|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Edwards H. Ч Advanced Calculus: A Differential Forms Approach |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Abel summation 412 426
Abel's theorem 411Ч412
Absolute convergence 409 439n
Addition formulas for 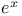 253 (Ex. 2(b)) 253 (Ex. 2(b))
Addition formulas for general exponentials 256 (Ex. 10)
Addition formulas for trigonometric functions 252 (Ex. 1(e))
Affine manifolds 129
Affine maps 8 86Ч87
Affine maps decomposed as a decomposition of simple maps 10Ч11 15 104Ч105 199 200
Algebra of forms, the 90n
Algebraic functions 381Ч383
Almost everywhere convergence 435
Alternating Series Test 377 (Ex. 9)
Analytic functions 299
Approximating sums 25Ч26 29 197Ч198 208Ч213 400 426
Archimedean laws 366 373 377
arcsine function 140 (Ex. 8) 386
arctan 146Ч147
Arithmetic mean 184 (Ex. 6)
Arithmetic modulo n 376 (Ex. 3Ч5)
Arzela's theorem 447 (Ex. 11)
Atlas 203
Banach spaces 448
Basis of a vector space 115Ч117
Betti numbers 327 (Ex. 10)
Binomial coefficients 90n 304 424Ч425
Binomial series 304Ч306
Bolzano Ч Weierstrass theorem 393
Boundary of a surface-with-boundary 215 223
Boundedness of domains 31
Boundedness of functions 31
Cancellation on interior boundaries as the underlying idea of the Fundamental Theorem 59 65Ч66 72
Canonical form for linear maps 119
Cauchy convergence criterion 456Ч457
Cauchy Convergence Criterion for complex numbers 292 310
Cauchy Convergence Criterion in definition of fc-dimensional volume 197
Cauchy Convergence Criterion in definition of integrals 30
Cauchy Convergence Criterion in definition of real numbers 368
Cauchy Convergence Criterion in successive approximations 230
Cauchy Ч Riemann equations 283 296
Cauchy's integral formula 298
Cauchy's polygon 254 (Ex. 5)
Cauchy's theorem 296
Cesaro summation 426 (Ex. 14)
Chain rule 143
Chain rule for complex functions 311 (Ex. 10)
Chain rule in Jacobian notation 102
Chain rule in matrix notation 101Ч102
Chain rule in proof of Stokes' Theorem 62 69Ч70 74
Chain rule in terms of Jacobians 144
Chain rule, principal statement 143
Chain rule, proof 153Ч156
Chain rule, proof for affine maps 87Ч90
Chain rule, reviewed 190
Chain rule, statement for affine maps 87
Closed forms 63 (Ex. 8) 71Ч72 274 320Ч326
Compactness, definition 392
Compactness, related theorems 393Ч398
Completeness of Banach spaces 448
Completeness of Lebesgue integrable functions 442
Completeness of real number system 373Ч375
complex numbers 289Ч291
Computational rules, governing forms and pullbacks 11Ч13 20 42Ч43 86 88Ч89 142Ч143
Computational rules, governing the computation of derived forms 60 68 73 220
Conditional convergence 410n
Conductivity 334
Conformal coordinates 283Ч286
Confusion 26
Conjugate of a complex number 309
Conservative force fields 64 (Ex. 9)
Constraints, examples 164Ч168
Constraints, non-singular 168
Constructive mathematics 463Ч466
Content 197n
Continued fractions 377Ч379 (Ex. 12Ч15)
Continuity equation 332
Continuity of a force field 24
Continuity of a function of two variables 31
Continuity of complex functions 293
Continuity of k-forms 143
Continuity of maps between Banach spaces 451
Continuity, main definition 390
Convergence (see Cauchy Convergence Criterion)
Coulomb's law 335
Cramer's rule 109
Critical points 170
Cross products of vectors 266 (Ex. 5Ч7)
Curl 267
CURVES (see also Manifolds)
Curves, defined by equations 39
Curves, defined by parameters 39
d'Alembertian 347
Decimal approximation 27 (Ex. 2) 380
Decimal fractions 366Ч367 380
Determinants, definition 101
Determinants, method of evaluation 103Ч104 (Ex. 2)
Determinants, reason for name 101n
dielectric constant 241
Differentiability of complex functions 293
Differentiability of k-forms 73
Differentiability of maps 143
Differentiability of maps between Banach spaces 451
Differentiability, main definition 390
Differentiability, reviewed 190
Differentiable manifolds 192
Differential equations, describing families of curves 277 (Ex. 2)
