Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Jensen F. — Introduction to Computational Chemistry
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Introduction to Computational ChemistryАвтор: Jensen F. Аннотация: Introduction to Computational Chemistry Frank Jensen Odense University, Denmark Computational chemistry is a rapidly emerging and developing area, combining theoretical models with computers to investigate a variety of chemical phenomena. Increasingly applied throughout chemistry, computational methods are becoming an integral part of modern chemical research. Introduction to Computational Chemistry provides a comprehensive account of the fundamental principles underlying different methods, ranging from classical to sophisticated quantum models. Although the main focus is on molecular structures and energetics, subjects such as molecular properties, dynamical aspects, relativistic methods and qualitative models are also covered. Introduction to Computational Chemistry features:
Язык: Рубрика: Химия /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Издание: 1-stГод издания: 1998Количество страниц: 429Добавлена в каталог: 19.02.2007Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
11 25 23 8 23 14 8 15 18 302 300 299 301 305 367 139 183 1,3-Butadiene 27 89 3-21G, 6-31G, 6-311G basis sets 159 Activation energy 307 Active molecular orbitals, MCSCF methods 119 Adiabatic approximation 53 56 Adiabatic connection formula 409 Adiabatic Connection Model (ACM) 187 Aliasing, in pseudospectral methods 174 Allowed reaction, Woodward — Hoffmann rules 356 AMBER force field 40 Amplitudes, in coupled cluster theory 133 Angular correlation, in electron correlation 153 Annihilation operator, second quantization 411 Antarafacial, Woodward — Hoffmann rules 357 Antisymmetrizing operator 59 Atom types, in force field 7 8 Atomic basin 223 Atomic Natural Orbitals (ANO) 161 Atomic orbital (AO) 65 150 Atomic Polar Tensor (APT), use for atomic charges 226 Atomic units 54 415 Atoms In Molecules (AIM) 223 Attractors, electron density analysis 223 Augmented Hessian, function optimization 320 Austin Model 1 (AMI) 87 Autocorrelation function, in simulations 380 Averaged Coupled-Pair Functional (ACPF) 139 Avoided crossing 56 356 Axis of inertia 300 B3LYP functional 188 B3P86 functional 188 B3PW91 functional 188 B88 exchange functional 185 B95 functional 187 Basis set convergence 153 163 165 Basis Set Superposition Error (BSSE) 172 Becke 3 parameter functional (B3) functional 88 Becke and Roussel (BR) functional 185 Bell correction, tunnelling 391 Bell, Evans, Polanyi (BEP) principle 364 Bending energy, in force fields 11 BLYP functional 188 Boltzman probability function 374 Bond critical points, electron density analysis 225 Bond dipole 24 Bond dissociation 111 Bond Order (BO) 219 Born model, solvation model 395 Born-Oppenheimer approximation (BO) 3 53 56 Boys localization of molecular orbitals 228 BP86 functional 188 BPW91 functional 188 Bra 55 Bracket 55 Breit interaction, relativistic effects 210 Brillouins theorem 104 Brownian dynamics 389 Broyden — Fletcher — Goldfarb — Shanno (BFGS) update in optimizations 321 Brueckner theory 138 Buckingham potential 19 Cage critical point, electron density analysis 226 Canonical molecular orbitals 63 Canonical momentum operator 248 Car and Parrinello (CP) method 388 CASMP2, CASPT2 methods 132 CASVB method 202 Cavity, in reaction field models 393 CBS-4, CBS-q, CBS-Q and CBS-APNO methods 167 cc-pCVDZ, cc-pCVTZ, cc-pCVQZ, cc-pCV5Z basis sets 162 cc-pVDZ, cc-pVTZ, cc-pVQZ, cc-pV5Z, cc-pV6Z basis sets 162 CC2, CC3 methods 139 CCD, CCSD, CCSDT methods 134 CCDPPA, CCSDPPA methods 261 CCSD + T(CCSD), CCSD(T), CCSD(TQ) methods 138 CFF91/93/95 force field 40 Chain optimization 329 Charge controlled reactions 348 Charge iteration, in Huckel theory 93 CHARMM force field 40 Chemical Hamiltonian Approach (CHA) 173 Chemist’s notation, for two-electron integrals 67 CID, CISD, CISDT, CISDTQ methods 107 CIS method 147 Claisen reaction 304 Class I force fields 41 Class II force fields 30 41 Closed-shell wave function 70 Coarse-grained sampling, in simulations 