1.20
Perfect group 2.3.9(2) 4.1.3 5.2.2
Periodic cyclic homology 6.1.12
Periodicity operator 6.1.18 6.1.34
PID (principal ideal domain) 1.3.1 remarks 3 3.1.20
Plus-construction (+-construction) 5.2.2
Plus-construction (+-construction), functoriality of 5.2.4
Poincare conjecture remarks following 2.4.5 5.2.5
Poincare homology 3-sphere 4.1.27 5.2.5 5.2.16
Projection (self-adjoint) 6.3.8
Projective module 1.1.1
Projective module, characterization of 1.1.2
Projective variety 3.1.2(7) remarks remarks
Property T remarks following 2.3.8
Pseudo-isotopy remarks following 4.4.25
Pull-back (of vector bundle) 1.6.2
Q-construction 5.3.19
Quadratic reciprocity law 4.4.10
Quaternion algebra symbol 4.4.28
Quaternions 2.2.9 4.4.11
Quillen's Theorem, comparing the +-construction and Q-construction 5.3.20
Quillen's Theorem, on finite generation of K-groups 5.3.12
Quillen's Theorem, on if-theory of finite fields 5.3.2
Quillen's Theorem, on localization 5.3.27
Radical (of a ring) 1.3.6
Ramified field extension 4.4.6 4.4.9
Ramified prime ideal 1.4.24
Rank (of a module) 1.3.1 1.3.11 1.3.12
Reduced C*-algebra 6.3.9
Reduced cyclic complex 6.1.40
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте





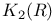
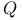
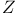
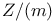

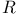 and
and 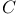
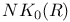
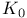 of Laurent polynomial rings
of Laurent polynomial rings 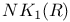
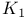 of Laurent polynomial rings
of Laurent polynomial rings ![$k[v, v^{-1}]$](/math_tex/58056f63554b7eeba3b36b61ebdc6cce82.gif)
![$\mathbb Z[\sqrt{D}]$](/math_tex/9b7b742bd0293f590bf52e15d0c0b8e982.gif)
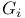 to
to