Differential equations, elementary techniques of solution 270Ч276
Differential equations, fundamental existence theorem 245Ч251 320
Differential equations, generalized existence theorem 315
Differential equations, stated in terms of differentials 272 313Ч314
Differential forms 73 (see also Forms)
Differentiation under the integral sign 392 (Ex. 16) 399
Directional derivatives 149 (Ex. 7)
Dirichlet problem 288
Div (divergence) 268
Divergence of a flow 61
Divergence theorem 73 268
Dot product 172 269
Double series 407Ч409
Electrical forces (see Coulomb's Law)
electromagnetic field 343
Elementary functions 384
Elimination of variables in linear equations 76Ч79
Elimination Theorem statement 158
Elimination Theorem statement for rational numbers 365
Elimination Theorem statement in proof of Implicit Function Theorem 158
Elimination Theorem statement, proof 226Ч232
Elimination Theorem statement, reviewed 191
Envelopes 194 (Ex. 7)
Equality of mixed partials 63 (Ex. 6) 74Ч75 218
Euclidean algorithm 376 (Ex. 6)
Euler 402Ч404
Evaluation of 2-forms 12Ч13
exact differential equations 274
Exact forms 63 (Ex. 8) 71Ч72 273 320Ч326
Exact sequences of affine maps 131 (Ex. 4)
Exponential function 253 (Ex. 2) 311
Exponentials of matrices 253 (Ex. 4) 254
Exterior derivatives 73
Exterior powers of matrices (see Matrices)
Factorial function 421Ч425 (Ex. 10 11)
Faraday's Law of Induction 71 (Ex. 5) 342
Flows, constant planar flows 2Ч4
Flows, constant spatial flows 5Ч7
Flows, general discussion 328Ч333
Flows, planar flow from unit source 23 (Ex. 2)
Flows, relation between direction of flow and corresponding (nЧ1) form 21 (Ex. 5 6)
Flows, spatial flow from unit source 24 (Ex. 3) 288
Folium of Descartes 141 (Ex. 9) 193
force (see Work)
| Forms, basic definitions 88
Forms, non-constant forms 142
Forms, on Banach spaces 452 454Ч455
Fredholm alternative 126 (Ex. 12)
Functions (see Algebraic functions Elementary Maps Transcendental Polynomials)
Fundamental theorem of algebra 306Ч307 312
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, as the case 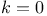 of Stokes' Theorem 73 of Stokes' Theorem 73
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, in vector notation 268
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, proof 53Ч55
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, related to independence of parameter 58 (Ex. 13)
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, related to Poincare's Lemma 327 (Ex. 9)
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, reviewed 391 (Ex. 4)
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, statement 52
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, uses 52Ч53
Gamma function 423 (Ex. 10(n))
Gauss and the lattice point problem 35 (Ex. 2)
Gauss Ч Seidel iteration 240 (Ex. 2 3) 241 242
Gauss' theorem (see Divergence Theorem)
Geometric mean 184 (Ex. 6)
Goldbach conjecture 464Ч465
Golden section 379n
Grad (gradient) 267
Gravity (see Newton's Law of Gravity)
Green's theorem in the plane 73
Harmonic functions, analyticity of 308
Harmonic functions, as solutions of Laplace's equation 278
Harmonic functions, definition 278
heat capacity 334
Heat equation 333
Heine Ч Borel theorem 205 393
Holder inequality 174Ч175
Homology, homology basis 323Ч324
Homology, homology theory 320
Homology, simple cases 75 (Ex. 5Ч6)
Hyperbolic functions 253 (Ex. 3)
Image of a map 81
Implicit differentiation, description of the method 144Ч145
Implicit differentiation, examples 145Ч147 150Ч151
Implicit differentiation, proof 156Ч157
Implicit Function Theorem, examples 134Ч139
Implicit Function Theorem, for affine maps 105Ч108
Implicit Function Theorem, for analytic functions 307Ч308
Implicit Function Theorem, for differentiable maps 133Ч134
Implicit Function Theorem, for maps between Banach spaces 451Ч452
Implicit Function Theorem, proof 232Ч234
Implicit Function Theorem, proof reduced to Elimination Theorem 157Ч159
Implicit Function Theorem, reviewed 191
Improper integrals 401
Independence of parameter, for surface integrals 47