377 Combination rules for van der Waals parameters 22 Combinatorial explosion 339 Commutator 258 Complete Active Space Self-Consistent Field (CASSCF) method 119 Complete Neglect of Differential Overlap (CNDO) model 83 Conceited reaction 356 Conductor-like Screening Model (COSMO) for solvation 396 Configuration Interaction (CI) 101 Configurational State Functions (CSF) 103 Conical intersection 364 Conjugate Gradient (CG) optimization 318 Conjugate Peak Refinement (CPR) optimization 330 Conjugated systems 27 Connected, in coupled cluster theory 133 Conrotatory, Woodward — Hoffmann rules 360 Contracted basis set 156 Contracted Gaussian Type Orbitals (CGTOs) 157 Coordinate driving 336 Cope rearrangement 367 369 Core integrals 67 Correlation consistent basis sets 162 Correlation functions, in simulations 380 COSMIC force field 40 Coulomb correlation 99 Coulomb gauge 249 Coulomb hole 99 Coulomb integral 61 67 Coulomb operator 61 Coulson — Fischer (CF) function, in valence bond methods 197 Counterpoise (CP) correction 172 Coupled Cluster (CC) methods 132 Coupled Electron Pair Approximation (CEPA) method 139 Coupled Hartree — Fock (CHF) 248 Coupled Perturbed Hartree — Fock (CPHF) 244 Covalent contribution to the wave function 111 196 Creation operators, in second quantization 411 Cross terms in force field energies 25 Cross-correlation function in simulations 380 Cubic response function 261 Cusp, of a wave function 140 214 Cut-off distance, in force field methods 42 CVFF force field 40 Cyclododecane 45 Cycloheptadecane 340 Damping, for achieving SCF convergence 72 Darwin correction, in relativistic methods 209 Davidon — Fletcher — Powell (DFP) update for optimization 321 Davidson algorithm for diagonalizing large matrices 109 Davidson correction, for higher-order excitations 137 Dealiasing, in connection with pseudospectral methods 174 Degree of contraction of basis sets 157 Delocalized internal coordinates 327 Density fitting 191 Density Functional Theory (DFT) 177 Density matrix 66 229 Dewar benzene 367 Diagonal correction, for non-Born-Oppenheimer effects 56 Diagonal term in force field energy functions 25 Diamagnetic Spin-Orbit (DSO) 250 Diamagnetic term 250 dielectric constant 24 Diels — Alder reaction 304 350 358 Different Orbitals for Different Spins (DODS) 70 Diffuse basis function 156 Diffusion methods, for global optimization 343 Dipole moment 236 270 286 Dirac equation 205 207 Dirac — Fock 213 Direct CI methods 109 Direct Inversion in the Iterative Subspace (DIIS) 73 Direct MP2, CCSD methods 142 Direct SCF methods 77 Disconnected, in coupled cluster theory 133 Dispersion force 19 Disrotatory, Woodward — Hoffmann rules 360 Distance geometry methods 343 Distributed Multipole Analysis (DMA) 222 Distribution functions in simulations 378 Double Zeta plus Polarization (DZP) basis set 153 Double, Triple, Quadruple Zeta (DZ, TZ, QZ), basis set 152 Doubles, doubly excited configurations 100 Douglas — Kroll transformation 215 DREIDING force field 40 Dummy atom 37 417 Dunning — Huzinaga basis sets 160 Dynamic properties 235 Dynamical electron correlation 118 EAS force field 40 ECEPP force field 40 Edmiston — Ruedenberg localization of molecular orbitals 228 EFF force field 40 Effective Core Potential (ECP) 171 Eigenvector Following (EF) optimization method 320 electric field 247 Electron Correlation (EC) 98 Electron propagator 258 Electronegativity 353 Electronic chemical potential 353 Electronic Hamilton operator 54 Electrostatic energy 23 Electrostatic Potential (ESP) 220 Elimination reactions 370 Embedding 344 Energy representation, of propagators 257 Ensemble 375 377 Enthalpy 299 303 373 entropy 299 303 373 Equation Of Motion (EOM) methods 261 Ergodic hypothesis 375 Error function 33 73 316 335 ESFF force field 40 Euler integration 344 Even-tempered basis set 155 Ewald sum methods 387 Exchange integral 61 67 Exchange operator 61 Excited Slater determinant 99 Excited states 147 Extended Huckel Method (EHM) 92 Extended Huckel Theory (EHT) 92 Extrapolation, for achieving SCF convergence 72 Fast Multipole Moment (FMM) method 80 387 Fermi Contact (FC) operator 212 251 Fermi