Independence of parameter, general case 222
Independence of parameter, proof 208Ч213
Independence of parameter, statement 207
Integers 366
Integrability conditions 315
Integrals (see also Improper integrals Lebesque
Integrals, as area under a curve 56 (Ex. 4) 65
Integrals, as functions of S 224Ч225
Integrals, basic properties 49Ч51
Integrals, defined as a limit of sums 30Ч31
Integrals, definition reviewed 400
Integrals, difficulty of defining surface integrals 44Ч48
Integrals, double integrals as iterated integrals 51
Integrals, general properties 219Ч223
Integrals, intuitive description of meaning 24Ч27
Integrals, main theorem 204Ч213
Integrals, of complex†1-forms 294Ч295
Integrating factors 275
Integration by parts 222
Intermediate Value Theorem 159n
Inverse function theorem 454 (Ex. 14 15)
Inverse matrix, formula for 111Ч112
Isoperimetric inequality 188Ч190 (Ex. 19)
Iteration 240 (Ex. 1)
Jacobians 100
Lagrange multipliers 161
Lagrange multipliers, examples 166Ч169 170Ч190
Lagrange multipliers, restatement using differentiable manifolds 192Ч193
Lagrange multipliers, statement of method 169
Laplace's equation 278 288
Laplacian 334
Lebesgue dominated convergence theorem 437Ч438
Lebesgue integration, completeness of space of Lebesgue integrable functions 442Ч446
Lebesgue integration, examples and motivation 426Ч431
Lebesgue integration, main theorem 436
Lebesgue integration, passing to a limit under the integral sign 437Ч441
Lebesgue integration, proof 431Ч435
Leibniz notation 458Ч460
Leibniz's formula 419 (Ex. 1)
Level surfaces 80n
Lexicographic order for k-forms 90Ч91
Light as an electromagnetic phenomenon 348
Line integrals 265Ч266
Linear maps 117Ч122 123
Lines of force 71 (Ex. 6)
Liouville's theorem 311 (Ex. 9)
Logarithm function 386 (Ex. 2)
Lorentz transformations 350
Magnetic forces 341
Magnetic permeability 345
Manifolds, affine 129
Manifolds, compact, oriented, differentiable manifolds-with-boundary 219
Manifolds, compact, oriented, differentiable surfaces 203
Manifolds, compact, oriented, differentiable surfaces-with-boundary 214
Manifolds, differentiable 192
Manifolds, solving differential equations 314
Manifolds, usefulness of term 129n
Mappings (see Maps)
Maps, affine maps 8
Maps, differentiable maps 143
Maps, linear maps 117Ч122 123
Maps, origin of term 8
Mass and energy 351Ч354
Matrices, exterior powers 97Ч100
Matrices, formula for inverse 111Ч112
Matrices, minors of 101
Matrices, of coefficients of an affine map 94
Matrices, products 95Ч97
Matrices, transposes 98
Maxima and minima 160Ч183
Maxwell's equations of electrodynamics 340Ч348
Mesh size (of a subdivision) 30
Microscope, describing meaning of differentiability 151Ч153
Microscope, in proof of independence of parameter 211Ч212
Microscope, in rate of convergence of successive approximations 234 (Ex. 2)
Microscope, related to integrals 222
Minkowski's inequality 185 (Ex. 9) 448
MODULO (see Arithmetic modulo n)
Modulus of a complex number 291
Natural numbers 357Ч359
Natural numbers, decimal notation 358
Newton on Уaction at a distanceФ 340n
Newton's Law of Gravity 23 (Ex. 1) 335
Newton's method, error estimates 243Ч244
Newton's method, in computation of nih roots 262Ч263
Newton's method, statement 242Ч243
Newton's theorems on the gravitational field of a spherical shell 336Ч337
Norms on vector spaces 447Ч448
One-to-one 81n
Onto as an adjective 79n
Orientations of a surface by a non-zero 2-form 45
Orientations of integrals 29 29n
Orientations of integrals over manifolds 221Ч222
Orientations of n-space 131 (Ex. 3)
Orientations of planar flows 3
Orientations of space (right- or left-handed) 17
Orientations of spatial flows 5
Orientations of the boundary of an oriented manifold-with-boundary 219Ч220
Orientations of the boundary of an oriented solid 66Ч67
Oriented area 6 20
Oriented area, formula for 14 (Ex. 5)
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



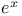
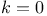 of Stokes' Theorem
of Stokes' Theorem