correlation 99 Fermi hole 99 Field gradient 213 236 First quantization 411 First-order corrections, in perturbation methods 124 125 First-Order Regular Approximation (FORA) method 209 Fletcher — Reeves conjugate gradient optimization 318 Fluctuation potential, in electron correlation methods 127 Fluctuation, in simulation methods 378 Fock operator 62 Foldy — Wouthuysen transformation 215 Forbidden reaction, Woodward — Hoffmann rules 356 Force Field (FF) 6 Force field energy 8 Force field parameters 30 Four component wave function, in relativistic methods 206 213 Four index transformation of two-electron integrals 105 Fourier series 15 Free Energy Perturbation (FEP) methods 381 Frequency representation, of propagators 257 Frontier Molecular Orbital (FMO) theory 347 Frozen core, frozen virtual orbitals 101 Fukui function 352 Full CI 106 268 Full Optimized Reaction Space (FORS) 119 Functional, definition 177 Gauge Including/Invariant Atomic Orbitals (GIAO), for calculating magnetic properties 252 Gauge origin, in magnetic interactions 248 Gaunt interaction, in relativisitic methods 210 Gaussian product rule 68 222 Gaussian Type Orbitals (GTO) 151 Gaussian-1, Gaussian-2 models, Gl, G2, G2(MP2), G2(MP2, SVP), G2Q 165 General contraction of basis sets 157 General Hartree — Fock method 76 Generalized Atomic Polar Tensor (GAPT), for atomic charges 226 Generalized Born model, solvation 395 Generalized Born/Surface Area (GB/SA), solvation model 397 Generalized frequencies 314 Generalized Gradient Approximation (GGA), in density functional theory 184 Generalized momentum operator 248 Generalized Valence Bond (GVB) method 202 Genetic Algorithms (GA) for global optimization 342 Geometry Direct Inversion in the Iterative Subspace (GDIIS) for optimizations 335 Ghost orbitals 173 Gibbs free energy 299 Global minimum 339 Gonzales — Schlegel method for following an IRC 345 Gradient Extremal (GE) 338 Gradient norm minimization 333 Gradient of a function 238 Greens function 257 GROMOS force field 40 Gross atomic charge 218 Half-and-Half method in density functional theory 187 Half-Electron method (HE) 71 Hammond postulate 365 Hard and Soft Acid and Base (HSAB) principle 353 Hardness, defined from the electron density 353 Hartree — Fock (HF) 59 63 Hartree — Fock limit 69 268 Heat bath 386 heat capacity 298 378 Heat of formation 29 90 Heitler — London (HL) function, in valence bond methods 196 Hellmann — Feynman force 254 Hellmann — Feynman theorem 241 409 Helmholtz free energy 298 373 374 Hermitic operator 54 123 407 Hessian, in optimization methods 319 Hestenes — Stiefel conjugate gradient optimization 318 Higher RPA (HRPA), in propagator methods 261 Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (HOMO) 348 Hill potential 19
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



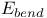 in force field energies
in force field energies 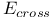 in force field energies
in force field energies 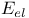 in force field energies
in force field energies 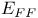 , the force field energy
, the force field energy 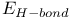 in force field energies
in force field energies 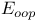 in force field energies
in force field energies 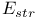 in force field energies
in force field energies 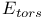 in force field energies
in force field energies 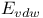 in force field energies
in force field energies 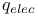 , partition function
, partition function 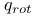 , partition function
, partition function 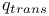 , partition function
, partition function 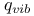 , partition function
, partition function  reaction
reaction 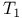 -diagnostic, in coupled cluster methods
-diagnostic, in coupled cluster methods 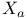 method
method